Jiaqian Wang
MemRL: Self-Evolving Agents via Runtime Reinforcement Learning on Episodic Memory
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:The hallmark of human intelligence is the ability to master new skills through Constructive Episodic Simulation-retrieving past experiences to synthesize solutions for novel tasks. While Large Language Models possess strong reasoning capabilities, they struggle to emulate this self-evolution: fine-tuning is computationally expensive and prone to catastrophic forgetting, while existing memory-based methods rely on passive semantic matching that often retrieves noise. To address these challenges, we propose MemRL, a framework that enables agents to self-evolve via non-parametric reinforcement learning on episodic memory. MemRL explicitly separates the stable reasoning of a frozen LLM from the plastic, evolving memory. Unlike traditional methods, MemRL employs a Two-Phase Retrieval mechanism that filters candidates by semantic relevance and then selects them based on learned Q-values (utility). These utilities are continuously refined via environmental feedback in an trial-and-error manner, allowing the agent to distinguish high-value strategies from similar noise. Extensive experiments on HLE, BigCodeBench, ALFWorld, and Lifelong Agent Bench demonstrate that MemRL significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines. Our analysis experiments confirm that MemRL effectively reconciles the stability-plasticity dilemma, enabling continuous runtime improvement without weight updates.
Targeted aspect based multimodal sentiment analysis:an attention capsule extraction and multi-head fusion network
Mar 13, 2021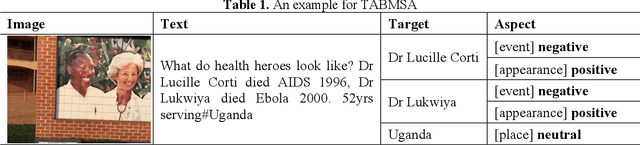
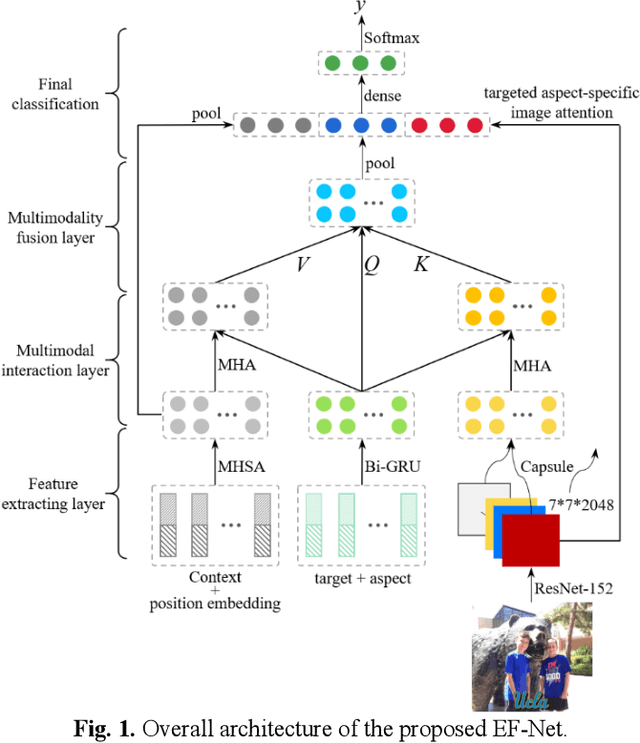
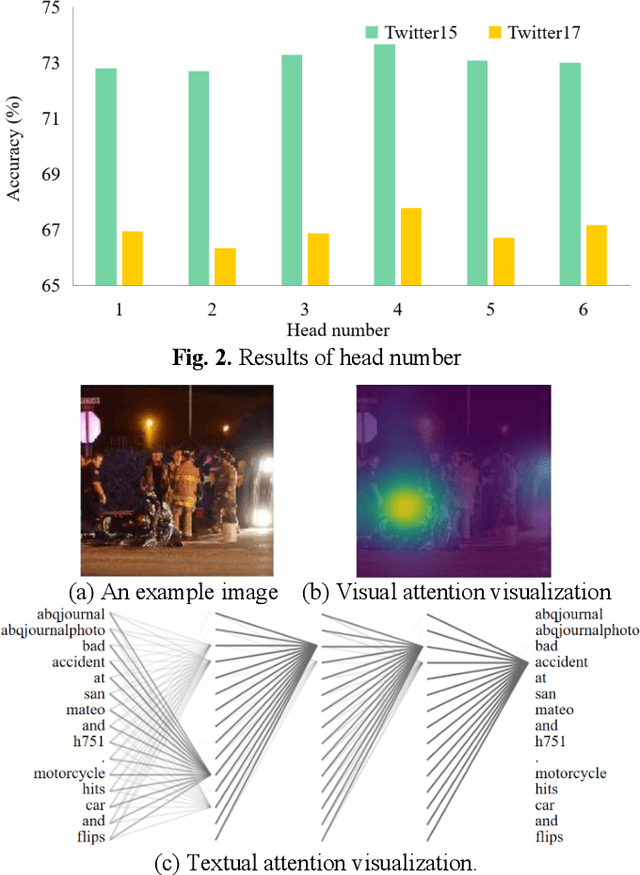
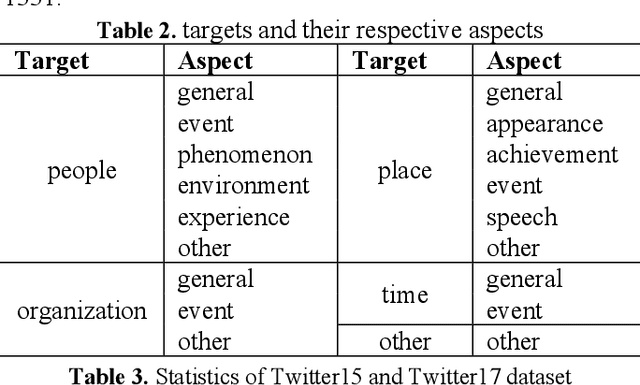
Abstract:Multimodal sentiment analysis has currently identified its significance in a variety of domains. For the purpose of sentiment analysis, different aspects of distinguishing modalities, which correspond to one target, are processed and analyzed. In this work, we propose the targeted aspect-based multimodal sentiment analysis (TABMSA) for the first time. Furthermore, an attention capsule extraction and multi-head fusion network (EF-Net) on the task of TABMSA is devised. The multi-head attention (MHA) based network and the ResNet-152 are employed to deal with texts and images, respectively. The integration of MHA and capsule network aims to capture the interaction among the multimodal inputs. In addition to the targeted aspect, the information from the context and the image is also incorporated for sentiment delivered. We evaluate the proposed model on two manually annotated datasets. the experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed model for this new task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge