Jiang Gui
Addressing Overthinking in Large Vision-Language Models via Gated Perception-Reasoning Optimization
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have exhibited strong reasoning capabilities through chain-of-thought mechanisms that generate step-by-step rationales. However, such slow-thinking approaches often lead to overthinking, where models produce excessively verbose responses even for simple queries, resulting in test-time inefficiency and even degraded accuracy. Prior work has attempted to mitigate this issue via adaptive reasoning strategies, but these methods largely overlook a fundamental bottleneck: visual perception failures. We argue that stable reasoning critically depends on low-level visual grounding, and that reasoning errors often originate from imperfect perception rather than insufficient deliberation. To address this limitation, we propose Gated Perception-Reasoning Optimization (GPRO), a meta-reasoning controller that dynamically routes computation among three decision paths at each generation step: a lightweight fast path, a slow perception path for re-examining visual inputs, and a slow reasoning path for internal self-reflection. To learn this distinction, we derive large-scale failure attribution supervision from approximately 790k samples, using teacher models to distinguish perceptual hallucinations from reasoning errors. We then train the controller with multi-objective reinforcement learning to optimize the trade-off between task accuracy and computational cost under uncertainty. Experiments on five benchmarks demonstrate that GPRO substantially improves both accuracy and efficiency, outperforming recent slow-thinking methods while generating significantly shorter responses.
SoundMind: RL-Incentivized Logic Reasoning for Audio-Language Models
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:While large language models have shown reasoning capabilities, their application to the audio modality, particularly in large audio-language models (ALMs), remains significantly underdeveloped. Addressing this gap requires a systematic approach, involving a capable base model, high-quality reasoning-oriented audio data, and effective training algorithms. In this study, we present a comprehensive solution: we introduce the Audio Logical Reasoning (ALR) dataset, consisting of 6,446 text-audio annotated samples specifically designed for complex reasoning tasks. Building on this resource, we propose SoundMind, a rule-based reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm tailored to endow ALMs with deep bimodal reasoning abilities. By training Qwen2.5-Omni-7B on the ALR dataset using SoundMind, our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in audio logical reasoning. This work highlights the impact of combining high-quality, reasoning-focused datasets with specialized RL techniques, advancing the frontier of auditory intelligence in language models. Our code and the proposed dataset are available at https://github.com/xid32/SoundMind.
Music's Multimodal Complexity in AVQA: Why We Need More than General Multimodal LLMs
May 27, 2025Abstract:While recent Multimodal Large Language Models exhibit impressive capabilities for general multimodal tasks, specialized domains like music necessitate tailored approaches. Music Audio-Visual Question Answering (Music AVQA) particularly underscores this, presenting unique challenges with its continuous, densely layered audio-visual content, intricate temporal dynamics, and the critical need for domain-specific knowledge. Through a systematic analysis of Music AVQA datasets and methods, this position paper identifies that specialized input processing, architectures incorporating dedicated spatial-temporal designs, and music-specific modeling strategies are critical for success in this domain. Our study provides valuable insights for researchers by highlighting effective design patterns empirically linked to strong performance, proposing concrete future directions for incorporating musical priors, and aiming to establish a robust foundation for advancing multimodal musical understanding. This work is intended to inspire broader attention and further research, supported by a continuously updated anonymous GitHub repository of relevant papers: https://github.com/xid32/Survey4MusicAVQA.
Assessing and Mitigating Medical Knowledge Drift and Conflicts in Large Language Models
May 12, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have great potential in the field of health care, yet they face great challenges in adapting to rapidly evolving medical knowledge. This can lead to outdated or contradictory treatment suggestions. This study investigated how LLMs respond to evolving clinical guidelines, focusing on concept drift and internal inconsistencies. We developed the DriftMedQA benchmark to simulate guideline evolution and assessed the temporal reliability of various LLMs. Our evaluation of seven state-of-the-art models across 4,290 scenarios demonstrated difficulties in rejecting outdated recommendations and frequently endorsing conflicting guidance. Additionally, we explored two mitigation strategies: Retrieval-Augmented Generation and preference fine-tuning via Direct Preference Optimization. While each method improved model performance, their combination led to the most consistent and reliable results. These findings underscore the need to improve LLM robustness to temporal shifts to ensure more dependable applications in clinical practice.
Learning Musical Representations for Music Performance Question Answering
Feb 10, 2025
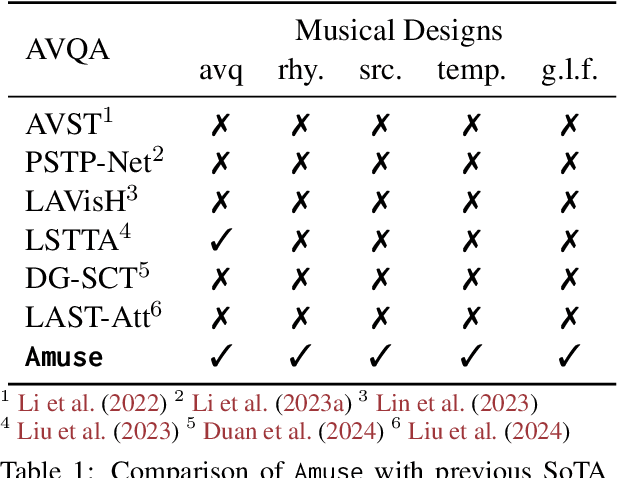

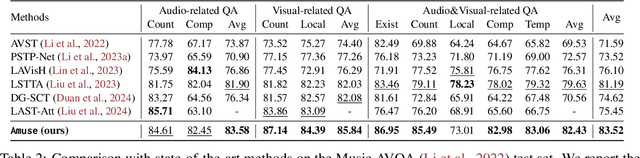
Abstract:Music performances are representative scenarios for audio-visual modeling. Unlike common scenarios with sparse audio, music performances continuously involve dense audio signals throughout. While existing multimodal learning methods on the audio-video QA demonstrate impressive capabilities in general scenarios, they are incapable of dealing with fundamental problems within the music performances: they underexplore the interaction between the multimodal signals in performance and fail to consider the distinctive characteristics of instruments and music. Therefore, existing methods tend to answer questions regarding musical performances inaccurately. To bridge the above research gaps, (i) given the intricate multimodal interconnectivity inherent to music data, our primary backbone is designed to incorporate multimodal interactions within the context of music; (ii) to enable the model to learn music characteristics, we annotate and release rhythmic and music sources in the current music datasets; (iii) for time-aware audio-visual modeling, we align the model's music predictions with the temporal dimension. Our experiments show state-of-the-art effects on the Music AVQA datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/xid32/Amuse.
Temporal Working Memory: Query-Guided Segment Refinement for Enhanced Multimodal Understanding
Feb 09, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal foundation models (MFMs) have demonstrated significant success in tasks such as visual captioning, question answering, and image-text retrieval. However, these models face inherent limitations due to their finite internal capacity, which restricts their ability to process extended temporal sequences, a crucial requirement for comprehensive video and audio analysis. To overcome these challenges, we introduce a specialized cognitive module, temporal working memory (TWM), which aims to enhance the temporal modeling capabilities of MFMs. It selectively retains task-relevant information across temporal dimensions, ensuring that critical details are preserved throughout the processing of video and audio content. The TWM uses a query-guided attention approach to focus on the most informative multimodal segments within temporal sequences. By retaining only the most relevant content, TWM optimizes the use of the model's limited capacity, enhancing its temporal modeling ability. This plug-and-play module can be easily integrated into existing MFMs. With our TWM, nine state-of-the-art models exhibit significant performance improvements across tasks such as video captioning, question answering, and video-text retrieval. By enhancing temporal modeling, TWM extends the capability of MFMs to handle complex, time-sensitive data effectively. Our code is available at https://github.com/xid32/NAACL_2025_TWM.
Residual Kolmogorov-Arnold Network for Enhanced Deep Learning
Oct 07, 2024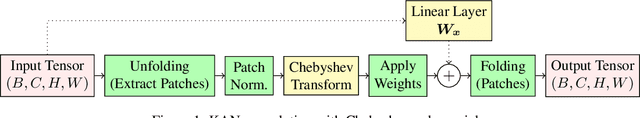
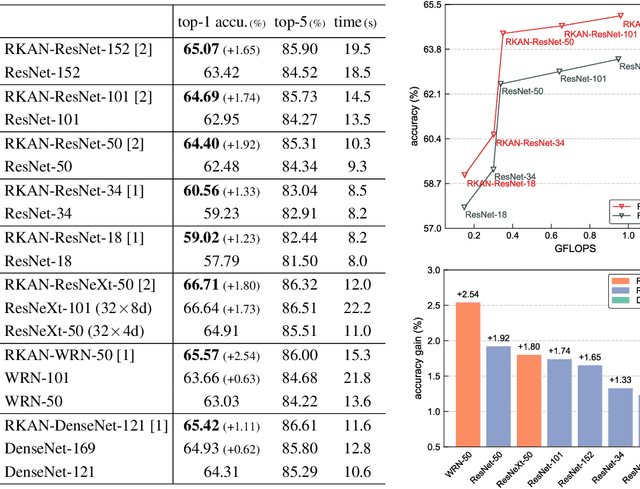
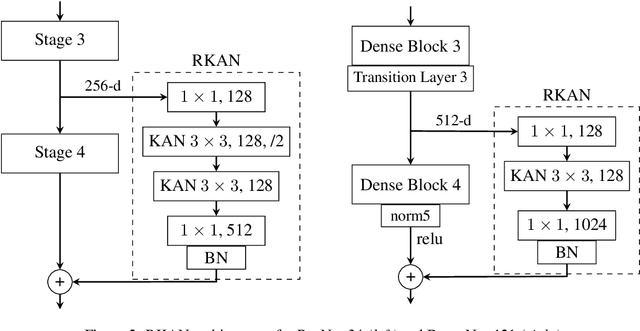
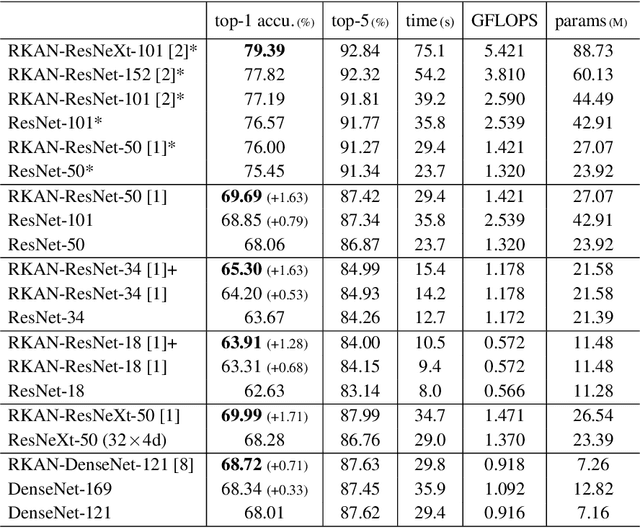
Abstract:Despite the strong performance in many computer vision tasks, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) can sometimes struggle to efficiently capture long-range, complex non-linear dependencies in deeper layers of the network. We address this limitation by introducing Residual KAN, which incorporates the Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN) within the CNN framework as a residual component. Our approach uses Chebyshev polynomials as the basis for KAN convolutions that enables more expressive and adaptive feature representations while maintaining computational efficiency. The proposed RKAN blocks, when integrated into established architectures such as ResNet and DenseNet, offer consistent improvements over the baseline models on various well-known benchmarks. Our results demonstrate the potential of RKAN to enhance the capabilities of deep CNNs in visual data.
Memory-Efficient Sparse Pyramid Attention Networks for Whole Slide Image Analysis
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:Whole Slide Images (WSIs) are crucial for modern pathological diagnosis, yet their gigapixel-scale resolutions and sparse informative regions pose significant computational challenges. Traditional dense attention mechanisms, widely used in computer vision and natural language processing, are impractical for WSI analysis due to the substantial data scale and the redundant processing of uninformative areas. To address these challenges, we propose Memory-Efficient Sparse Pyramid Attention Networks with Shifted Windows (SPAN), drawing inspiration from state-of-the-art sparse attention techniques in other domains. SPAN introduces a sparse pyramid attention architecture that hierarchically focuses on informative regions within the WSI, aiming to reduce memory overhead while preserving critical features. Additionally, the incorporation of shifted windows enables the model to capture long-range contextual dependencies essential for accurate classification. We evaluated SPAN on multiple public WSI datasets, observing its competitive performance. Unlike existing methods that often struggle to model spatial and contextual information due to memory constraints, our approach enables the accurate modeling of these crucial features. Our study also highlights the importance of key design elements in attention mechanisms, such as the shifted-window scheme and the hierarchical structure, which contribute substantially to the effectiveness of SPAN in WSI analysis. The potential of SPAN for memory-efficient and effective analysis of WSI data is thus demonstrated, and the code will be made publicly available following the publication of this work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge