Jianhe Yuan
HANDAL: A Dataset of Real-World Manipulable Object Categories with Pose Annotations, Affordances, and Reconstructions
Aug 02, 2023Abstract:We present the HANDAL dataset for category-level object pose estimation and affordance prediction. Unlike previous datasets, ours is focused on robotics-ready manipulable objects that are of the proper size and shape for functional grasping by robot manipulators, such as pliers, utensils, and screwdrivers. Our annotation process is streamlined, requiring only a single off-the-shelf camera and semi-automated processing, allowing us to produce high-quality 3D annotations without crowd-sourcing. The dataset consists of 308k annotated image frames from 2.2k videos of 212 real-world objects in 17 categories. We focus on hardware and kitchen tool objects to facilitate research in practical scenarios in which a robot manipulator needs to interact with the environment beyond simple pushing or indiscriminate grasping. We outline the usefulness of our dataset for 6-DoF category-level pose+scale estimation and related tasks. We also provide 3D reconstructed meshes of all objects, and we outline some of the bottlenecks to be addressed for democratizing the collection of datasets like this one.
Ensemble Generative Cleaning with Feedback Loops for Defending Adversarial Attacks
Apr 23, 2020
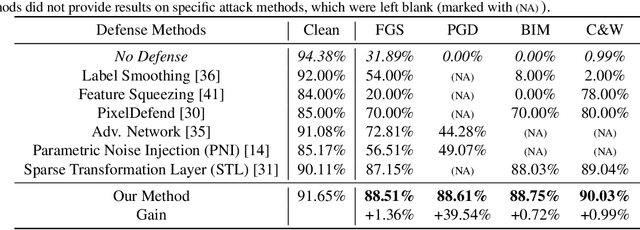


Abstract:Effective defense of deep neural networks against adversarial attacks remains a challenging problem, especially under powerful white-box attacks. In this paper, we develop a new method called ensemble generative cleaning with feedback loops (EGC-FL) for effective defense of deep neural networks. The proposed EGC-FL method is based on two central ideas. First, we introduce a transformed deadzone layer into the defense network, which consists of an orthonormal transform and a deadzone-based activation function, to destroy the sophisticated noise pattern of adversarial attacks. Second, by constructing a generative cleaning network with a feedback loop, we are able to generate an ensemble of diverse estimations of the original clean image. We then learn a network to fuse this set of diverse estimations together to restore the original image. Our extensive experimental results demonstrate that our approach improves the state-of-art by large margins in both white-box and black-box attacks. It significantly improves the classification accuracy for white-box PGD attacks upon the second best method by more than 29% on the SVHN dataset and more than 39% on the challenging CIFAR-10 dataset.
Snowball: Iterative Model Evolution and Confident Sample Discovery for Semi-Supervised Learning on Very Small Labeled Datasets
Sep 04, 2019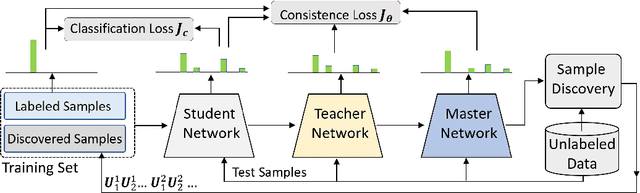
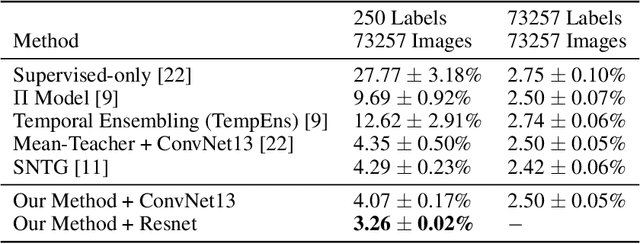
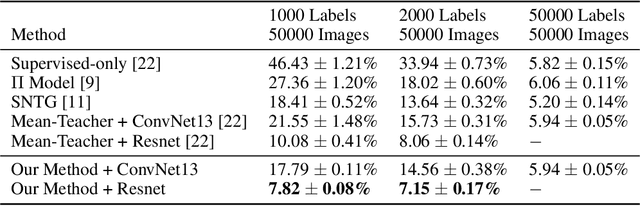
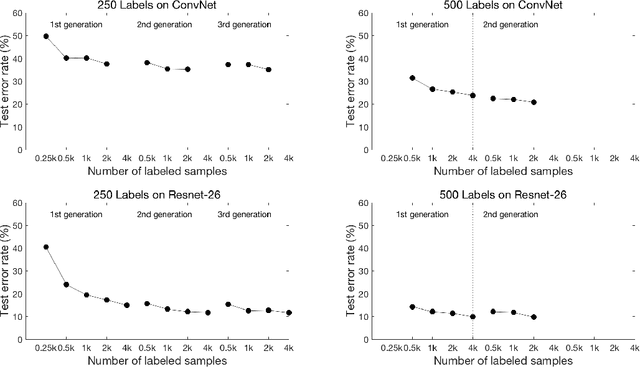
Abstract:In this work, we develop a joint sample discovery and iterative model evolution method for semi-supervised learning on very small labeled training sets. We propose a master-teacher-student model framework to provide multi-layer guidance during the model evolution process with multiple iterations and generations. The teacher model is constructed by performing an exponential moving average of the student models obtained from past training steps. The master network combines the knowledge of the student and teacher models with additional access to newly discovered samples. The master and teacher models are then used to guide the training of the student network by enforcing the consistence between their predictions of unlabeled samples and evolve all models when more and more samples are discovered. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that the discovering confident samples from the unlabeled dataset, once coupled with the above master-teacher-student network evolution, can significantly improve the overall semi-supervised learning performance. For example, on the CIFAR-10 dataset, with a very small set of 250 labeled samples, our method achieves an error rate of 11.81 %, more than 38 % lower than the state-of-the-art method Mean-Teacher (49.91 %).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge