Jinghong Nan
Event-Based Dense Reconstruction Pipeline
Mar 23, 2022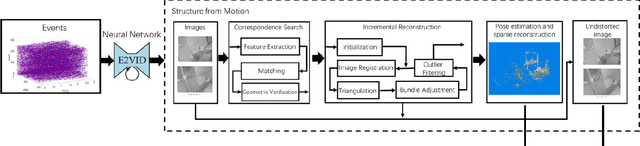
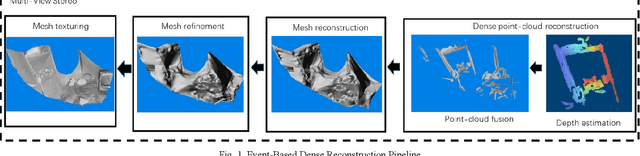

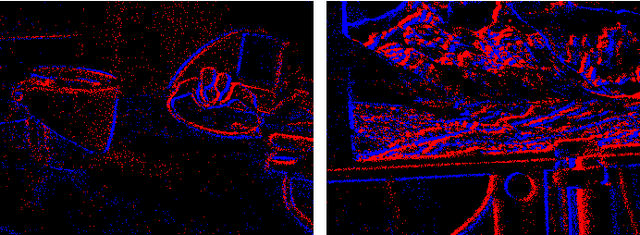
Abstract:Event cameras are a new type of sensors that are different from traditional cameras. Each pixel is triggered asynchronously by event. The trigger event is the change of the brightness irradiated on the pixel. If the increment or decrement of brightness is higher than a certain threshold, an event is output. Compared with traditional cameras, event cameras have the advantages of high dynamic range and no motion blur. Since events are caused by the apparent motion of intensity edges, the majority of 3D reconstructed maps consist only of scene edges, i.e., semi-dense maps, which is not enough for some applications. In this paper, we propose a pipeline to realize event-based dense reconstruction. First, deep learning is used to reconstruct intensity images from events. And then, structure from motion (SfM) is used to estimate camera intrinsic, extrinsic and sparse point cloud. Finally, multi-view stereo (MVS) is used to complete dense reconstruction.
State-aware Anti-drift Robust Correlation Tracking
Jun 28, 2018
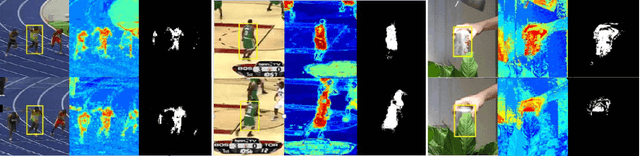

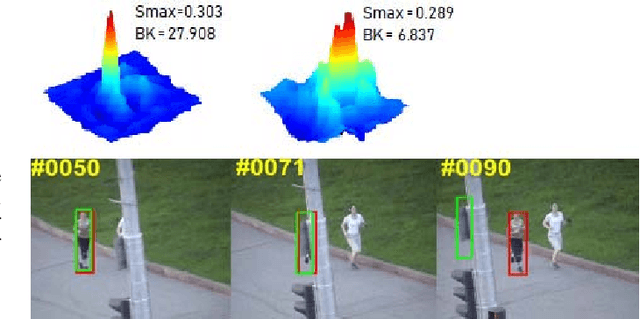
Abstract:Correlation filter (CF) based trackers have aroused increasing attentions in visual tracking field due to the superior performance on several datasets while maintaining high running speed. For each frame, an ideal filter is trained in order to discriminate the target from its surrounding background. Considering that the target always undergoes external and internal interference during tracking procedure, the trained filter should take consideration of not only the external distractions but also the target appearance variation synchronously. To this end, we present a State-aware Anti-drift Tracker (SAT) in this paper, which jointly model the discrimination and reliability information in filter learning. Specifically, global context patches are incorporated into filter training stage to better distinguish the target from backgrounds. Meanwhile, a color-based reliable mask is learned to encourage the filter to focus on more reliable regions suitable for tracking. We show that the proposed optimization problem could be efficiently solved using Alternative Direction Method of Multipliers and fully carried out in Fourier domain. Extensive experiments are conducted on OTB-100 datasets to compare the SAT tracker (both hand-crafted feature and CNN feature) with other relevant state-of-the-art methods. Both quantitative and qualitative evaluations further demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed work.
Correlation Tracking via Robust Region Proposals
Jun 14, 2018


Abstract:Recently, correlation filter-based trackers have received extensive attention due to their simplicity and superior speed. However, such trackers perform poorly when the target undergoes occlusion, viewpoint change or other challenging attributes due to pre-defined sampling strategy. To tackle these issues, in this paper, we propose an adaptive region proposal scheme to facilitate visual tracking. To be more specific, a novel tracking monitoring indicator is advocated to forecast tracking failure. Afterwards, we incorporate detection and scale proposals respectively, to recover from model drift as well as handle aspect ratio variation. We test the proposed algorithm on several challenging sequences, which have demonstrated that the proposed tracker performs favourably against state-of-the-art trackers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge