Jim Warren
Explanation Beyond Intuition: A Testable Criterion for Inherent Explainability
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Inherent explainability is the gold standard in Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI). However, there is not a consistent definition or test to demonstrate inherent explainability. Work to date either characterises explainability through metrics, or appeals to intuition - "we know it when we see it". We propose a globally applicable criterion for inherent explainability. The criterion uses graph theory for representing and decomposing models for structure-local explanation, and recomposing them into global explanations. We form the structure-local explanations as annotations, a verifiable hypothesis-evidence structure that allows for a range of explanatory methods to be used. This criterion matches existing intuitions on inherent explainability, and provides justifications why a large regression model may not be explainable but a sparse neural network could be. We differentiate explainable -- a model that allows for explanation -- and \textit{explained} -- one that has a verified explanation. Finally, we provide a full explanation of PREDICT -- a Cox proportional hazards model of cardiovascular disease risk, which is in active clinical use in New Zealand. It follows that PREDICT is inherently explainable. This work provides structure to formalise other work on explainability, and allows regulators a flexible but rigorous test that can be used in compliance frameworks.
PropNEAT -- Efficient GPU-Compatible Backpropagation over NeuroEvolutionary Augmenting Topology Networks
Nov 06, 2024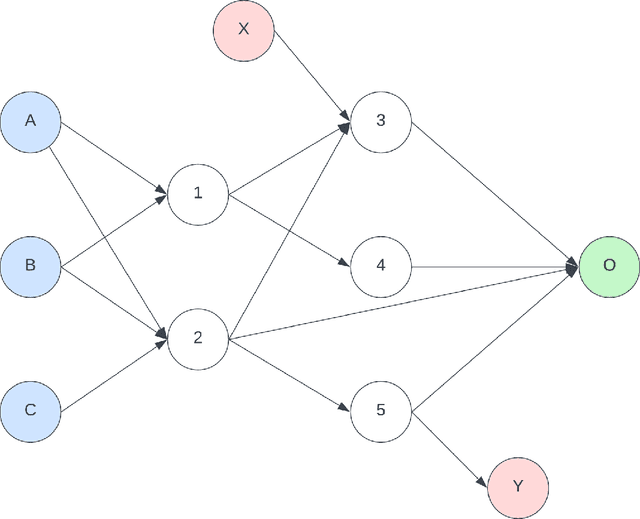



Abstract:We introduce PropNEAT, a fast backpropagation implementation of NEAT that uses a bidirectional mapping of the genome graph to a layer-based architecture that preserves the NEAT genomes whilst enabling efficient GPU backpropagation. We test PropNEAT on 58 binary classification datasets from the Penn Machine Learning Benchmarks database, comparing the performance against logistic regression, dense neural networks and random forests, as well as a densely retrained variant of the final PropNEAT model. PropNEAT had the second best overall performance, behind Random Forest, though the difference between the models was not statistically significant apart from between Random Forest in comparison with logistic regression and the PropNEAT retrain models. PropNEAT was substantially faster than a naive backpropagation method, and both were substantially faster and had better performance than the original NEAT implementation. We demonstrate that the per-epoch training time for PropNEAT scales linearly with network depth, and is efficient on GPU implementations for backpropagation. This implementation could be extended to support reinforcement learning or convolutional networks, and is able to find sparser and smaller networks with potential for applications in low-power contexts.
DeepQR: Neural-based Quality Ratings for Learnersourced Multiple-Choice Questions
Nov 19, 2021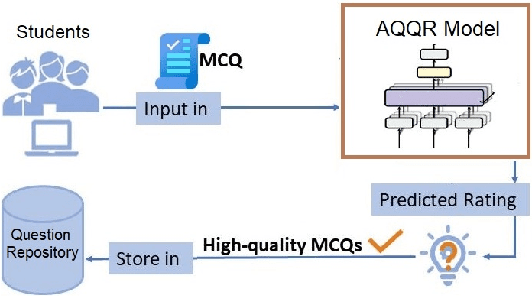
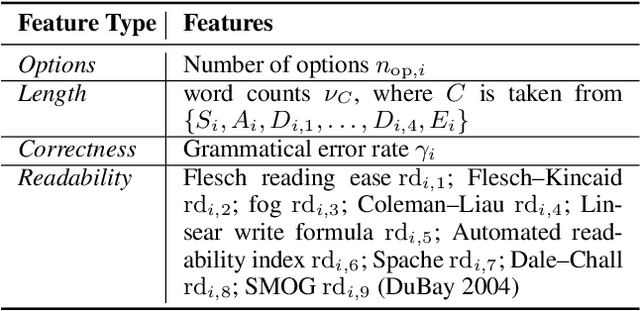
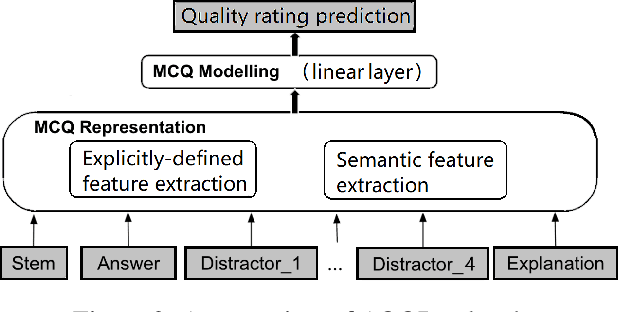

Abstract:Automated question quality rating (AQQR) aims to evaluate question quality through computational means, thereby addressing emerging challenges in online learnersourced question repositories. Existing methods for AQQR rely solely on explicitly-defined criteria such as readability and word count, while not fully utilising the power of state-of-the-art deep-learning techniques. We propose DeepQR, a novel neural-network model for AQQR that is trained using multiple-choice-question (MCQ) datasets collected from PeerWise, a widely-used learnersourcing platform. Along with designing DeepQR, we investigate models based on explicitly-defined features, or semantic features, or both. We also introduce a self-attention mechanism to capture semantic correlations between MCQ components, and a contrastive-learning approach to acquire question representations using quality ratings. Extensive experiments on datasets collected from eight university-level courses illustrate that DeepQR has superior performance over six comparative models.
A chatbot architecture for promoting youth resilience
May 15, 2020



Abstract:E-health technologies have the potential to provide scalable and accessible interventions for youth mental health. As part of a developing an ecosystem of e-screening and e-therapy tools for New Zealand young people, a dialog agent, Headstrong, has been designed to promote resilience with methods grounded in cognitive behavioral therapy and positive psychology. This paper describes the architecture underlying the chatbot. The architecture supports a range of over 20 activities delivered in a 4-week program by relatable personas. The architecture provides a visual authoring interface to its content management system. In addition to supporting the original adolescent resilience chatbot, the architecture has been reused to create a 3-week 'stress-detox' intervention for undergraduates, and subsequently for a chatbot to support young people with the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, with all three systems having been used in field trials. The Headstrong architecture illustrates the feasibility of creating a domain-focused authoring environment in the context of e-therapy that supports non-technical expert input and rapid deployment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge