Jiatong Bai
Multi-modal Iterative and Deep Fusion Frameworks for Enhanced Passive DOA Sensing via a Green Massive H2AD MIMO Receiver
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:Most existing DOA estimation methods assume ideal source incident angles with minimal noise. Moreover, directly using pre-estimated angles to calculate weighted coefficients can lead to performance loss. Thus, a green multi-modal (MM) fusion DOA framework is proposed to realize a more practical, low-cost and high time-efficiency DOA estimation for a H$^2$AD array. Firstly, two more efficient clustering methods, global maximum cos\_similarity clustering (GMaxCS) and global minimum distance clustering (GMinD), are presented to infer more precise true solutions from the candidate solution sets. Based on this, an iteration weighted fusion (IWF)-based method is introduced to iteratively update weighted fusion coefficients and the clustering center of the true solution classes by using the estimated values. Particularly, the coarse DOA calculated by fully digital (FD) subarray, serves as the initial cluster center. The above process yields two methods called MM-IWF-GMaxCS and MM-IWF-GMinD. To further provide a higher-accuracy DOA estimation, a fusion network (fusionNet) is proposed to aggregate the inferred two-part true angles and thus generates two effective approaches called MM-fusionNet-GMaxCS and MM-fusionNet-GMinD. The simulation outcomes show the proposed four approaches can achieve the ideal DOA performance and the CRLB. Meanwhile, proposed MM-fusionNet-GMaxCS and MM-fusionNet-GMinD exhibit superior DOA performance compared to MM-IWF-GMaxCS and MM-IWF-GMinD, especially in extremely-low SNR range.
Machine learning-based Near-field Emitter Localization via Grouped Hybrid Analog and Digital Massive MIMO Receive Array
Jun 14, 2024



Abstract:A fully-digital massive MIMO receive array is promising to meet the high-resolution requirement of near-field (NF) emitter localization, but it also results in the significantly increasing of hardware costs and algorithm complexity. In order to meet the future demand for green communication while maintaining high performance, the grouped hybrid analog and digital (HAD) structure is proposed for NF DOA estimation, which divides the large-scale receive array into small-scale groups and each group contains several subarrays. Thus the NF direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation problem is viewed as far-field (FF) within each group, and some existing methods such as MUSIC, Root-MUSIC, ESPRIT, etc., can be adopted. Then by angle calibration, a candidate position set is generated. To eliminate the phase ambiguity arising from the HAD structure and obtain the emitter position, two low-complexity clustering-based methods, minimum sample distance clustering (MSDC) and range scatter diagram (RSD) - angle scatter diagram (ASD)-based DBSCAN (RSD-ASD-DBSCAN), are proposed based on the distribution features of samples in the candidate position set. Then to further improve the localization accuracy, a model-driven regression network (RegNet) is designed, which consists of a multi-layer neural network (MLNN) for false solution elimination and a perceptron for angle fusion. Finally, the Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) of NF emitter localization for the proposed grouped HAD structure is also derived. The simulation results show that the proposed methods can achieve CRLB at different SNR regions, the RegNet has great performance advantages at low SNR regions and the clustering-based methods have much lower complexity.
Two Power Allocation and Beamforming Strategies for Active IRS-aided Wireless Network via Machine Learning
Jun 09, 2024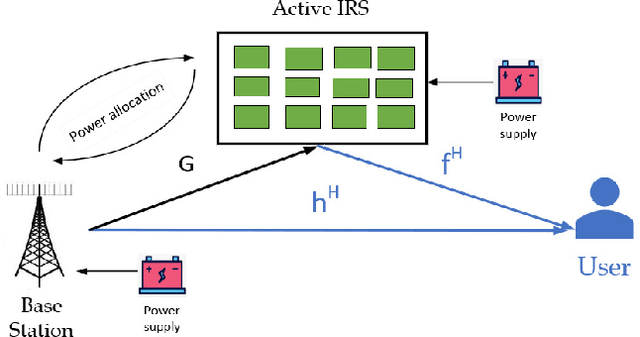
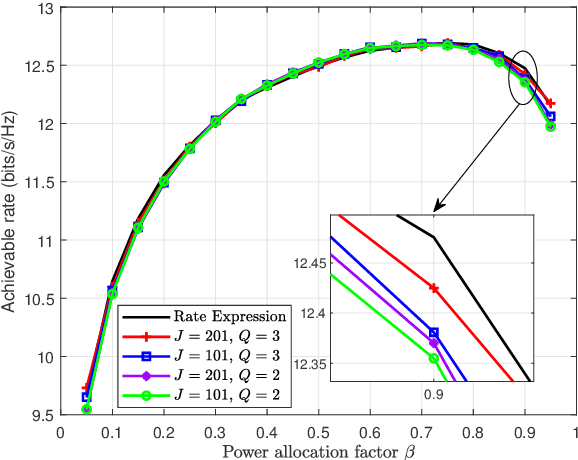
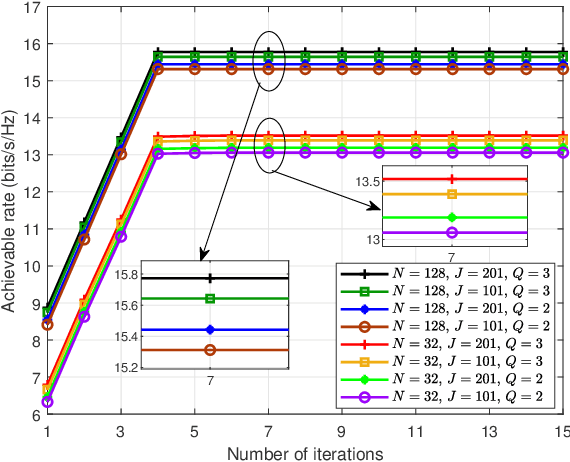
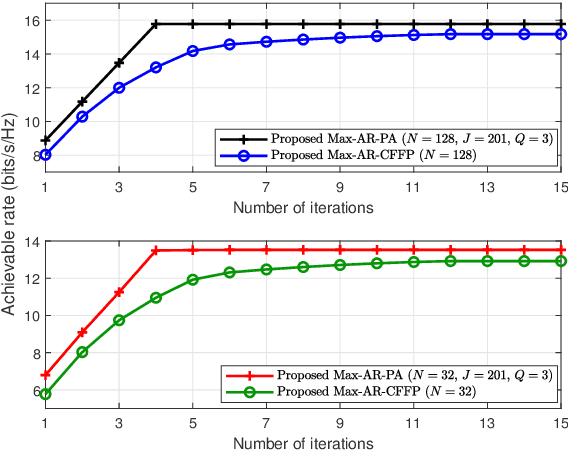
Abstract:This paper models an active intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) -assisted wireless communication network, which has the ability to adjust power between BS and IRS. We aim to maximize the signal-to-noise ratio of user by jointly designing power allocation (PA) factor, active IRS phase shift matrix, and beamforming vector of BS, subject to a total power constraint. To tackle this non-convex problem, we solve this problem by alternately optimizing these variables. Firstly, the PA factor is designed via polynomial regression method. Next, BS beamforming vector and IRS phase shift matrix are obtained by Dinkelbach's transform and successive convex approximation methods. To reduce the high computational complexity of the above proposed algorithm, we maximize achievable rate (AR) and use closed-form fractional programming method to transform the original problem into an equivalent form. Then, we address this problem by iteratively optimizing auxiliary variables, BS and IRS beamformings. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithms can effectively improve the AR performance compared to fixed PA strategies, aided by passive IRS, and without IRS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge