Jiyoon Kim
APT: Adaptive Personalized Training for Diffusion Models with Limited Data
Jul 03, 2025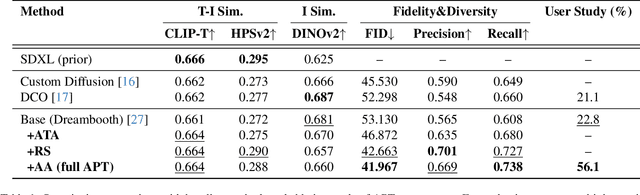
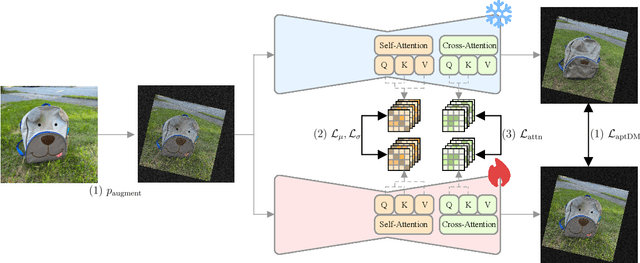
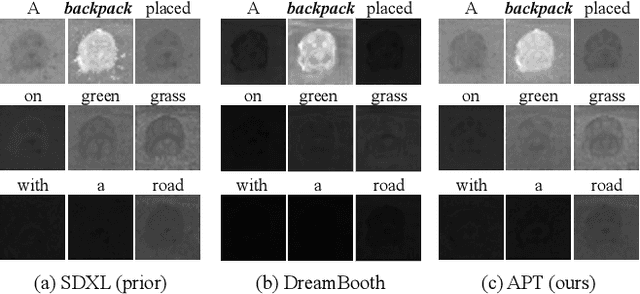

Abstract:Personalizing diffusion models using limited data presents significant challenges, including overfitting, loss of prior knowledge, and degradation of text alignment. Overfitting leads to shifts in the noise prediction distribution, disrupting the denoising trajectory and causing the model to lose semantic coherence. In this paper, we propose Adaptive Personalized Training (APT), a novel framework that mitigates overfitting by employing adaptive training strategies and regularizing the model's internal representations during fine-tuning. APT consists of three key components: (1) Adaptive Training Adjustment, which introduces an overfitting indicator to detect the degree of overfitting at each time step bin and applies adaptive data augmentation and adaptive loss weighting based on this indicator; (2)Representation Stabilization, which regularizes the mean and variance of intermediate feature maps to prevent excessive shifts in noise prediction; and (3) Attention Alignment for Prior Knowledge Preservation, which aligns the cross-attention maps of the fine-tuned model with those of the pretrained model to maintain prior knowledge and semantic coherence. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that APT effectively mitigates overfitting, preserves prior knowledge, and outperforms existing methods in generating high-quality, diverse images with limited reference data.
* CVPR 2025 camera ready. Project page: https://lgcnsai.github.io/apt
Column-wise Quantization of Weights and Partial Sums for Accurate and Efficient Compute-In-Memory Accelerators
Feb 11, 2025



Abstract:Compute-in-memory (CIM) is an efficient method for implementing deep neural networks (DNNs) but suffers from substantial overhead from analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), especially as ADC precision increases. Low-precision ADCs can re- duce this overhead but introduce partial-sum quantization errors degrading accuracy. Additionally, low-bit weight constraints, im- posed by cell limitations and the need for multiple cells for higher- bit weights, present further challenges. While fine-grained partial- sum quantization has been studied to lower ADC resolution effectively, weight granularity, which limits overall partial-sum quantized accuracy, remains underexplored. This work addresses these challenges by aligning weight and partial-sum quantization granularities at the column-wise level. Our method improves accuracy while maintaining dequantization overhead, simplifies training by removing two-stage processes, and ensures robustness to memory cell variations via independent column-wise scale factors. We also propose an open-source CIM-oriented convolution framework to handle fine-grained weights and partial-sums effi- ciently, incorporating a novel tiling method and group convolution. Experimental results on ResNet-20 (CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100) and ResNet-18 (ImageNet) show accuracy improvements of 0.99%, 2.69%, and 1.01%, respectively, compared to the best-performing related works. Additionally, variation analysis reveals the robust- ness of our method against memory cell variations. These findings highlight the effectiveness of our quantization scheme in enhancing accuracy and robustness while maintaining hardware efficiency in CIM-based DNN implementations. Our code is available at https://github.com/jiyoonkm/ColumnQuant.
CROPS: Model-Agnostic Training-Free Framework for Safe Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models
Jan 09, 2025Abstract:With advances in diffusion models, image generation has shown significant performance improvements. This raises concerns about the potential abuse of image generation, such as the creation of explicit or violent images, commonly referred to as Not Safe For Work (NSFW) content. To address this, the Stable Diffusion model includes several safety checkers to censor initial text prompts and final output images generated from the model. However, recent research has shown that these safety checkers have vulnerabilities against adversarial attacks, allowing them to generate NSFW images. In this paper, we find that these adversarial attacks are not robust to small changes in text prompts or input latents. Based on this, we propose CROPS (Circular or RandOm Prompts for Safety), a model-agnostic framework that easily defends against adversarial attacks generating NSFW images without requiring additional training. Moreover, we develop an approach that utilizes one-step diffusion models for efficient NSFW detection (CROPS-1), further reducing computational resources. We demonstrate the superiority of our method in terms of performance and applicability.
Unexplored Faces of Robustness and Out-of-Distribution: Covariate Shifts in Environment and Sensor Domains
Apr 25, 2024



Abstract:Computer vision applications predict on digital images acquired by a camera from physical scenes through light. However, conventional robustness benchmarks rely on perturbations in digitized images, diverging from distribution shifts occurring in the image acquisition process. To bridge this gap, we introduce a new distribution shift dataset, ImageNet-ES, comprising variations in environmental and camera sensor factors by directly capturing 202k images with a real camera in a controllable testbed. With the new dataset, we evaluate out-of-distribution (OOD) detection and model robustness. We find that existing OOD detection methods do not cope with the covariate shifts in ImageNet-ES, implying that the definition and detection of OOD should be revisited to embrace real-world distribution shifts. We also observe that the model becomes more robust in both ImageNet-C and -ES by learning environment and sensor variations in addition to existing digital augmentations. Lastly, our results suggest that effective shift mitigation via camera sensor control can significantly improve performance without increasing model size. With these findings, our benchmark may aid future research on robustness, OOD, and camera sensor control for computer vision. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/Edw2n/ImageNet-ES.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge