Jiantao Wang
IRFundusSet: An Integrated Retinal Fundus Dataset with a Harmonized Healthy Label
Feb 27, 2024Abstract:Ocular conditions are a global concern and computational tools utilizing retinal fundus color photographs can aid in routine screening and management. Obtaining comprehensive and sufficiently sized datasets, however, is non-trivial for the intricate retinal fundus, which exhibits heterogeneities within pathologies, in addition to variations from demographics and acquisition. Moreover, retinal fundus datasets in the public space suffer fragmentation in the organization of data and definition of a healthy observation. We present Integrated Retinal Fundus Set (IRFundusSet), a dataset that consolidates, harmonizes and curates several public datasets, facilitating their consumption as a unified whole and with a consistent is_normal label. IRFundusSet comprises a Python package that automates harmonization and avails a dataset object in line with the PyTorch approach. Moreover, images are physically reviewed and a new is_normal label is annotated for a consistent definition of a healthy observation. Ten public datasets are initially considered with a total of 46064 images, of which 25406 are curated for a new is_normal label and 3515 are deemed healthy across the sources.
ConCare: Personalized Clinical Feature Embedding via Capturing the Healthcare Context
Nov 27, 2019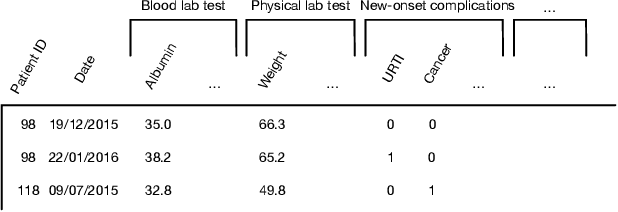
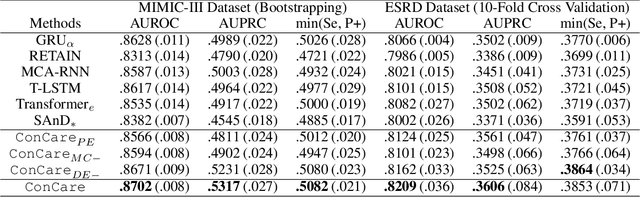
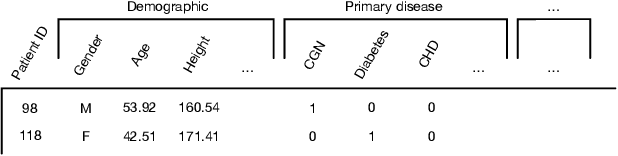
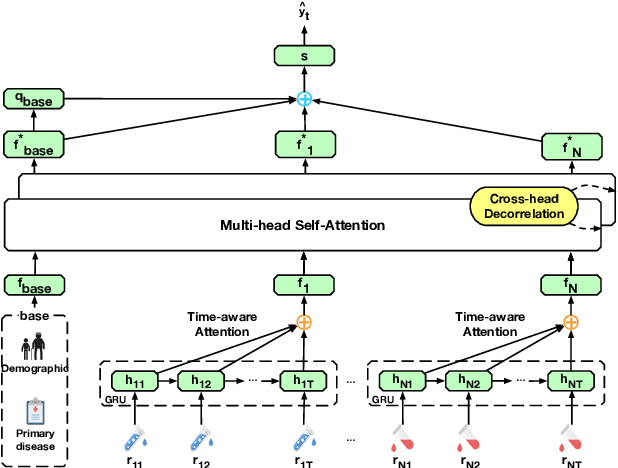
Abstract:Predicting the patient's clinical outcome from the historical electronic medical records (EMR) is a fundamental research problem in medical informatics. Most deep learning-based solutions for EMR analysis concentrate on learning the clinical visit embedding and exploring the relations between visits. Although those works have shown superior performances in healthcare prediction, they fail to explore the personal characteristics during the clinical visits thoroughly. Moreover, existing works usually assume that the more recent record weights more in the prediction, but this assumption is not suitable for all conditions. In this paper, we propose ConCare to handle the irregular EMR data and extract feature interrelationship to perform individualized healthcare prediction. Our solution can embed the feature sequences separately by modeling the time-aware distribution. ConCare further improves the multi-head self-attention via the cross-head decorrelation, so that the inter-dependencies among dynamic features and static baseline information can be effectively captured to form the personal health context. Experimental results on two real-world EMR datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of ConCare. The medical findings extracted by ConCare are also empirically confirmed by human experts and medical literature.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge