Jinhyun Jang
Descriptive Image-Text Matching with Graded Contextual Similarity
May 15, 2025Abstract:Image-text matching aims to build correspondences between visual and textual data by learning their pairwise similarities. Most existing approaches have adopted sparse binary supervision, indicating whether a pair of images and sentences matches or not. However, such sparse supervision covers a limited subset of image-text relationships, neglecting their inherent many-to-many correspondences; an image can be described in numerous texts at different descriptive levels. Moreover, existing approaches overlook the implicit connections from general to specific descriptions, which form the underlying rationale for the many-to-many relationships between vision and language. In this work, we propose descriptive image-text matching, called DITM, to learn the graded contextual similarity between image and text by exploring the descriptive flexibility of language. We formulate the descriptiveness score of each sentence with cumulative term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF) to balance the pairwise similarity according to the keywords in the sentence. Our method leverages sentence descriptiveness to learn robust image-text matching in two key ways: (1) to refine the false negative labeling, dynamically relaxing the connectivity between positive and negative pairs, and (2) to build more precise matching, aligning a set of relevant sentences in a generic-to-specific order. By moving beyond rigid binary supervision, DITM enhances the discovery of both optimal matches and potential positive pairs. Extensive experiments on MS-COCO, Flickr30K, and CxC datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in representing complex image-text relationships compared to state-of-the-art approaches. In addition, DITM enhances the hierarchical reasoning ability of the model, supported by the extensive analysis on HierarCaps benchmark.
Improving Visual Recognition with Hyperbolical Visual Hierarchy Mapping
Apr 01, 2024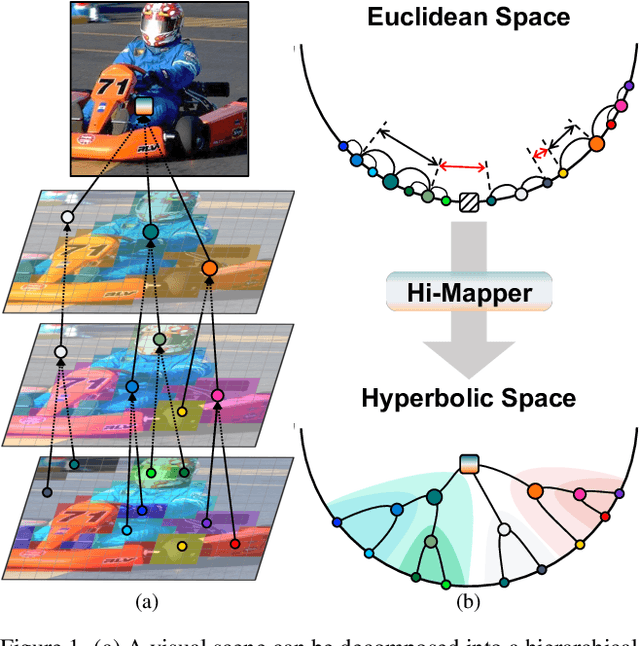
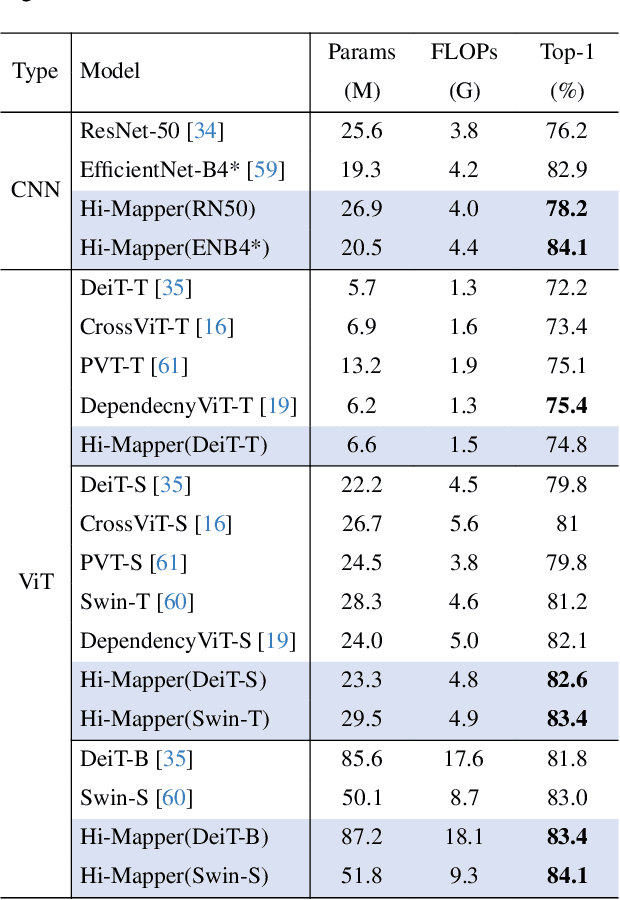
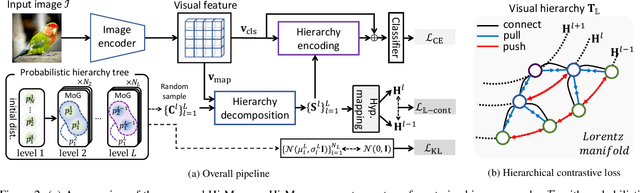
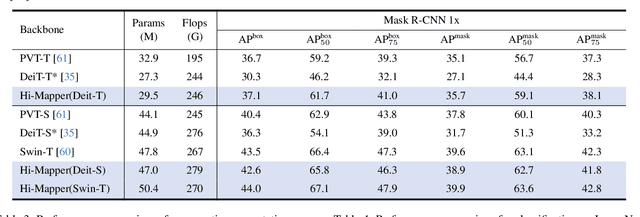
Abstract:Visual scenes are naturally organized in a hierarchy, where a coarse semantic is recursively comprised of several fine details. Exploring such a visual hierarchy is crucial to recognize the complex relations of visual elements, leading to a comprehensive scene understanding. In this paper, we propose a Visual Hierarchy Mapper (Hi-Mapper), a novel approach for enhancing the structured understanding of the pre-trained Deep Neural Networks (DNNs). Hi-Mapper investigates the hierarchical organization of the visual scene by 1) pre-defining a hierarchy tree through the encapsulation of probability densities; and 2) learning the hierarchical relations in hyperbolic space with a novel hierarchical contrastive loss. The pre-defined hierarchy tree recursively interacts with the visual features of the pre-trained DNNs through hierarchy decomposition and encoding procedures, thereby effectively identifying the visual hierarchy and enhancing the recognition of an entire scene. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Hi-Mapper significantly enhances the representation capability of DNNs, leading to an improved performance on various tasks, including image classification and dense prediction tasks.
Knowing Where to Focus: Event-aware Transformer for Video Grounding
Aug 14, 2023Abstract:Recent DETR-based video grounding models have made the model directly predict moment timestamps without any hand-crafted components, such as a pre-defined proposal or non-maximum suppression, by learning moment queries. However, their input-agnostic moment queries inevitably overlook an intrinsic temporal structure of a video, providing limited positional information. In this paper, we formulate an event-aware dynamic moment query to enable the model to take the input-specific content and positional information of the video into account. To this end, we present two levels of reasoning: 1) Event reasoning that captures distinctive event units constituting a given video using a slot attention mechanism; and 2) moment reasoning that fuses the moment queries with a given sentence through a gated fusion transformer layer and learns interactions between the moment queries and video-sentence representations to predict moment timestamps. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the event-aware dynamic moment queries, outperforming state-of-the-art approaches on several video grounding benchmarks.
Semantic-aware Network for Aerial-to-Ground Image Synthesis
Aug 14, 2023Abstract:Aerial-to-ground image synthesis is an emerging and challenging problem that aims to synthesize a ground image from an aerial image. Due to the highly different layout and object representation between the aerial and ground images, existing approaches usually fail to transfer the components of the aerial scene into the ground scene. In this paper, we propose a novel framework to explore the challenges by imposing enhanced structural alignment and semantic awareness. We introduce a novel semantic-attentive feature transformation module that allows to reconstruct the complex geographic structures by aligning the aerial feature to the ground layout. Furthermore, we propose semantic-aware loss functions by leveraging a pre-trained segmentation network. The network is enforced to synthesize realistic objects across various classes by separately calculating losses for different classes and balancing them. Extensive experiments including comparisons with previous methods and ablation studies show the effectiveness of the proposed framework both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Probabilistic Prompt Learning for Dense Prediction
Apr 03, 2023Abstract:Recent progress in deterministic prompt learning has become a promising alternative to various downstream vision tasks, enabling models to learn powerful visual representations with the help of pre-trained vision-language models. However, this approach results in limited performance for dense prediction tasks that require handling more complex and diverse objects, since a single and deterministic description cannot sufficiently represent the entire image. In this paper, we present a novel probabilistic prompt learning to fully exploit the vision-language knowledge in dense prediction tasks. First, we introduce learnable class-agnostic attribute prompts to describe universal attributes across the object class. The attributes are combined with class information and visual-context knowledge to define the class-specific textual distribution. Text representations are sampled and used to guide the dense prediction task using the probabilistic pixel-text matching loss, enhancing the stability and generalization capability of the proposed method. Extensive experiments on different dense prediction tasks and ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge