Pedro Colon-Hernandez
Can Language Models Take A Hint? Prompting for Controllable Contextualized Commonsense Inference
Oct 03, 2024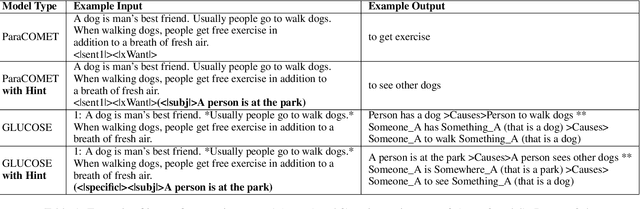

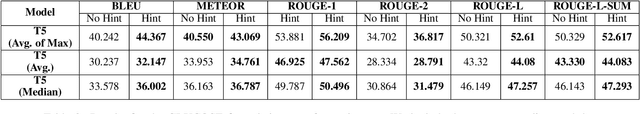
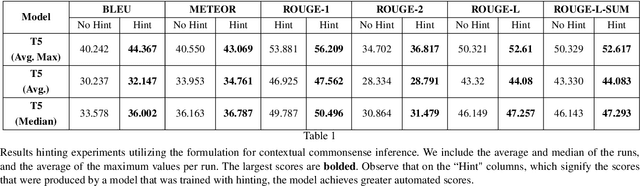
Abstract:Generating commonsense assertions within a given story context remains a difficult task for modern language models. Previous research has addressed this problem by aligning commonsense inferences with stories and training language generation models accordingly. One of the challenges is determining which topic or entity in the story should be the focus of an inferred assertion. Prior approaches lack the ability to control specific aspects of the generated assertions. In this work, we introduce "hinting," a data augmentation technique that enhances contextualized commonsense inference. "Hinting" employs a prefix prompting strategy using both hard and soft prompts to guide the inference process. To demonstrate its effectiveness, we apply "hinting" to two contextual commonsense inference datasets: ParaCOMET and GLUCOSE, evaluating its impact on both general and context-specific inference. Furthermore, we evaluate "hinting" by incorporating synonyms and antonyms into the hints. Our results show that "hinting" does not compromise the performance of contextual commonsense inference while offering improved controllability.
Modeling Empathic Similarity in Personal Narratives
May 23, 2023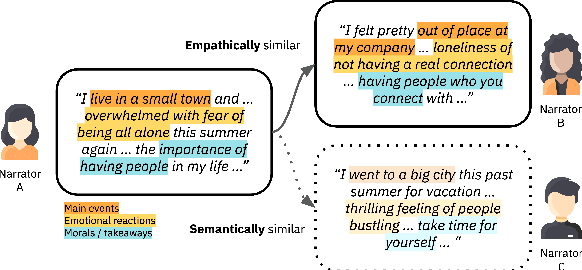

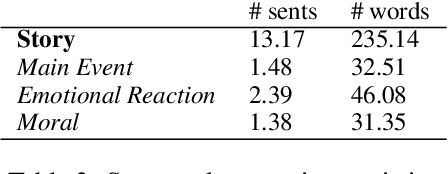
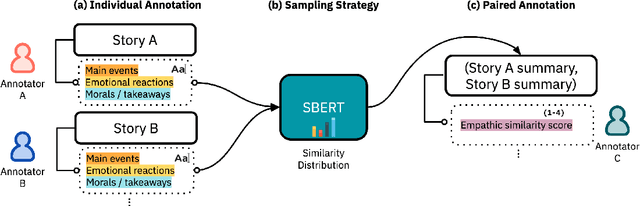
Abstract:The most meaningful connections between people are often fostered through expression of shared vulnerability and emotional experiences in personal narratives. We introduce a new task of identifying similarity in personal stories based on empathic resonance, i.e., the extent to which two people empathize with each others' experiences, as opposed to raw semantic or lexical similarity, as has predominantly been studied in NLP. Using insights from social psychology, we craft a framework that operationalizes empathic similarity in terms of three key features of stories: main events, emotional trajectories, and overall morals or takeaways. We create EmpathicStories, a dataset of 1,500 personal stories annotated with our empathic similarity features, and 2,000 pairs of stories annotated with empathic similarity scores. Using our dataset, we fine-tune a model to compute empathic similarity of story pairs, and show that this outperforms semantic similarity models on automated correlation and retrieval metrics. Through a user study with 150 participants, we also assess the effect our model has on retrieving stories that users empathize with, compared to naive semantic similarity-based retrieval, and find that participants empathized significantly more with stories retrieved by our model. Our work has strong implications for the use of empathy-aware models to foster human connection and empathy between people.
Adversarial Transformer Language Models for Contextual Commonsense Inference
Feb 10, 2023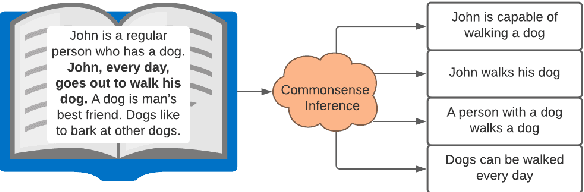
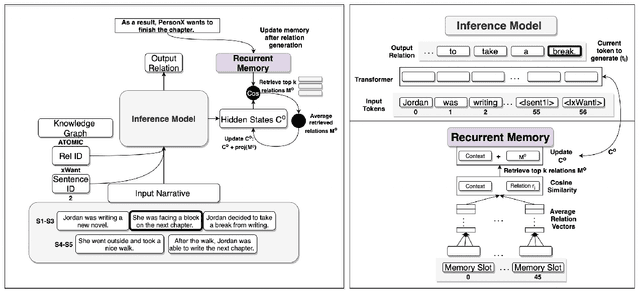
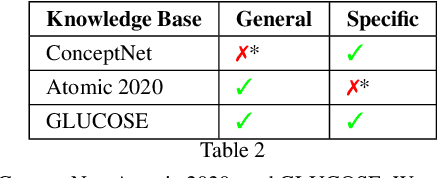
Abstract:Contextualized or discourse aware commonsense inference is the task of generating coherent commonsense assertions (i.e., facts) from a given story, and a particular sentence from that story. Some problems with the task are: lack of controllability for topics of the inferred facts; lack of commonsense knowledge during training; and, possibly, hallucinated or false facts. In this work, we utilize a transformer model for this task and develop techniques to address the aforementioned problems in the task. We control the inference by introducing a new technique we call "hinting". Hinting is a kind of language model prompting, that utilizes both hard prompts (specific words) and soft prompts (virtual learnable templates). This serves as a control signal to advise the language model "what to talk about". Next, we establish a methodology for performing joint inference with multiple commonsense knowledge bases. Joint inference of commonsense requires care, because it is imprecise and the level of generality is more flexible. You want to be sure that the results "still make sense" for the context. To this end, we align the textual version of assertions from three knowledge graphs (ConceptNet, ATOMIC2020, and GLUCOSE) with a story and a target sentence. This combination allows us to train a single model to perform joint inference with multiple knowledge graphs. We show experimental results for the three knowledge graphs on joint inference. Our final contribution is exploring a GAN architecture that generates the contextualized commonsense assertions and scores them as to their plausibility through a discriminator. The result is an integrated system for contextual commonsense inference in stories, that can controllably generate plausible commonsense assertions, and takes advantage of joint inference between multiple commonsense knowledge bases.
RetroGAN: A Cyclic Post-Specialization System for Improving Out-of-Knowledge and Rare Word Representations
Aug 30, 2021
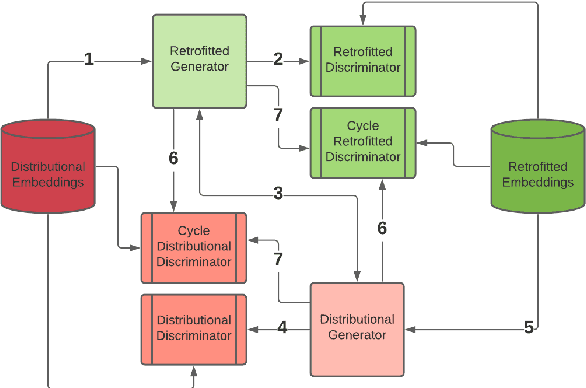
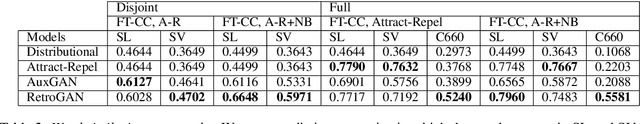
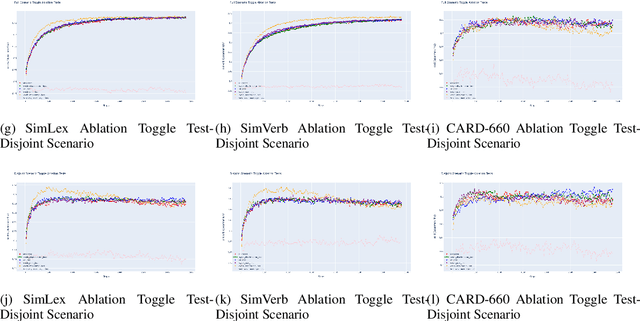
Abstract:Retrofitting is a technique used to move word vectors closer together or further apart in their space to reflect their relationships in a Knowledge Base (KB). However, retrofitting only works on concepts that are present in that KB. RetroGAN uses a pair of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to learn a one-to-one mapping between concepts and their retrofitted counterparts. It applies that mapping (post-specializes) to handle concepts that do not appear in the original KB in a manner similar to how some natural language systems handle out-of-vocabulary entries. We test our system on three word-similarity benchmarks and a downstream sentence simplification task and achieve the state of the art (CARD-660). Altogether, our results demonstrate our system's effectiveness for out-of-knowledge and rare word generalization.
Combining pre-trained language models and structured knowledge
Feb 05, 2021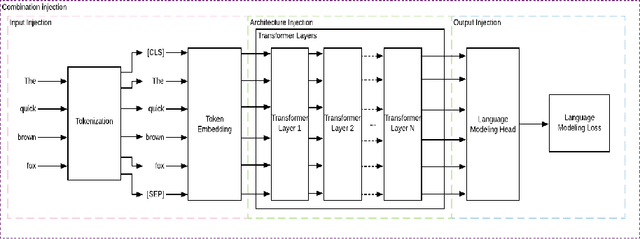
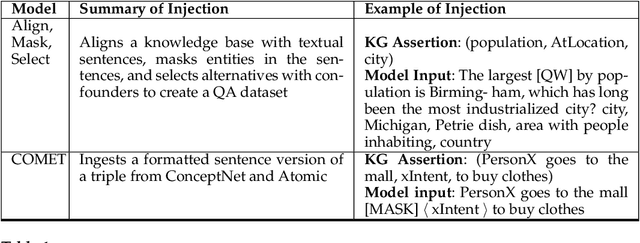
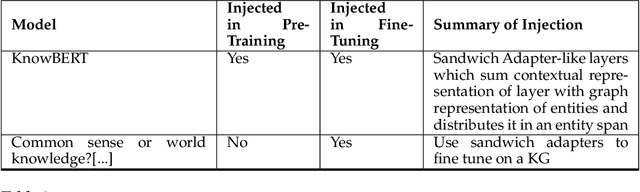
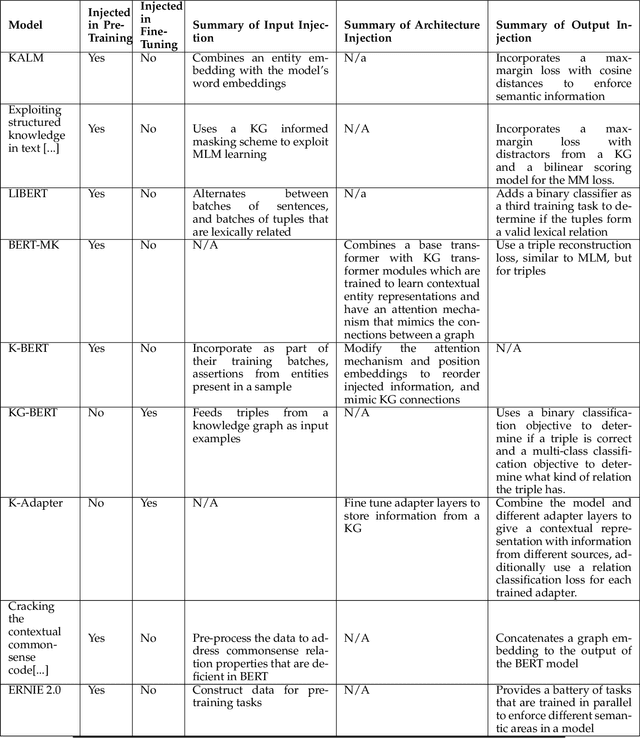
Abstract:In recent years, transformer-based language models have achieved state of the art performance in various NLP benchmarks. These models are able to extract mostly distributional information with some semantics from unstructured text, however it has proven challenging to integrate structured information, such as knowledge graphs into these models. We examine a variety of approaches to integrate structured knowledge into current language models and determine challenges, and possible opportunities to leverage both structured and unstructured information sources. From our survey, we find that there are still opportunities at exploiting adapter-based injections and that it may be possible to further combine various of the explored approaches into one system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge