Jocelyn Shen
Words Like Knives: Backstory-Personalized Modeling and Detection of Violent Communication
May 27, 2025Abstract:Conversational breakdowns in close relationships are deeply shaped by personal histories and emotional context, yet most NLP research treats conflict detection as a general task, overlooking the relational dynamics that influence how messages are perceived. In this work, we leverage nonviolent communication (NVC) theory to evaluate LLMs in detecting conversational breakdowns and assessing how relationship backstory influences both human and model perception of conflicts. Given the sensitivity and scarcity of real-world datasets featuring conflict between familiar social partners with rich personal backstories, we contribute the PersonaConflicts Corpus, a dataset of N=5,772 naturalistic simulated dialogues spanning diverse conflict scenarios between friends, family members, and romantic partners. Through a controlled human study, we annotate a subset of dialogues and obtain fine-grained labels of communication breakdown types on individual turns, and assess the impact of backstory on human and model perception of conflict in conversation. We find that the polarity of relationship backstories significantly shifted human perception of communication breakdowns and impressions of the social partners, yet models struggle to meaningfully leverage those backstories in the detection task. Additionally, we find that models consistently overestimate how positively a message will make a listener feel. Our findings underscore the critical role of personalization to relationship contexts in enabling LLMs to serve as effective mediators in human communication for authentic connection.
Resonance: Drawing from Memories to Imagine Positive Futures through AI-Augmented Journaling
Mar 31, 2025



Abstract:People inherently use experiences of their past while imagining their future, a capability that plays a crucial role in mental health. Resonance is an AI-powered journaling tool designed to augment this ability by offering AI-generated, action-oriented suggestions for future activities based on the user's own past memories. Suggestions are offered when a new memory is logged and are followed by a prompt for the user to imagine carrying out the suggestion. In a two-week randomized controlled study (N=55), we found that using Resonance significantly improved mental health outcomes, reducing the users' PHQ8 scores, a measure of current depression, and increasing their daily positive affect, particularly when they would likely act on the suggestion. Notably, the effectiveness of the suggestions was higher when they were personal, novel, and referenced the user's logged memories. Finally, through open-ended feedback, we discuss the factors that encouraged or hindered the use of the tool.
* 17 pages, 13 figures
HEART-felt Narratives: Tracing Empathy and Narrative Style in Personal Stories with LLMs
May 27, 2024Abstract:Empathy serves as a cornerstone in enabling prosocial behaviors, and can be evoked through sharing of personal experiences in stories. While empathy is influenced by narrative content, intuitively, people respond to the way a story is told as well, through narrative style. Yet the relationship between empathy and narrative style is not fully understood. In this work, we empirically examine and quantify this relationship between style and empathy using LLMs and large-scale crowdsourcing studies. We introduce a novel, theory-based taxonomy, HEART (Human Empathy and Narrative Taxonomy) that delineates elements of narrative style that can lead to empathy with the narrator of a story. We establish the performance of LLMs in extracting narrative elements from HEART, showing that prompting with our taxonomy leads to reasonable, human-level annotations beyond what prior lexicon-based methods can do. To show empirical use of our taxonomy, we collect a dataset of empathy judgments of stories via a large-scale crowdsourcing study with N=2,624 participants. We show that narrative elements extracted via LLMs, in particular, vividness of emotions and plot volume, can elucidate the pathways by which narrative style cultivates empathy towards personal stories. Our work suggests that such models can be used for narrative analyses that lead to human-centered social and behavioral insights.
EmpathicStories++: A Multimodal Dataset for Empathy towards Personal Experiences
May 24, 2024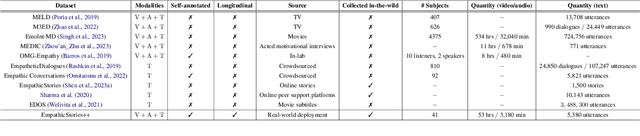
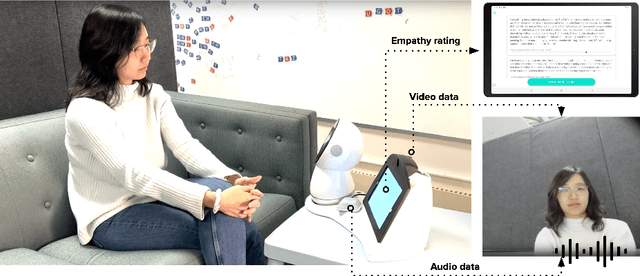
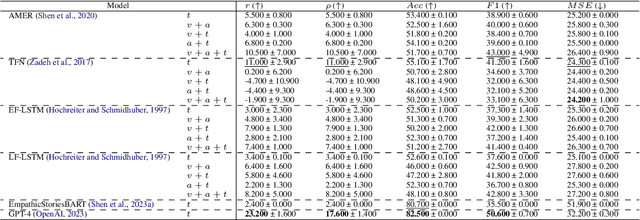
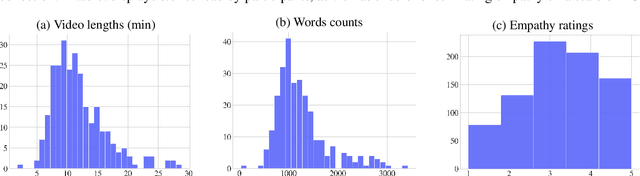
Abstract:Modeling empathy is a complex endeavor that is rooted in interpersonal and experiential dimensions of human interaction, and remains an open problem within AI. Existing empathy datasets fall short in capturing the richness of empathy responses, often being confined to in-lab or acted scenarios, lacking longitudinal data, and missing self-reported labels. We introduce a new multimodal dataset for empathy during personal experience sharing: the EmpathicStories++ dataset (https://mitmedialab.github.io/empathic-stories-multimodal/) containing 53 hours of video, audio, and text data of 41 participants sharing vulnerable experiences and reading empathically resonant stories with an AI agent. EmpathicStories++ is the first longitudinal dataset on empathy, collected over a month-long deployment of social robots in participants' homes, as participants engage in natural, empathic storytelling interactions with AI agents. We then introduce a novel task of predicting individuals' empathy toward others' stories based on their personal experiences, evaluated in two contexts: participants' own personal shared story context and their reflections on stories they read. We benchmark this task using state-of-the-art models to pave the way for future improvements in contextualized and longitudinal empathy modeling. Our work provides a valuable resource for further research in developing empathetic AI systems and understanding the intricacies of human empathy within genuine, real-world settings.
Modeling Empathic Similarity in Personal Narratives
May 23, 2023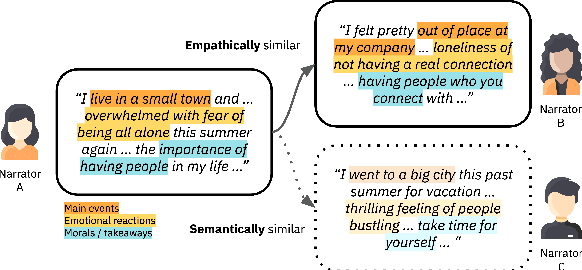

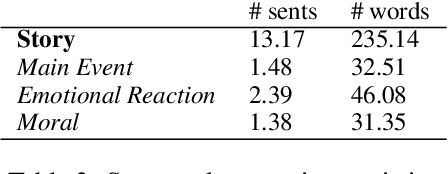
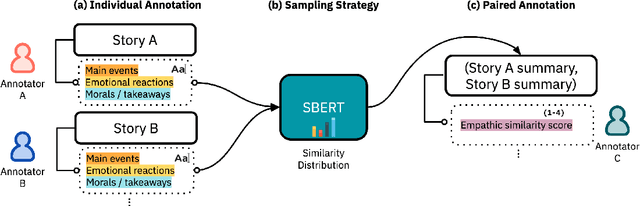
Abstract:The most meaningful connections between people are often fostered through expression of shared vulnerability and emotional experiences in personal narratives. We introduce a new task of identifying similarity in personal stories based on empathic resonance, i.e., the extent to which two people empathize with each others' experiences, as opposed to raw semantic or lexical similarity, as has predominantly been studied in NLP. Using insights from social psychology, we craft a framework that operationalizes empathic similarity in terms of three key features of stories: main events, emotional trajectories, and overall morals or takeaways. We create EmpathicStories, a dataset of 1,500 personal stories annotated with our empathic similarity features, and 2,000 pairs of stories annotated with empathic similarity scores. Using our dataset, we fine-tune a model to compute empathic similarity of story pairs, and show that this outperforms semantic similarity models on automated correlation and retrieval metrics. Through a user study with 150 participants, we also assess the effect our model has on retrieving stories that users empathize with, compared to naive semantic similarity-based retrieval, and find that participants empathized significantly more with stories retrieved by our model. Our work has strong implications for the use of empathy-aware models to foster human connection and empathy between people.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge