Jingyuan Zhao
PsychEval: A Multi-Session and Multi-Therapy Benchmark for High-Realism AI Psychological Counselor
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:To develop a reliable AI for psychological assessment, we introduce \texttt{PsychEval}, a multi-session, multi-therapy, and highly realistic benchmark designed to address three key challenges: \textbf{1) Can we train a highly realistic AI counselor?} Realistic counseling is a longitudinal task requiring sustained memory and dynamic goal tracking. We propose a multi-session benchmark (spanning 6-10 sessions across three distinct stages) that demands critical capabilities such as memory continuity, adaptive reasoning, and longitudinal planning. The dataset is annotated with extensive professional skills, comprising over 677 meta-skills and 4577 atomic skills. \textbf{2) How to train a multi-therapy AI counselor?} While existing models often focus on a single therapy, complex cases frequently require flexible strategies among various therapies. We construct a diverse dataset covering five therapeutic modalities (Psychodynamic, Behaviorism, CBT, Humanistic Existentialist, and Postmodernist) alongside an integrative therapy with a unified three-stage clinical framework across six core psychological topics. \textbf{3) How to systematically evaluate an AI counselor?} We establish a holistic evaluation framework with 18 therapy-specific and therapy-shared metrics across Client-Level and Counselor-Level dimensions. To support this, we also construct over 2,000 diverse client profiles. Extensive experimental analysis fully validates the superior quality and clinical fidelity of our dataset. Crucially, \texttt{PsychEval} transcends static benchmarking to serve as a high-fidelity reinforcement learning environment that enables the self-evolutionary training of clinically responsible and adaptive AI counselors.
Ultrasound-Guided Assistive Robots for Scoliosis Assessment with Optimization-based Control and Variable Impedance
Mar 04, 2022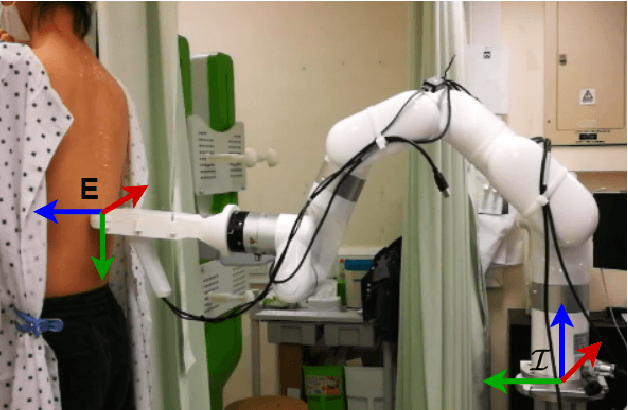
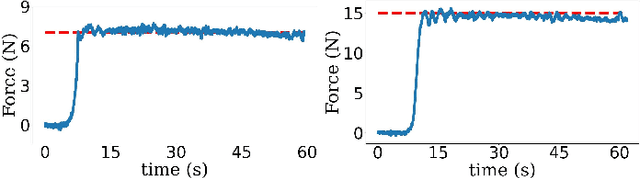
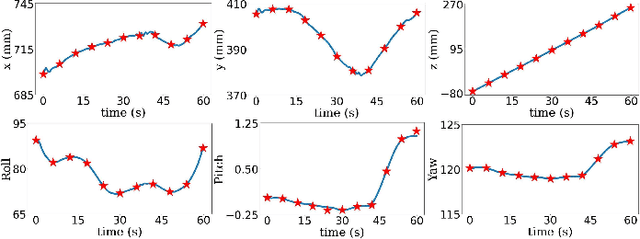
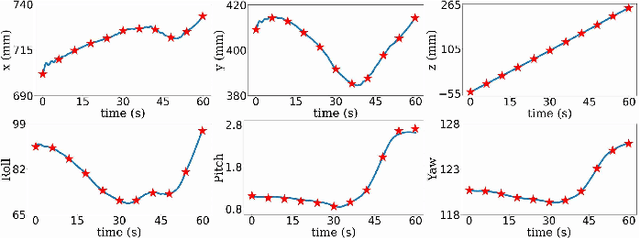
Abstract:Assistive robots for healthcare have seen a growing demand due to the great potential of relieving medical practitioners from routine jobs. In this paper, we investigate the development of an optimization-based control framework for an ultrasound-guided assistive robot to perform scoliosis assessment. A conventional procedure for scoliosis assessment with ultrasound imaging typically requires a medical practitioner to slide an ultrasound probe along a patient's back. To automate this type of procedure, we need to consider multiple objectives, such as contact force, position, orientation, energy, posture, etc. To address the aforementioned components, we propose to formulate the control framework design as a quadratic programming problem with each objective weighed by its task priority subject to a set of equality and inequality constraints. In addition, as the robot needs to establish constant contact with the patient during spine scanning, we incorporate variable impedance regulation of the end-effector position and orientation in the control architecture to enhance safety and stability during the physical human-robot interaction. Wherein, the variable impedance gains are retrieved by learning from the medical expert's demonstrations. The proposed methodology is evaluated by conducting real-world experiments of autonomous scoliosis assessment with a robot manipulator xArm. The effectiveness is verified by the obtained coronal spinal images of both a phantom and a human subject.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge