Matthew Huggins
The Interaction Flow Editor: A New Human-Robot Interaction RapidPrototyping Interface
Aug 31, 2021



Abstract:Human-robot interaction can be regarded as a flow between users and robots. Designing good interaction flows takes a lot of effort and needs to be field tested. Unfortunately, the interaction flow design process is often very disjointed, with users experiencing prototypes, designers forming those prototypes, and developers implementing them as independent processes. In this paper, we present the Interaction Flow Editor (IFE), a new human-robot interaction prototyping tool that enables everyday users to create and modify their own interactions, while still providing a full suite of features that is powerful enough for developers and designers to create complex interactions. We also discuss the Flow Engine, a flexible and adaptable framework for executing robot interaction flows authors through the IFE. Finally, we present our case study results that demonstrates how older adults, aged 70 and above, can design and iterate interactions in real-time on a robot using the IFE.
Combining pre-trained language models and structured knowledge
Feb 05, 2021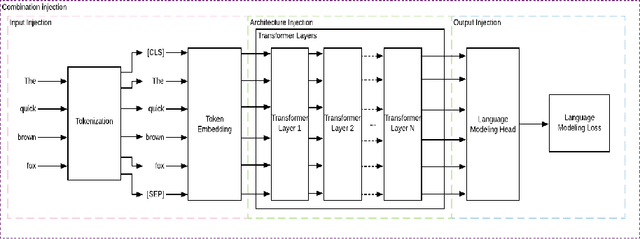
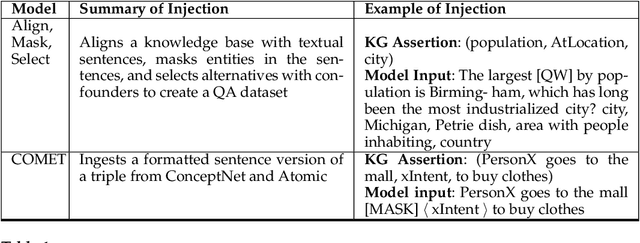
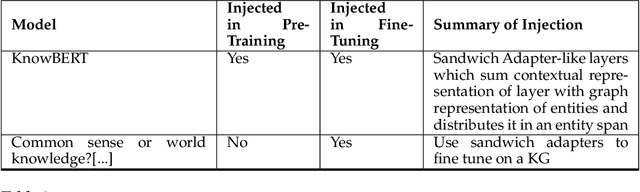
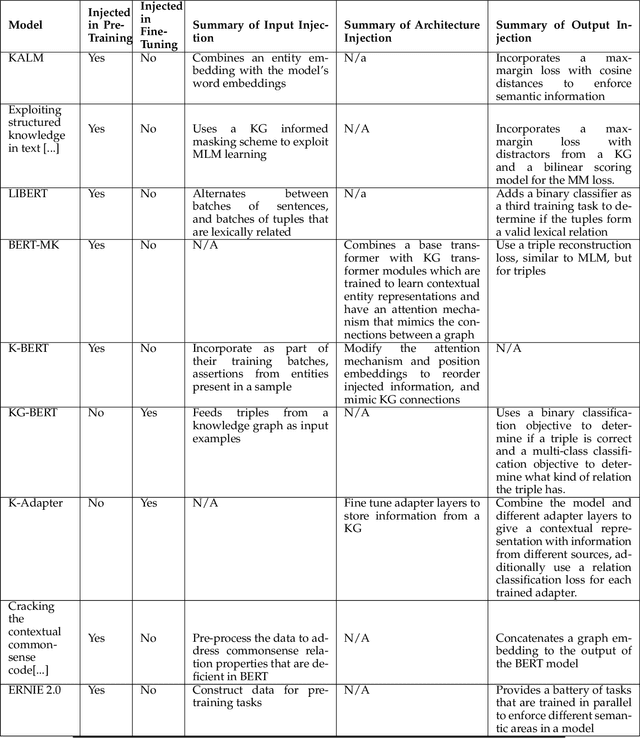
Abstract:In recent years, transformer-based language models have achieved state of the art performance in various NLP benchmarks. These models are able to extract mostly distributional information with some semantics from unstructured text, however it has proven challenging to integrate structured information, such as knowledge graphs into these models. We examine a variety of approaches to integrate structured knowledge into current language models and determine challenges, and possible opportunities to leverage both structured and unstructured information sources. From our survey, we find that there are still opportunities at exploiting adapter-based injections and that it may be possible to further combine various of the explored approaches into one system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge