John E. Ortega
Large-Language Memorization During the Classification of United States Supreme Court Cases
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Large-language models (LLMs) have been shown to respond in a variety of ways for classification tasks outside of question-answering. LLM responses are sometimes called "hallucinations" since the output is not what is ex pected. Memorization strategies in LLMs are being studied in detail, with the goal of understanding how LLMs respond. We perform a deep dive into a classification task based on United States Supreme Court (SCOTUS) decisions. The SCOTUS corpus is an ideal classification task to study for LLM memory accuracy because it presents significant challenges due to extensive sentence length, complex legal terminology, non-standard structure, and domain-specific vocabulary. Experimentation is performed with the latest LLM fine tuning and retrieval-based approaches, such as parameter-efficient fine-tuning, auto-modeling, and others, on two traditional category-based SCOTUS classification tasks: one with 15 labeled topics and another with 279. We show that prompt-based models with memories, such as DeepSeek, can be more robust than previous BERT-based models on both tasks scoring about 2 points better than previous models not based on prompting.
Lexicography Saves Lives (LSL): Automatically Translating Suicide-Related Language
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:Recent years have seen a marked increase in research that aims to identify or predict risk, intention or ideation of suicide. The majority of new tasks, datasets, language models and other resources focus on English and on suicide in the context of Western culture. However, suicide is global issue and reducing suicide rate by 2030 is one of the key goals of the UN's Sustainable Development Goals. Previous work has used English dictionaries related to suicide to translate into different target languages due to lack of other available resources. Naturally, this leads to a variety of ethical tensions (e.g.: linguistic misrepresentation), where discourse around suicide is not present in a particular culture or country. In this work, we introduce the 'Lexicography Saves Lives Project' to address this issue and make three distinct contributions. First, we outline ethical consideration and provide overview guidelines to mitigate harm in developing suicide-related resources. Next, we translate an existing dictionary related to suicidal ideation into 200 different languages and conduct human evaluations on a subset of translated dictionaries. Finally, we introduce a public website to make our resources available and enable community participation.
The First Multilingual Model For The Detection of Suicide Texts
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:Suicidal ideation is a serious health problem affecting millions of people worldwide. Social networks provide information about these mental health problems through users' emotional expressions. We propose a multilingual model leveraging transformer architectures like mBERT, XML-R, and mT5 to detect suicidal text across posts in six languages - Spanish, English, German, Catalan, Portuguese and Italian. A Spanish suicide ideation tweet dataset was translated into five other languages using SeamlessM4T. Each model was fine-tuned on this multilingual data and evaluated across classification metrics. Results showed mT5 achieving the best performance overall with F1 scores above 85%, highlighting capabilities for cross-lingual transfer learning. The English and Spanish translations also displayed high quality based on perplexity. Our exploration underscores the importance of considering linguistic diversity in developing automated multilingual tools to identify suicidal risk. Limitations exist around semantic fidelity in translations and ethical implications which provide guidance for future human-in-the-loop evaluations.
Semantic Role Labeling of NomBank Partitives
Dec 18, 2024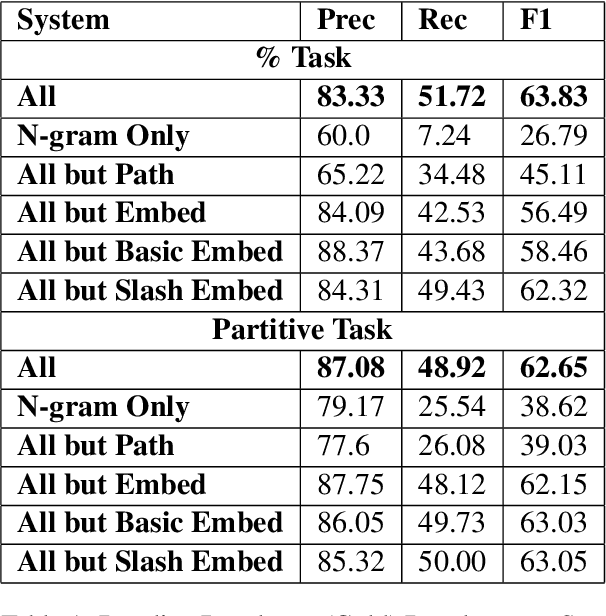
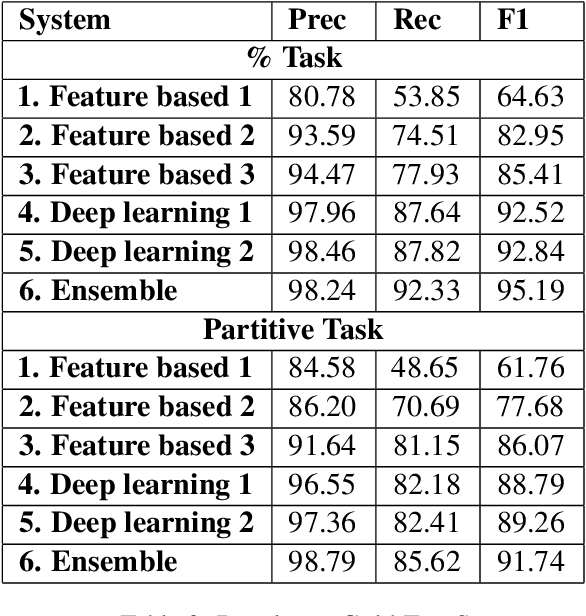
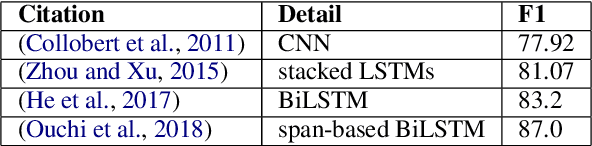
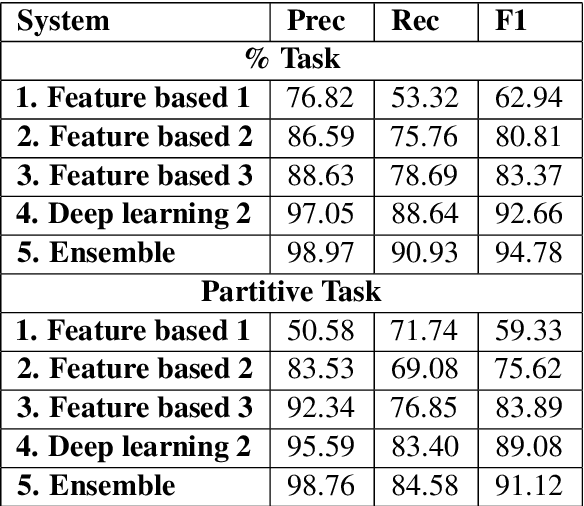
Abstract:This article is about Semantic Role Labeling for English partitive nouns (5%/REL of the price/ARG1; The price/ARG1 rose 5 percent/REL) in the NomBank annotated corpus. Several systems are described using traditional and transformer-based machine learning, as well as ensembling. Our highest scoring system achieves an F1 of 91.74% using "gold" parses from the Penn Treebank and 91.12% when using the Berkeley Neural parser. This research includes both classroom and experimental settings for system development.
Is Peer-Reviewing Worth the Effort?
Dec 18, 2024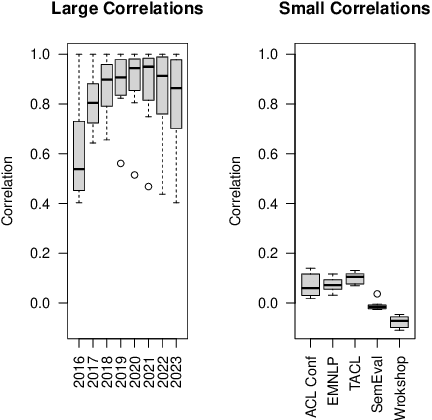
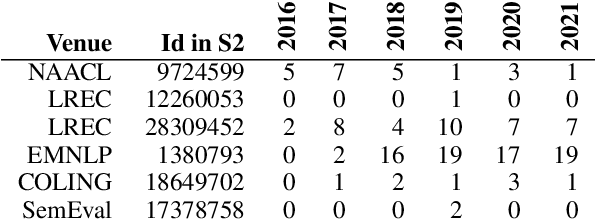
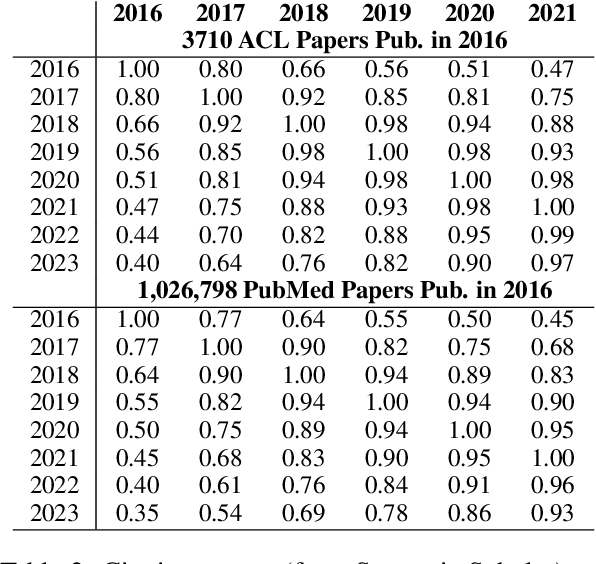
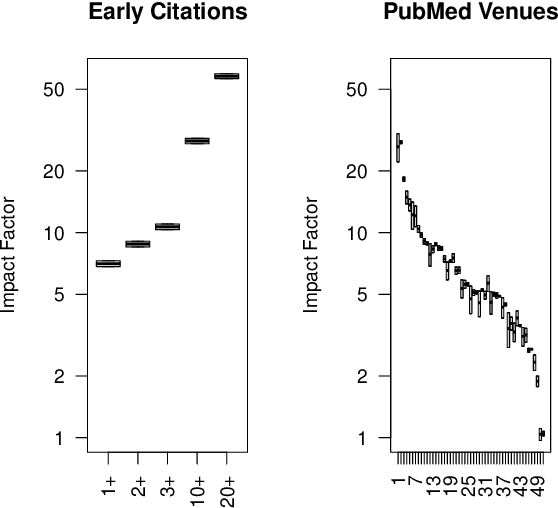
Abstract:How effective is peer-reviewing in identifying important papers? We treat this question as a forecasting task. Can we predict which papers will be highly cited in the future based on venue and "early returns" (citations soon after publication)? We show early returns are more predictive than venue. Finally, we end with constructive suggestions to address scaling challenges: (a) too many submissions and (b) too few qualified reviewers.
The Role of Handling Attributive Nouns in Improving Chinese-To-English Machine Translation
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Translating between languages with drastically different grammatical conventions poses challenges, not just for human interpreters but also for machine translation systems. In this work, we specifically target the translation challenges posed by attributive nouns in Chinese, which frequently cause ambiguities in English translation. By manually inserting the omitted particle X ('DE'). In news article titles from the Penn Chinese Discourse Treebank, we developed a targeted dataset to fine-tune Hugging Face Chinese to English translation models, specifically improving how this critical function word is handled. This focused approach not only complements the broader strategies suggested by previous studies but also offers a practical enhancement by specifically addressing a common error type in Chinese-English translation.
NLP Case Study on Predicting the Before and After of the Ukraine-Russia and Hamas-Israel Conflicts
Oct 08, 2024
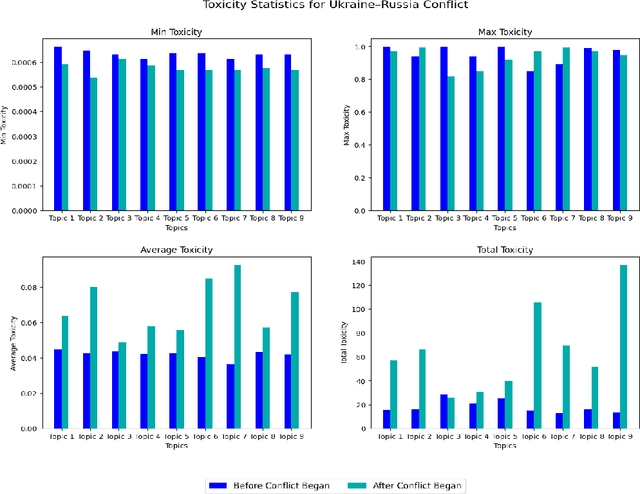
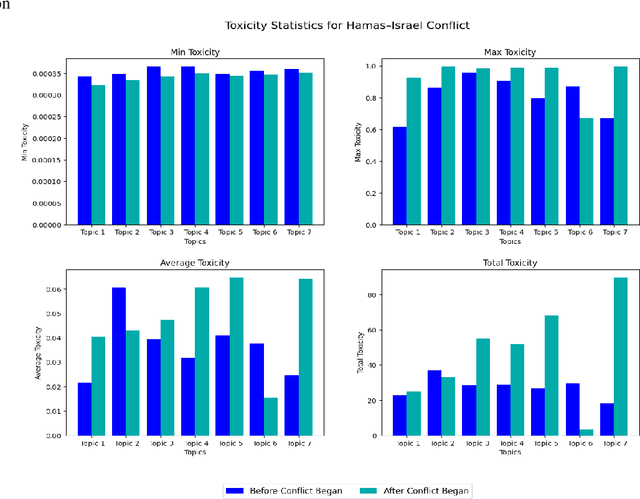
Abstract:We propose a method to predict toxicity and other textual attributes through the use of natural language processing (NLP) techniques for two recent events: the Ukraine-Russia and Hamas-Israel conflicts. This article provides a basis for exploration in future conflicts with hopes to mitigate risk through the analysis of social media before and after a conflict begins. Our work compiles several datasets from Twitter and Reddit for both conflicts in a before and after separation with an aim of predicting a future state of social media for avoidance. More specifically, we show that: (1) there is a noticeable difference in social media discussion leading up to and following a conflict and (2) social media discourse on platforms like Twitter and Reddit is useful in identifying future conflicts before they arise. Our results show that through the use of advanced NLP techniques (both supervised and unsupervised) toxicity and other attributes about language before and after a conflict is predictable with a low error of nearly 1.2 percent for both conflicts.
Predicting Anchored Text from Translation Memories for Machine Translation Using Deep Learning Methods
Sep 26, 2024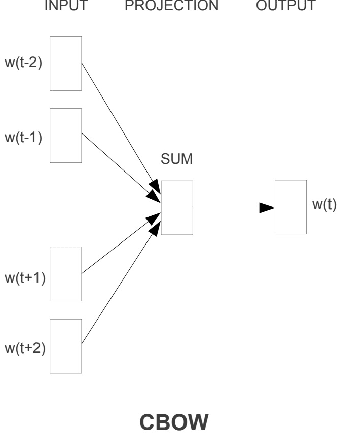
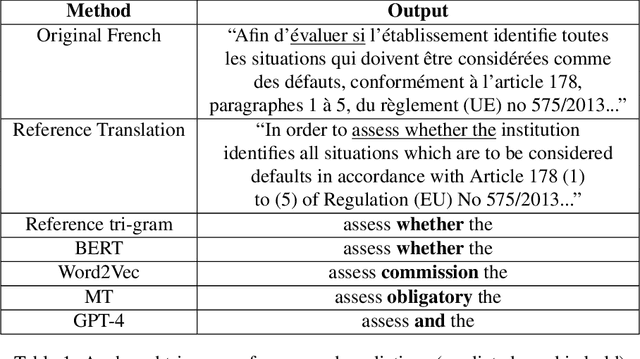

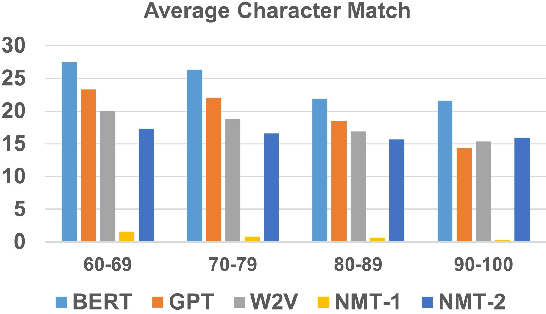
Abstract:Translation memories (TMs) are the backbone for professional translation tools called computer-aided translation (CAT) tools. In order to perform a translation using a CAT tool, a translator uses the TM to gather translations similar to the desired segment to translate (s'). Many CAT tools offer a fuzzy-match algorithm to locate segments (s) in the TM that are close in distance to s'. After locating two similar segments, the CAT tool will present parallel segments (s, t) that contain one segment in the source language along with its translation in the target language. Additionally, CAT tools contain fuzzy-match repair (FMR) techniques that will automatically use the parallel segments from the TM to create new TM entries containing a modified version of the original with the idea in mind that it will be the translation of s'. Most FMR techniques use machine translation as a way of "repairing" those words that have to be modified. In this article, we show that for a large part of those words which are anchored, we can use other techniques that are based on machine learning approaches such as Word2Vec. BERT, and even ChatGPT. Specifically, we show that for anchored words that follow the continuous bag-of-words (CBOW) paradigm, Word2Vec, BERT, and GPT-4 can be used to achieve similar and, for some cases, better results than neural machine translation for translating anchored words from French to English.
On Translating Technical Terminology: A Translation Workflow for Machine-Translated Acronyms
Sep 26, 2024Abstract:The typical workflow for a professional translator to translate a document from its source language (SL) to a target language (TL) is not always focused on what many language models in natural language processing (NLP) do - predict the next word in a series of words. While high-resource languages like English and French are reported to achieve near human parity using common metrics for measurement such as BLEU and COMET, we find that an important step is being missed: the translation of technical terms, specifically acronyms. Some state-of-the art machine translation systems like Google Translate which are publicly available can be erroneous when dealing with acronyms - as much as 50% in our findings. This article addresses acronym disambiguation for MT systems by proposing an additional step to the SL-TL (FR-EN) translation workflow where we first offer a new acronym corpus for public consumption and then experiment with a search-based thresholding algorithm that achieves nearly 10% increase when compared to Google Translate and OpusMT.
Nollywood: Let's Go to the Movies!
Jul 02, 2024Abstract:Nollywood, based on the idea of Bollywood from India, is a series of outstanding movies that originate from Nigeria. Unfortunately, while the movies are in English, they are hard to understand for many native speakers due to the dialect of English that is spoken. In this article, we accomplish two goals: (1) create a phonetic sub-title model that is able to translate Nigerian English speech to American English and (2) use the most advanced toxicity detectors to discover how toxic the speech is. Our aim is to highlight the text in these videos which is often times ignored for lack of dialectal understanding due the fact that many people in Nigeria speak a native language like Hausa at home.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge