Jim Chan
Learning to Personalize Recommendation based on Customers' Shopping Intents
May 10, 2023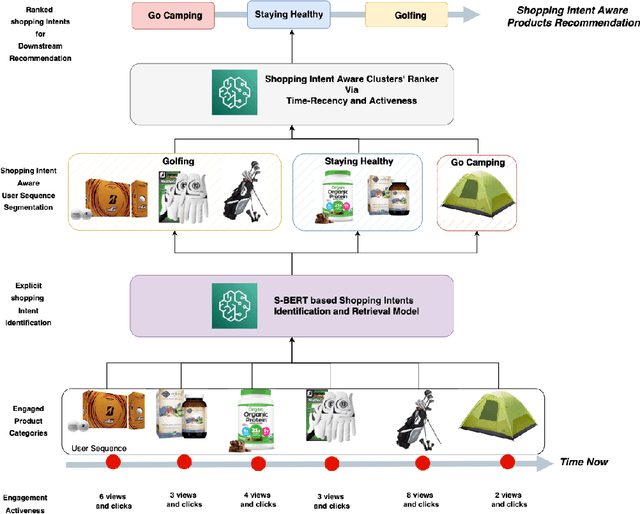
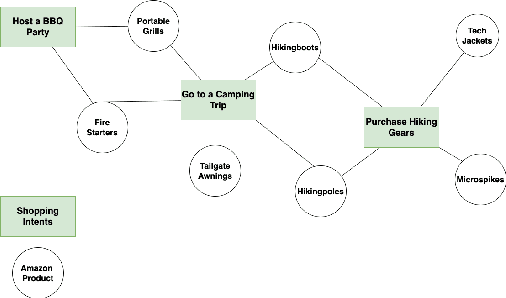
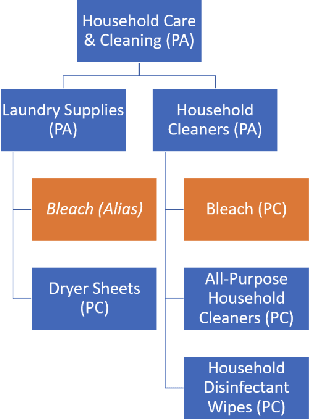
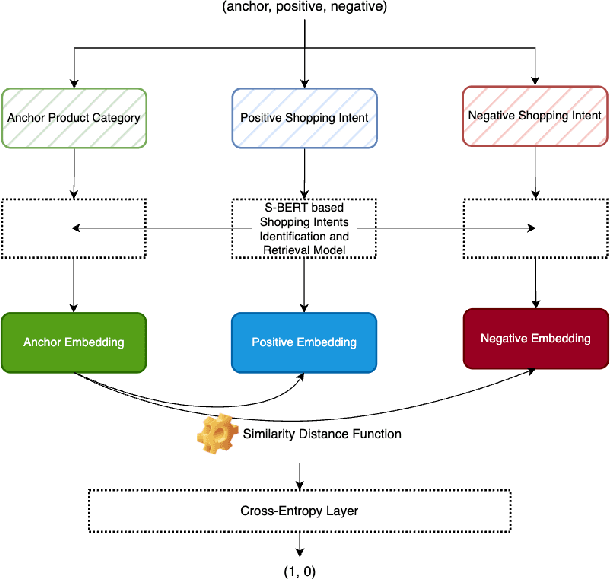
Abstract:Understanding the customers' high level shopping intent, such as their desire to go camping or hold a birthday party, is critically important for an E-commerce platform; it can help boost the quality of shopping experience by enabling provision of more relevant, explainable, and diversified recommendations. However, such high level shopping intent has been overlooked in the industry due to practical challenges. In this work, we introduce Amazon's new system that explicitly identifies and utilizes each customer's high level shopping intents for personalizing recommendations. We develop a novel technique that automatically identifies various high level goals being pursued by the Amazon customers, such as "go camping", and "preparing for a beach party". Our solution is in a scalable fashion (in 14 languages across 21 countries). Then a deep learning model maps each customer's online behavior, e.g. product search and individual item engagements, into a subset of high level shopping intents. Finally, a realtime ranker considers both the identified intents as well as the granular engagements to present personalized intent-aware recommendations. Extensive offline analysis ensures accuracy and relevance of the new recommendations and we further observe an 10% improvement in the business metrics. This system is currently serving online traffic at amazon.com, powering several production features, driving significant business impacts
Coarse-to-Fine Sparse Sequential Recommendation
Apr 04, 2022



Abstract:Sequential recommendation aims to model dynamic user behavior from historical interactions. Self-attentive methods have proven effective at capturing short-term dynamics and long-term preferences. Despite their success, these approaches still struggle to model sparse data, on which they struggle to learn high-quality item representations. We propose to model user dynamics from shopping intents and interacted items simultaneously. The learned intents are coarse-grained and work as prior knowledge for item recommendation. To this end, we present a coarse-to-fine self-attention framework, namely CaFe, which explicitly learns coarse-grained and fine-grained sequential dynamics. Specifically, CaFe first learns intents from coarse-grained sequences which are dense and hence provide high-quality user intent representations. Then, CaFe fuses intent representations into item encoder outputs to obtain improved item representations. Finally, we infer recommended items based on representations of items and corresponding intents. Experiments on sparse datasets show that CaFe outperforms state-of-the-art self-attentive recommenders by 44.03% NDCG@5 on average.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge