Jon Johnson
OrthoGeoLoRA: Geometric Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning for Structured Social Science Concept Retrieval on theWeb
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Large language models and text encoders increasingly power web-based information systems in the social sciences, including digital libraries, data catalogues, and search interfaces used by researchers, policymakers, and civil society. Full fine-tuning is often computationally and energy intensive, which can be prohibitive for smaller institutions and non-profit organizations in the Web4Good ecosystem. Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT), especially Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), reduces this cost by updating only a small number of parameters. We show that the standard LoRA update $ΔW = BA^\top$ has geometric drawbacks: gauge freedom, scale ambiguity, and a tendency toward rank collapse. We introduce OrthoGeoLoRA, which enforces an SVD-like form $ΔW = BΣA^\top$ by constraining the low-rank factors to be orthogonal (Stiefel manifold). A geometric reparameterization implements this constraint while remaining compatible with standard optimizers such as Adam and existing fine-tuning pipelines. We also propose a benchmark for hierarchical concept retrieval over the European Language Social Science Thesaurus (ELSST), widely used to organize social science resources in digital repositories. Experiments with a multilingual sentence encoder show that OrthoGeoLoRA outperforms standard LoRA and several strong PEFT variants on ranking metrics under the same low-rank budget, offering a more compute- and parameter-efficient path to adapt foundation models in resource-constrained settings.
Are Information Retrieval Approaches Good at Harmonising Longitudinal Survey Questions in Social Science?
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Automated detection of semantically equivalent questions in longitudinal social science surveys is crucial for long-term studies informing empirical research in the social, economic, and health sciences. Retrieving equivalent questions faces dual challenges: inconsistent representation of theoretical constructs (i.e. concept/sub-concept) across studies as well as between question and response options, and the evolution of vocabulary and structure in longitudinal text. To address these challenges, our multi-disciplinary collaboration of computer scientists and survey specialists presents a new information retrieval (IR) task of identifying concept (e.g. Housing, Job, etc.) equivalence across question and response options to harmonise longitudinal population studies. This paper investigates multiple unsupervised approaches on a survey dataset spanning 1946-2020, including probabilistic models, linear probing of language models, and pre-trained neural networks specialised for IR. We show that IR-specialised neural models achieve the highest overall performance with other approaches performing comparably. Additionally, the re-ranking of the probabilistic model's results with neural models only introduces modest improvements of 0.07 at most in F1-score. Qualitative post-hoc evaluation by survey specialists shows that models generally have a low sensitivity to questions with high lexical overlap, particularly in cases where sub-concepts are mismatched. Altogether, our analysis serves to further research on harmonising longitudinal studies in social science.
Revealing COVID-19's Social Dynamics: Diachronic Semantic Analysis of Vaccine and Symptom Discourse on Twitter
Oct 10, 2024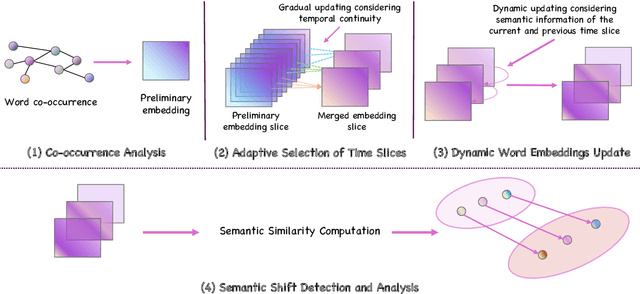
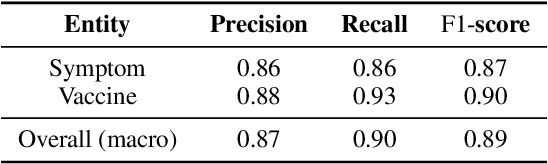
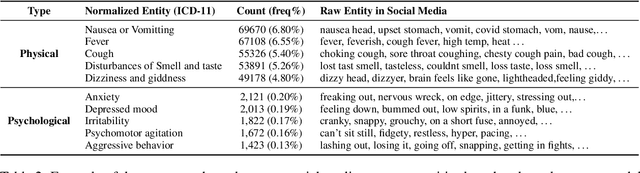
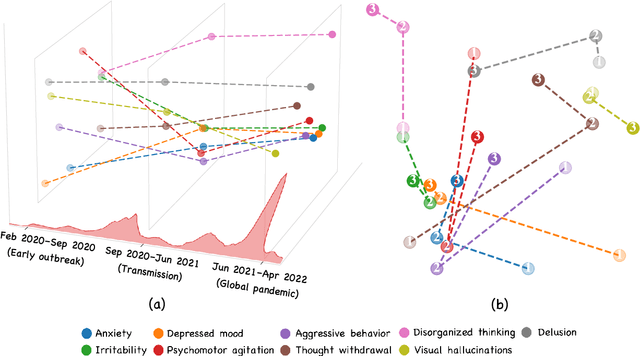
Abstract:Social media is recognized as an important source for deriving insights into public opinion dynamics and social impacts due to the vast textual data generated daily and the 'unconstrained' behavior of people interacting on these platforms. However, such analyses prove challenging due to the semantic shift phenomenon, where word meanings evolve over time. This paper proposes an unsupervised dynamic word embedding method to capture longitudinal semantic shifts in social media data without predefined anchor words. The method leverages word co-occurrence statistics and dynamic updating to adapt embeddings over time, addressing the challenges of data sparseness, imbalanced distributions, and synergistic semantic effects. Evaluated on a large COVID-19 Twitter dataset, the method reveals semantic evolution patterns of vaccine- and symptom-related entities across different pandemic stages, and their potential correlations with real-world statistics. Our key contributions include the dynamic embedding technique, empirical analysis of COVID-19 semantic shifts, and discussions on enhancing semantic shift modeling for computational social science research. This study enables capturing longitudinal semantic dynamics on social media to understand public discourse and collective phenomena.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge