Jiawei Lin
Kimi K2.5: Visual Agentic Intelligence
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2.5, an open-source multimodal agentic model designed to advance general agentic intelligence. K2.5 emphasizes the joint optimization of text and vision so that two modalities enhance each other. This includes a series of techniques such as joint text-vision pre-training, zero-vision SFT, and joint text-vision reinforcement learning. Building on this multimodal foundation, K2.5 introduces Agent Swarm, a self-directed parallel agent orchestration framework that dynamically decomposes complex tasks into heterogeneous sub-problems and executes them concurrently. Extensive evaluations show that Kimi K2.5 achieves state-of-the-art results across various domains including coding, vision, reasoning, and agentic tasks. Agent Swarm also reduces latency by up to $4.5\times$ over single-agent baselines. We release the post-trained Kimi K2.5 model checkpoint to facilitate future research and real-world applications of agentic intelligence.
ReLayout: Versatile and Structure-Preserving Design Layout Editing via Relation-Aware Design Reconstruction
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Automated redesign without manual adjustments marks a key step forward in the design workflow. In this work, we focus on a foundational redesign task termed design layout editing, which seeks to autonomously modify the geometric composition of a design based on user intents. To overcome the ambiguity of user needs expressed in natural language, we introduce four basic and important editing actions and standardize the format of editing operations. The underexplored task presents a unique challenge: satisfying specified editing operations while simultaneously preserving the layout structure of unedited elements. Besides, the scarcity of triplet (original design, editing operation, edited design) samples poses another formidable challenge. To this end, we present ReLayout, a novel framework for versatile and structure-preserving design layout editing that operates without triplet data. Specifically, ReLayout first introduces the relation graph, which contains the position and size relationships among unedited elements, as the constraint for layout structure preservation. Then, relation-aware design reconstruction (RADR) is proposed to bypass the data challenge. By learning to reconstruct a design from its elements, a relation graph, and a synthesized editing operation, RADR effectively emulates the editing process in a self-supervised manner. A multi-modal large language model serves as the backbone for RADR, unifying multiple editing actions within a single model and thus achieving versatile editing after fine-tuning. Qualitative, quantitative results and user studies show that ReLayout significantly outperforms the baseline models in terms of editing quality, accuracy, and layout structure preservation.
High-Altitude Balloon Station-Keeping with First Order Model Predictive Control
Nov 11, 2025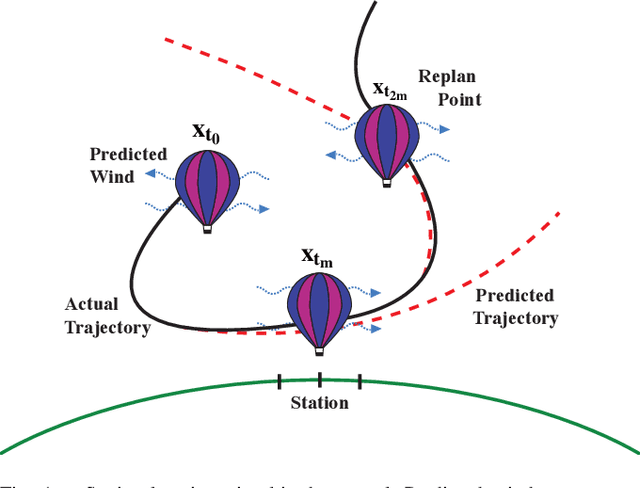
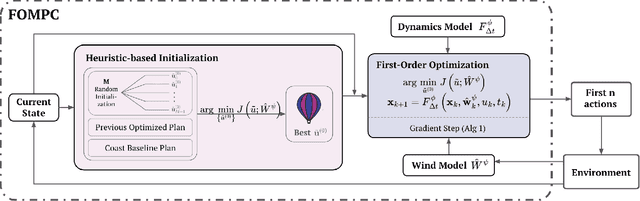
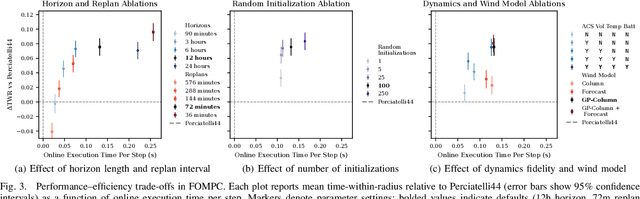
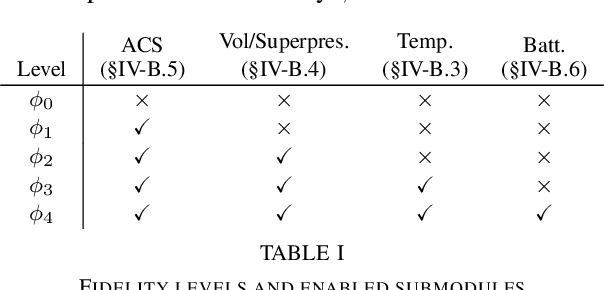
Abstract:High-altitude balloons (HABs) are common in scientific research due to their wide range of applications and low cost. Because of their nonlinear, underactuated dynamics and the partial observability of wind fields, prior work has largely relied on model-free reinforcement learning (RL) methods to design near-optimal control schemes for station-keeping. These methods often compare only against hand-crafted heuristics, dismissing model-based approaches as impractical given the system complexity and uncertain wind forecasts. We revisit this assumption about the efficacy of model-based control for station-keeping by developing First-Order Model Predictive Control (FOMPC). By implementing the wind and balloon dynamics as differentiable functions in JAX, we enable gradient-based trajectory optimization for online planning. FOMPC outperforms a state-of-the-art RL policy, achieving a 24% improvement in time-within-radius (TWR) without requiring offline training, though at the cost of greater online computation per control step. Through systematic ablations of modeling assumptions and control factors, we show that online planning is effective across many configurations, including under simplified wind and dynamics models.
PHYBench: Holistic Evaluation of Physical Perception and Reasoning in Large Language Models
Apr 22, 2025



Abstract:We introduce PHYBench, a novel, high-quality benchmark designed for evaluating reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in physical contexts. PHYBench consists of 500 meticulously curated physics problems based on real-world physical scenarios, designed to assess the ability of models to understand and reason about realistic physical processes. Covering mechanics, electromagnetism, thermodynamics, optics, modern physics, and advanced physics, the benchmark spans difficulty levels from high school exercises to undergraduate problems and Physics Olympiad challenges. Additionally, we propose the Expression Edit Distance (EED) Score, a novel evaluation metric based on the edit distance between mathematical expressions, which effectively captures differences in model reasoning processes and results beyond traditional binary scoring methods. We evaluate various LLMs on PHYBench and compare their performance with human experts. Our results reveal that even state-of-the-art reasoning models significantly lag behind human experts, highlighting their limitations and the need for improvement in complex physical reasoning scenarios. Our benchmark results and dataset are publicly available at https://phybench-official.github.io/phybench-demo/.
From Elements to Design: A Layered Approach for Automatic Graphic Design Composition
Dec 27, 2024Abstract:In this work, we investigate automatic design composition from multimodal graphic elements. Although recent studies have developed various generative models for graphic design, they usually face the following limitations: they only focus on certain subtasks and are far from achieving the design composition task; they do not consider the hierarchical information of graphic designs during the generation process. To tackle these issues, we introduce the layered design principle into Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) and propose a novel approach, called LaDeCo, to accomplish this challenging task. Specifically, LaDeCo first performs layer planning for a given element set, dividing the input elements into different semantic layers according to their contents. Based on the planning results, it subsequently predicts element attributes that control the design composition in a layer-wise manner, and includes the rendered image of previously generated layers into the context. With this insightful design, LaDeCo decomposes the difficult task into smaller manageable steps, making the generation process smoother and clearer. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of LaDeCo in design composition. Furthermore, we show that LaDeCo enables some interesting applications in graphic design, such as resolution adjustment, element filling, design variation, etc. In addition, it even outperforms the specialized models in some design subtasks without any task-specific training.
Continuous Execution of High-Level Collaborative Tasks for Heterogeneous Robot Teams
Jun 26, 2024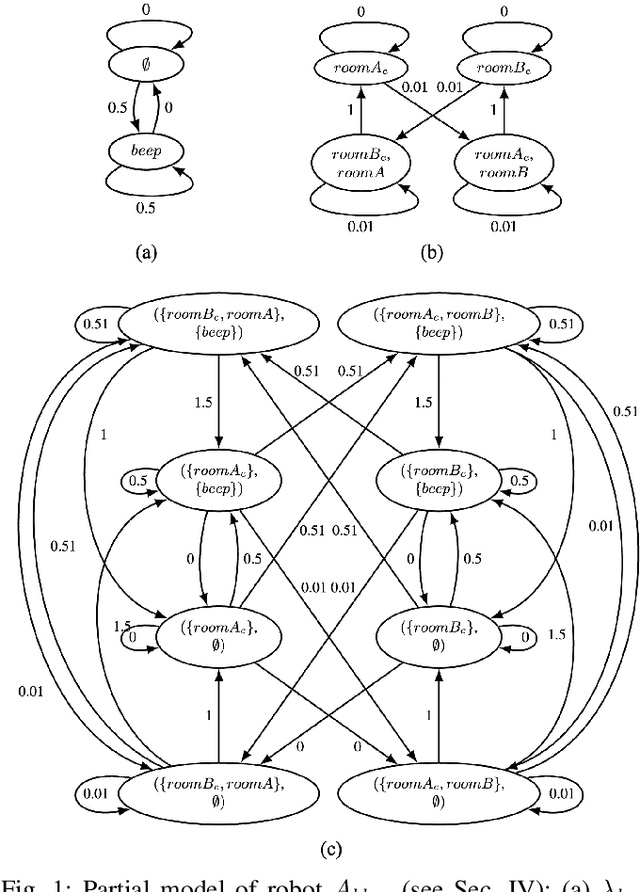



Abstract:We propose a control synthesis framework for a heterogeneous multi-robot system to satisfy collaborative tasks, where actions may take varying duration of time to complete. We encode tasks using the discrete logic LTL^\psi, which uses the concept of bindings to interleave robot actions and express information about relationship between specific task requirements and robot assignments. We present a synthesis approach to automatically generate a teaming assignment and corresponding discrete behavior that is correct-by-construction for continuous execution, while also implementing synchronization policies to ensure collaborative portions of the task are satisfied. We demonstrate our approach on a physical multi-robot system.
LayoutPrompter: Awaken the Design Ability of Large Language Models
Nov 11, 2023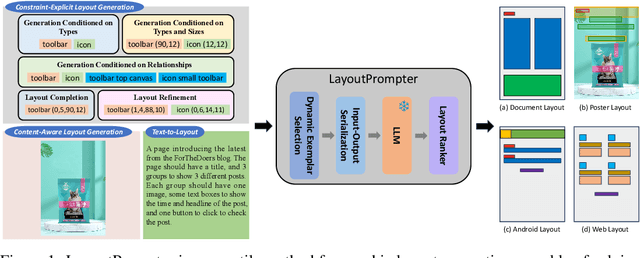

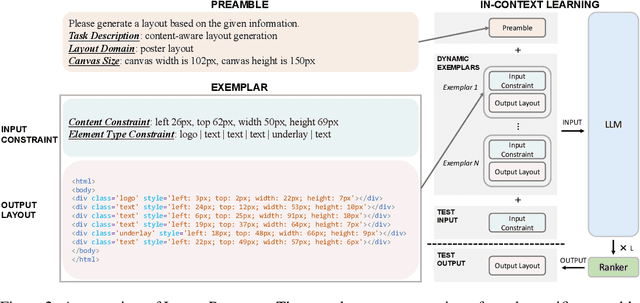

Abstract:Conditional graphic layout generation, which automatically maps user constraints to high-quality layouts, has attracted widespread attention today. Although recent works have achieved promising performance, the lack of versatility and data efficiency hinders their practical applications. In this work, we propose LayoutPrompter, which leverages large language models (LLMs) to address the above problems through in-context learning. LayoutPrompter is made up of three key components, namely input-output serialization, dynamic exemplar selection and layout ranking. Specifically, the input-output serialization component meticulously designs the input and output formats for each layout generation task. Dynamic exemplar selection is responsible for selecting the most helpful prompting exemplars for a given input. And a layout ranker is used to pick the highest quality layout from multiple outputs of LLMs. We conduct experiments on all existing layout generation tasks using four public datasets. Despite the simplicity of our approach, experimental results show that LayoutPrompter can compete with or even outperform state-of-the-art approaches on these tasks without any model training or fine-tuning. This demonstrates the effectiveness of this versatile and training-free approach. In addition, the ablation studies show that LayoutPrompter is significantly superior to the training-based baseline in a low-data regime, further indicating the data efficiency of LayoutPrompter. Our project is available at https://github.com/microsoft/LayoutGeneration/tree/main/LayoutPrompter.
A Parse-Then-Place Approach for Generating Graphic Layouts from Textual Descriptions
Aug 24, 2023



Abstract:Creating layouts is a fundamental step in graphic design. In this work, we propose to use text as the guidance to create graphic layouts, i.e., Text-to-Layout, aiming to lower the design barriers. Text-to-Layout is a challenging task, because it needs to consider the implicit, combined, and incomplete layout constraints from text, each of which has not been studied in previous work. To address this, we present a two-stage approach, named parse-then-place. The approach introduces an intermediate representation (IR) between text and layout to represent diverse layout constraints. With IR, Text-to-Layout is decomposed into a parse stage and a place stage. The parse stage takes a textual description as input and generates an IR, in which the implicit constraints from the text are transformed into explicit ones. The place stage generates layouts based on the IR. To model combined and incomplete constraints, we use a Transformer-based layout generation model and carefully design a way to represent constraints and layouts as sequences. Besides, we adopt the pretrain-then-finetune strategy to boost the performance of the layout generation model with large-scale unlabeled layouts. To evaluate our approach, we construct two Text-to-Layout datasets and conduct experiments on them. Quantitative results, qualitative analysis, and user studies demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge