Jinsong Wu
Failure-Aware Bimanual Teleoperation via Conservative Value Guided Assistance
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Teleoperation of high-precision manipulation is con-strained by tight success tolerances and complex contact dy-namics, which make impending failures difficult for human operators to anticipate under partial observability. This paper proposes a value-guided, failure-aware framework for bimanual teleoperation that provides compliant haptic assistance while pre-serving continuous human authority. The framework is trained entirely from heterogeneous offline teleoperation data containing both successful and failed executions. Task feasibility is mod-eled as a conservative success score learned via Conservative Value Learning, yielding a risk-sensitive estimate that remains reliable under distribution shift. During online operation, the learned success score regulates the level of assistance, while a learned actor provides a corrective motion direction. Both are integrated through a joint-space impedance interface on the master side, yielding continuous guidance that steers the operator away from failure-prone actions without overriding intent. Experimental results on contact-rich manipulation tasks demonstrate improved task success rates and reduced operator workload compared to conventional teleoperation and shared-autonomy baselines, indicating that conservative value learning provides an effective mechanism for embedding failure awareness into bilateral teleoperation. Experimental videos are available at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XDTsvzEkDRE
Learning Rhythmic Trajectories with Geometric Constraints for Laser-Based Skincare Procedures
Dec 21, 2023Abstract:The increasing deployment of robots has significantly enhanced the automation levels across a wide and diverse range of industries. This paper investigates the automation challenges of laser-based dermatology procedures in the beauty industry; This group of related manipulation tasks involves delivering energy from a cosmetic laser onto the skin with repetitive patterns. To automate this procedure, we propose to use a robotic manipulator and endow it with the dexterity of a skilled dermatology practitioner through a learning-from-demonstration framework. To ensure that the cosmetic laser can properly deliver the energy onto the skin surface of an individual, we develop a novel structured prediction-based imitation learning algorithm with the merit of handling geometric constraints. Notably, our proposed algorithm effectively tackles the imitation challenges associated with quasi-periodic motions, a common feature of many laser-based cosmetic tasks. The conducted real-world experiments illustrate the performance of our robotic beautician in mimicking realistic dermatological procedures; Our new method is shown to not only replicate the rhythmic movements from the provided demonstrations but also to adapt the acquired skills to previously unseen scenarios and subjects.
Region-controlled Style Transfer
Oct 24, 2023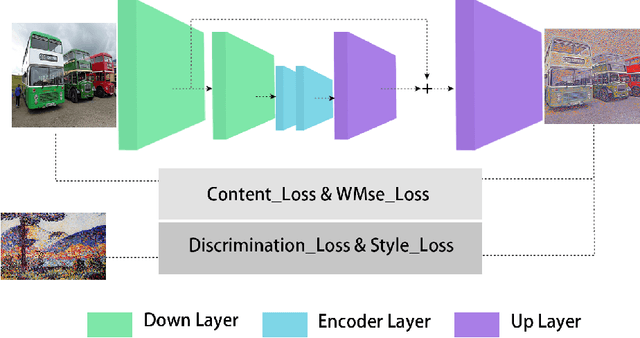

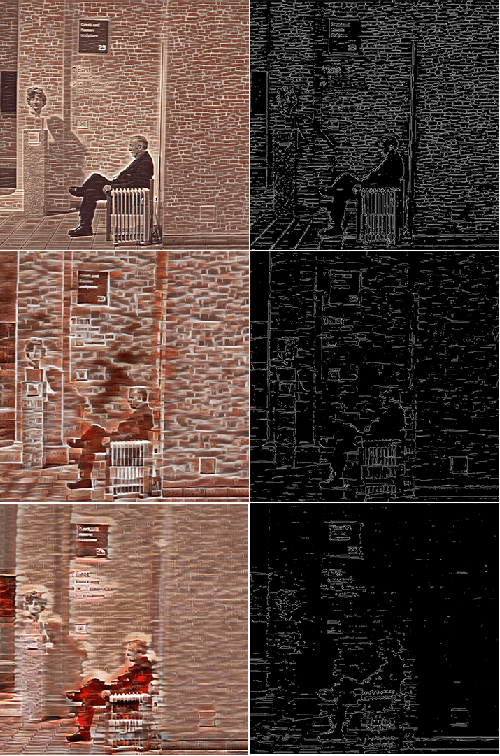

Abstract:Image style transfer is a challenging task in computational vision. Existing algorithms transfer the color and texture of style images by controlling the neural network's feature layers. However, they fail to control the strength of textures in different regions of the content image. To address this issue, we propose a training method that uses a loss function to constrain the style intensity in different regions. This method guides the transfer strength of style features in different regions based on the gradient relationship between style and content images. Additionally, we introduce a novel feature fusion method that linearly transforms content features to resemble style features while preserving their semantic relationships. Extensive experiments have demonstrated the effectiveness of our proposed approach.
Big Data Meet Cyber-Physical Systems: A Panoramic Survey
Oct 29, 2018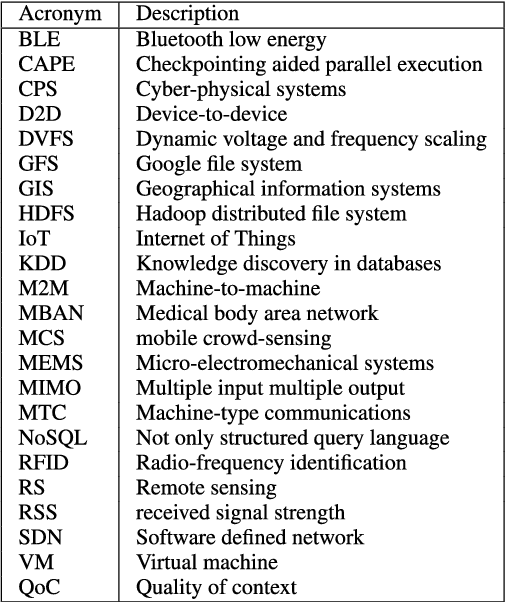


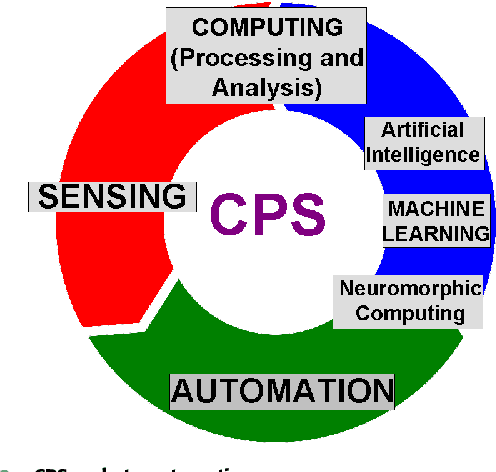
Abstract:The world is witnessing an unprecedented growth of cyber-physical systems (CPS), which are foreseen to revolutionize our world {via} creating new services and applications in a variety of sectors such as environmental monitoring, mobile-health systems, intelligent transportation systems and so on. The {information and communication technology }(ICT) sector is experiencing a significant growth in { data} traffic, driven by the widespread usage of smartphones, tablets and video streaming, along with the significant growth of sensors deployments that are anticipated in the near future. {It} is expected to outstandingly increase the growth rate of raw sensed data. In this paper, we present the CPS taxonomy {via} providing a broad overview of data collection, storage, access, processing and analysis. Compared with other survey papers, this is the first panoramic survey on big data for CPS, where our objective is to provide a panoramic summary of different CPS aspects. Furthermore, CPS {require} cybersecurity to protect {them} against malicious attacks and unauthorized intrusion, which {become} a challenge with the enormous amount of data that is continuously being generated in the network. {Thus, we also} provide an overview of the different security solutions proposed for CPS big data storage, access and analytics. We also discuss big data meeting green challenges in the contexts of CPS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge