Raman Chandrasekar
Is Peer-Reviewing Worth the Effort?
Dec 18, 2024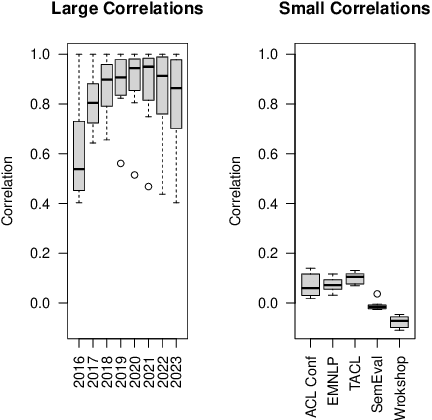
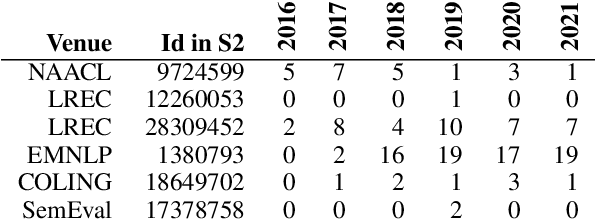
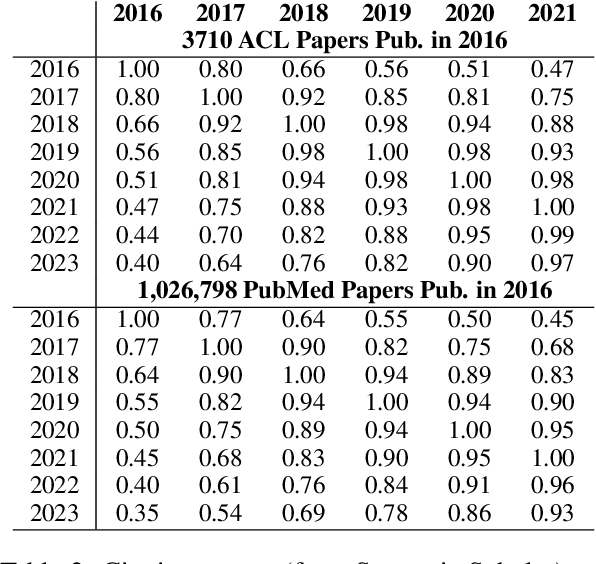
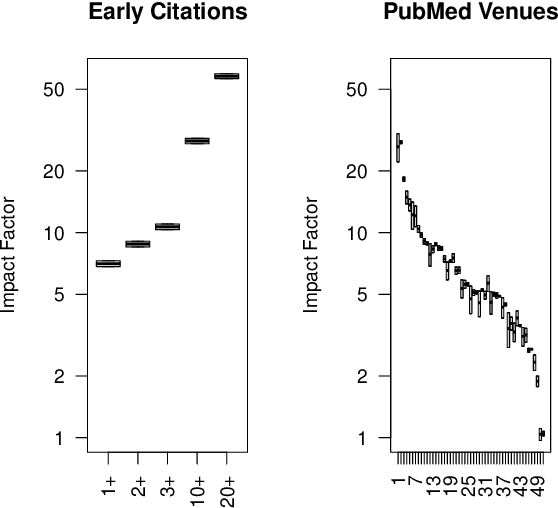
Abstract:How effective is peer-reviewing in identifying important papers? We treat this question as a forecasting task. Can we predict which papers will be highly cited in the future based on venue and "early returns" (citations soon after publication)? We show early returns are more predictive than venue. Finally, we end with constructive suggestions to address scaling challenges: (a) too many submissions and (b) too few qualified reviewers.
Academic Article Recommendation Using Multiple Perspectives
Jul 08, 2024



Abstract:We argue that Content-based filtering (CBF) and Graph-based methods (GB) complement one another in Academic Search recommendations. The scientific literature can be viewed as a conversation between authors and the audience. CBF uses abstracts to infer authors' positions, and GB uses citations to infer responses from the audience. In this paper, we describe nine differences between CBF and GB, as well as synergistic opportunities for hybrid combinations. Two embeddings will be used to illustrate these opportunities: (1) Specter, a CBF method based on BERT-like deepnet encodings of abstracts, and (2) ProNE, a GB method based on spectral clustering of more than 200M papers and 2B citations from Semantic Scholar.
Engineering an Intelligent Essay Scoring and Feedback System: An Experience Report
Mar 25, 2021

Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) / Machine Learning (ML)-based systems are widely sought-after commercial solutions that can automate and augment core business services. Intelligent systems can improve the quality of services offered and support scalability through automation. In this paper we describe our experience in engineering an exploratory system for assessing the quality of essays supplied by customers of a specialized recruitment support service. The problem domain is challenging because the open-ended customer-supplied source text has considerable scope for ambiguity and error, making models for analysis hard to build. There is also a need to incorporate specialized business domain knowledge into the intelligent processing systems. To address these challenges, we experimented with and exploited a number of cloud-based machine learning models and composed them into an application-specific processing pipeline. This design allows for modification of the underlying algorithms as more data and improved techniques become available. We describe our design, and the main challenges we faced, namely keeping a check on the quality control of the models, testing the software and deploying the computationally expensive ML models on the cloud.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge