Jinsung Lee
Classification Matters: Improving Video Action Detection with Class-Specific Attention
Jul 29, 2024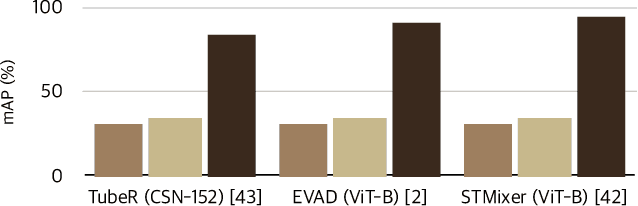
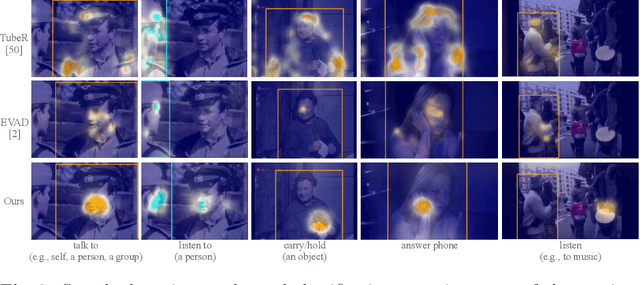
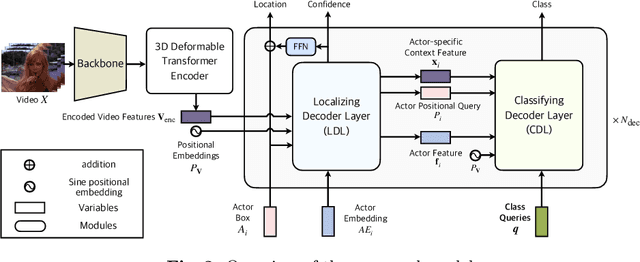
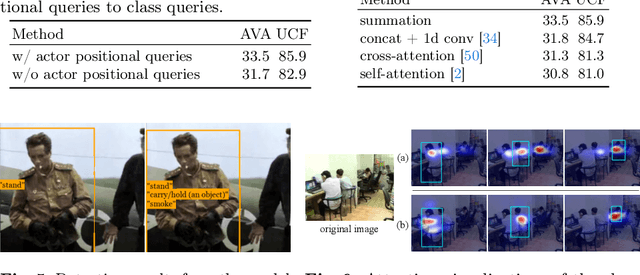
Abstract:Video action detection (VAD) aims to detect actors and classify their actions in a video. We figure that VAD suffers more from classification rather than localization of actors. Hence, we analyze how prevailing methods form features for classification and find that they prioritize actor regions, yet often overlooking the essential contextual information necessary for accurate classification. Accordingly, we propose to reduce the bias toward actor and encourage paying attention to the context that is relevant to each action class. By assigning a class-dedicated query to each action class, our model can dynamically determine where to focus for effective classification. The proposed model demonstrates superior performance on three challenging benchmarks with significantly fewer parameters and less computation.
Detector-Free Weakly Supervised Group Activity Recognition
Apr 05, 2022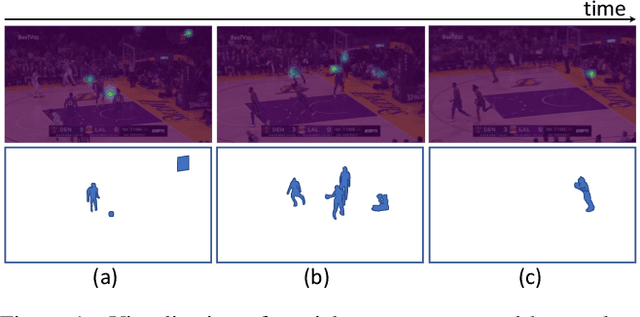
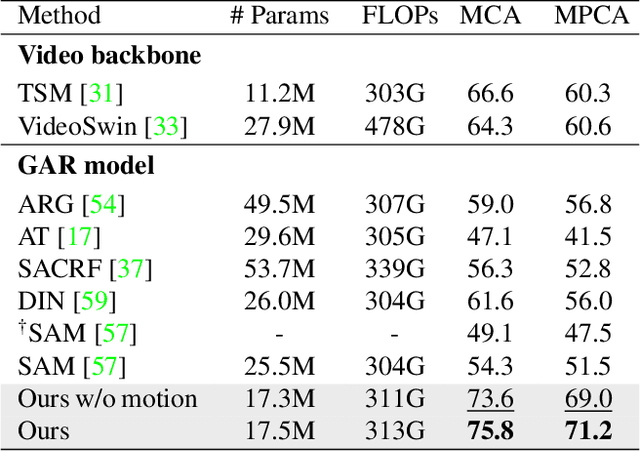
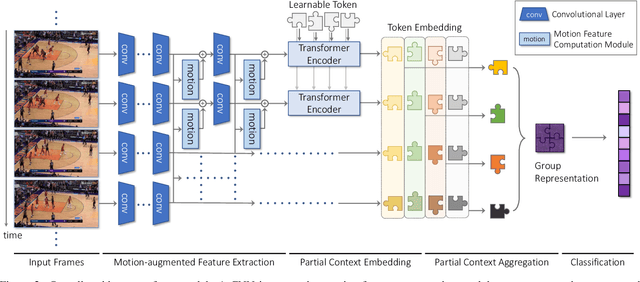
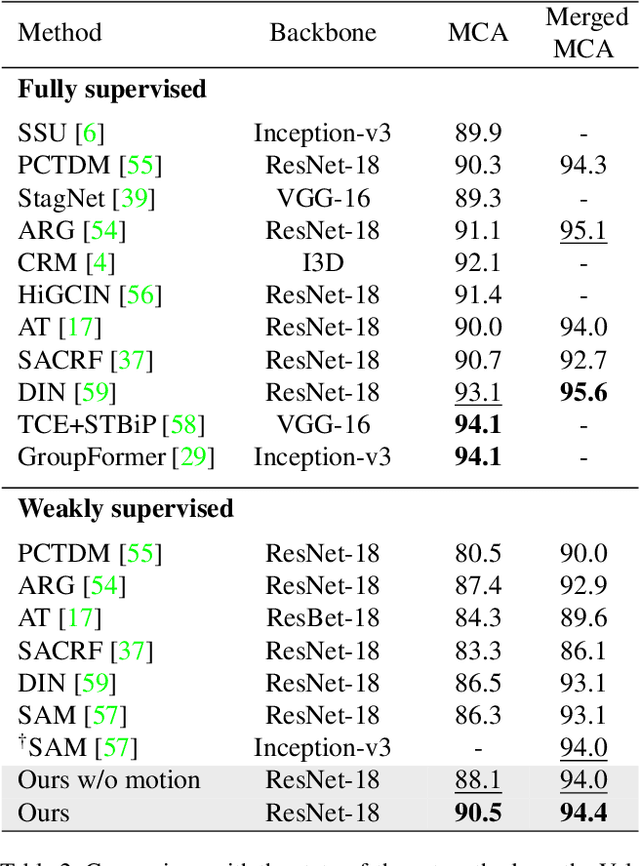
Abstract:Group activity recognition is the task of understanding the activity conducted by a group of people as a whole in a multi-person video. Existing models for this task are often impractical in that they demand ground-truth bounding box labels of actors even in testing or rely on off-the-shelf object detectors. Motivated by this, we propose a novel model for group activity recognition that depends neither on bounding box labels nor on object detector. Our model based on Transformer localizes and encodes partial contexts of a group activity by leveraging the attention mechanism, and represents a video clip as a set of partial context embeddings. The embedding vectors are then aggregated to form a single group representation that reflects the entire context of an activity while capturing temporal evolution of each partial context. Our method achieves outstanding performance on two benchmarks, Volleyball and NBA datasets, surpassing not only the state of the art trained with the same level of supervision, but also some of existing models relying on stronger supervision.
Controllable Garment Transfer
Apr 05, 2022
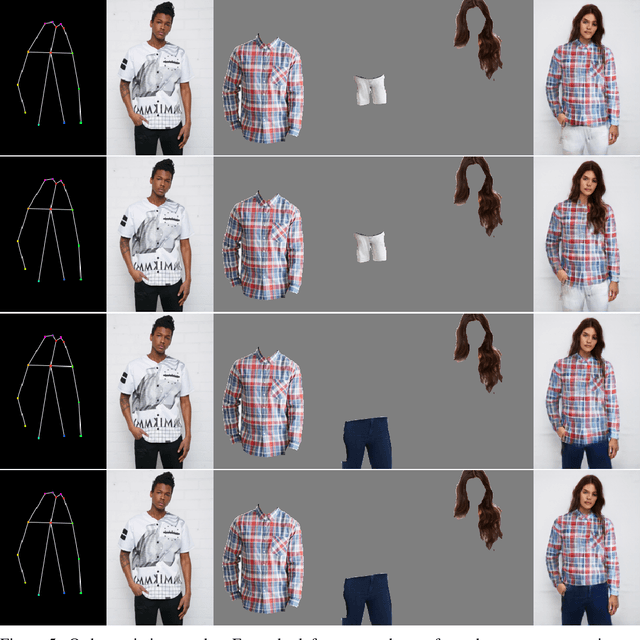
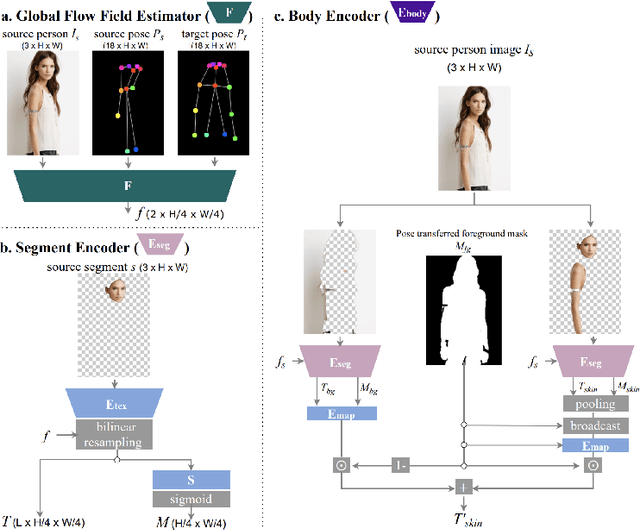


Abstract:Image-based garment transfer replaces the garment on the target human with the desired garment; this enables users to virtually view themselves in the desired garment. To this end, many approaches have been proposed using the generative model and have shown promising results. However, most fail to provide the user with on the fly garment modification functionality. We aim to add this customizable option of "garment tweaking" to our model to control garment attributes, such as sleeve length, waist width, and garment texture.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge