Jianye Pang
3D Shuffle-Mixer: An Efficient Context-Aware Vision Learner of Transformer-MLP Paradigm for Dense Prediction in Medical Volume
Apr 14, 2022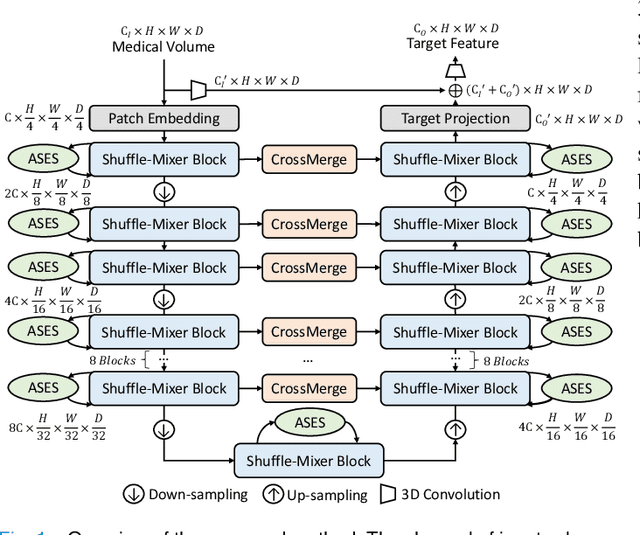
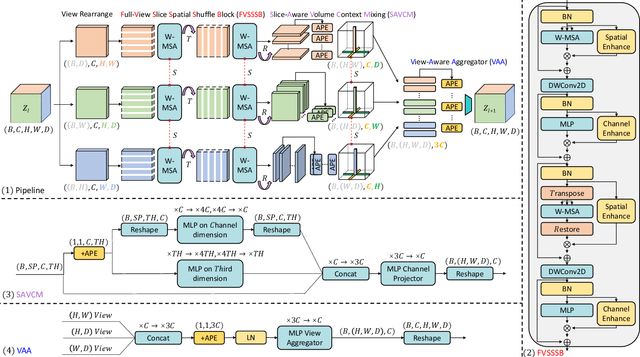
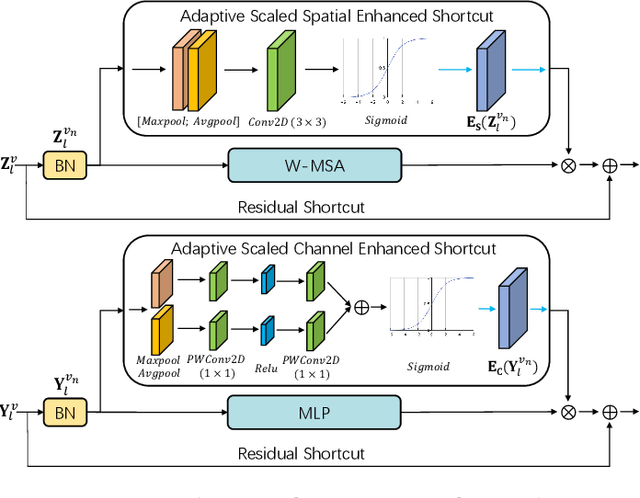
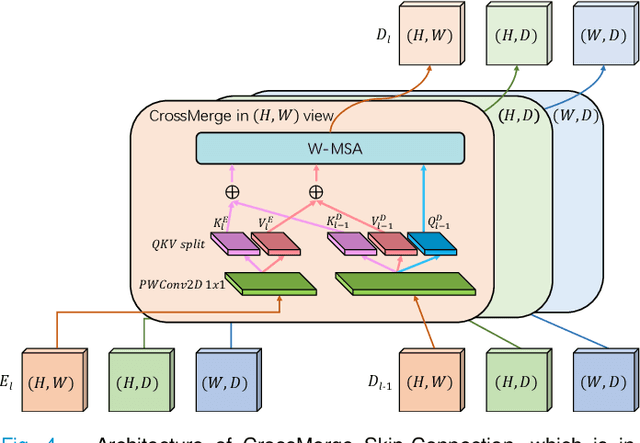
Abstract:Dense prediction in medical volume provides enriched guidance for clinical analysis. CNN backbones have met bottleneck due to lack of long-range dependencies and global context modeling power. Recent works proposed to combine vision transformer with CNN, due to its strong global capture ability and learning capability. However, most works are limited to simply applying pure transformer with several fatal flaws (i.e., lack of inductive bias, heavy computation and little consideration for 3D data). Therefore, designing an elegant and efficient vision transformer learner for dense prediction in medical volume is promising and challenging. In this paper, we propose a novel 3D Shuffle-Mixer network of a new Local Vision Transformer-MLP paradigm for medical dense prediction. In our network, a local vision transformer block is utilized to shuffle and learn spatial context from full-view slices of rearranged volume, a residual axial-MLP is designed to mix and capture remaining volume context in a slice-aware manner, and a MLP view aggregator is employed to project the learned full-view rich context to the volume feature in a view-aware manner. Moreover, an Adaptive Scaled Enhanced Shortcut is proposed for local vision transformer to enhance feature along spatial and channel dimensions adaptively, and a CrossMerge is proposed to skip-connects the multi-scale feature appropriately in the pyramid architecture. Extensive experiments demonstrate the proposed model outperforms other state-of-the-art medical dense prediction methods.
Disentangling semantic features of macromolecules in Cryo-Electron Tomography
Jun 27, 2021



Abstract:Cryo-electron tomography (Cryo-ET) is a 3D imaging technique that enables the systemic study of shape, abundance, and distribution of macromolecular structures in single cells in near-atomic resolution. However, the systematic and efficient $\textit{de novo}$ recognition and recovery of macromolecular structures captured by Cryo-ET are very challenging due to the structural complexity and imaging limits. Even macromolecules with identical structures have various appearances due to different orientations and imaging limits, such as noise and the missing wedge effect. Explicitly disentangling the semantic features of macromolecules is crucial for performing several downstream analyses on the macromolecules. This paper has addressed the problem by proposing a 3D Spatial Variational Autoencoder that explicitly disentangle the structure, orientation, and shift of macromolecules. Extensive experiments on both synthesized and real cryo-ET datasets and cross-domain evaluations demonstrate the efficacy of our method.
Experimental Analysis of Legendre Decomposition in Machine Learning
Aug 12, 2020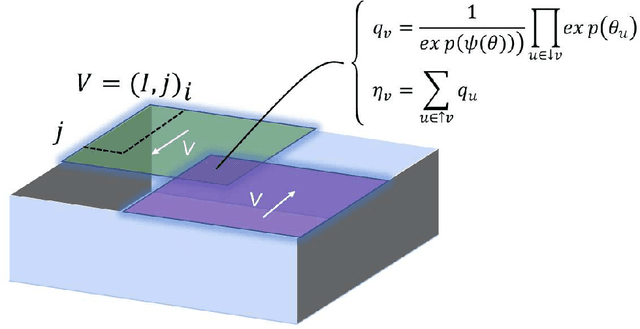
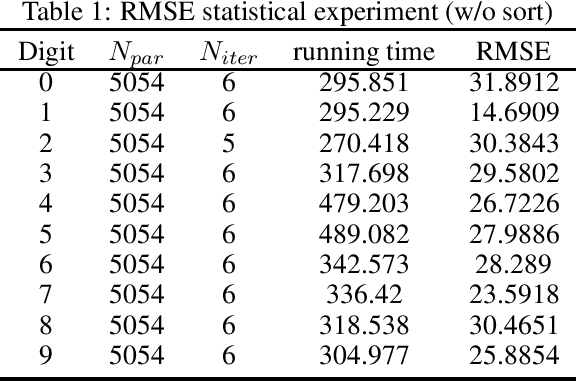
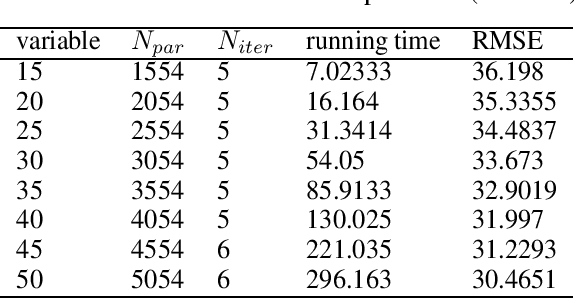
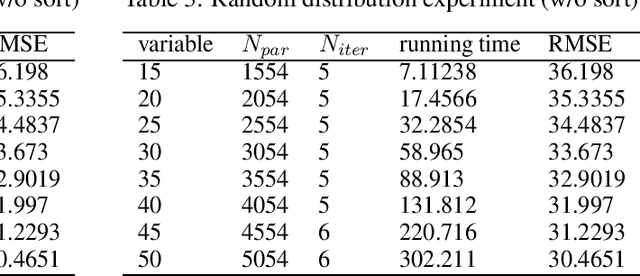
Abstract:In this technical report, we analyze Legendre decomposition for non-negative tensor in theory and application. In theory, the properties of dual parameters and dually flat manifold in Legendre decomposition are reviewed, and the process of tensor projection and parameter updating is analyzed. In application, a series of verification experiments and clustering experiments with parameters in submanifolds are carried out, hoping to find an effective lower dimensional representation of the input tensor. The experimental results show that the parameters in submanifolds have no ability to be directly represented as low-rank representations. Combined with analysis, we connect Legendre decomposition with neural networks and low-rank representation, and put forward some promising prospects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge