Chenwei Deng
State-aware Anti-drift Robust Correlation Tracking
Jun 28, 2018

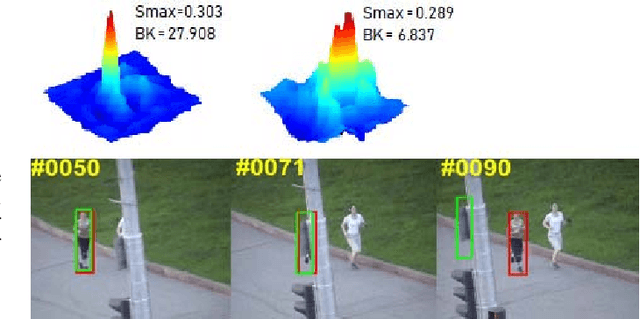
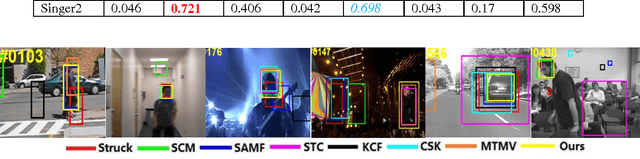
Abstract:Correlation filter (CF) based trackers have aroused increasing attentions in visual tracking field due to the superior performance on several datasets while maintaining high running speed. For each frame, an ideal filter is trained in order to discriminate the target from its surrounding background. Considering that the target always undergoes external and internal interference during tracking procedure, the trained filter should take consideration of not only the external distractions but also the target appearance variation synchronously. To this end, we present a State-aware Anti-drift Tracker (SAT) in this paper, which jointly model the discrimination and reliability information in filter learning. Specifically, global context patches are incorporated into filter training stage to better distinguish the target from backgrounds. Meanwhile, a color-based reliable mask is learned to encourage the filter to focus on more reliable regions suitable for tracking. We show that the proposed optimization problem could be efficiently solved using Alternative Direction Method of Multipliers and fully carried out in Fourier domain. Extensive experiments are conducted on OTB-100 datasets to compare the SAT tracker (both hand-crafted feature and CNN feature) with other relevant state-of-the-art methods. Both quantitative and qualitative evaluations further demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed work.
Adaptive Feature Representation for Visual Tracking
May 12, 2017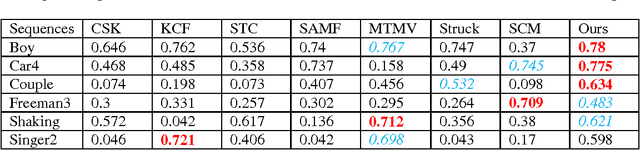
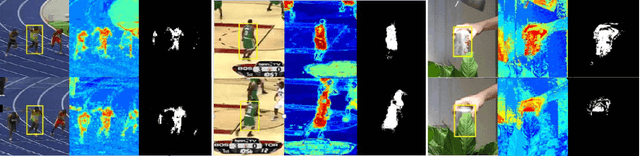
Abstract:Robust feature representation plays significant role in visual tracking. However, it remains a challenging issue, since many factors may affect the experimental performance. The existing method which combine different features by setting them equally with the fixed weight could hardly solve the issues, due to the different statistical properties of different features across various of scenarios and attributes. In this paper, by exploiting the internal relationship among these features, we develop a robust method to construct a more stable feature representation. More specifically, we utilize a co-training paradigm to formulate the intrinsic complementary information of multi-feature template into the efficient correlation filter framework. We test our approach on challenging se- quences with illumination variation, scale variation, deformation etc. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art methods favorably.
Dual Teaching: A Practical Semi-supervised Wrapper Method
Nov 12, 2016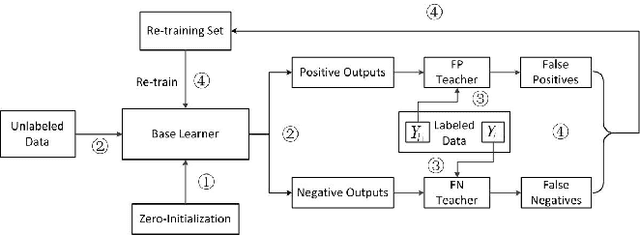

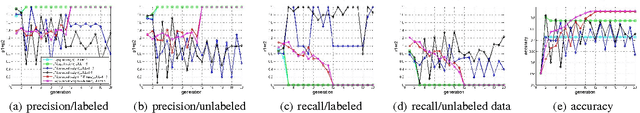

Abstract:Semi-supervised wrapper methods are concerned with building effective supervised classifiers from partially labeled data. Though previous works have succeeded in some fields, it is still difficult to apply semi-supervised wrapper methods to practice because the assumptions those methods rely on tend to be unrealistic in practice. For practical use, this paper proposes a novel semi-supervised wrapper method, Dual Teaching, whose assumptions are easy to set up. Dual Teaching adopts two external classifiers to estimate the false positives and false negatives of the base learner. Only if the recall of every external classifier is greater than zero and the sum of the precision is greater than one, Dual Teaching will train a base learner from partially labeled data as effectively as the fully-labeled-data-trained classifier. The effectiveness of Dual Teaching is proved in both theory and practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge