Jiang Cao
Acceleration of Atomistic NEGF: Algorithms, Parallelization, and Machine Learning
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:The Non-equilibrium Green's function (NEGF) formalism is a particularly powerful method to simulate the quantum transport properties of nanoscale devices such as transistors, photo-diodes, or memory cells, in the ballistic limit of transport or in the presence of various scattering sources such as electronphonon, electron-photon, or even electron-electron interactions. The inclusion of all these mechanisms has been first demonstrated in small systems, composed of a few atoms, before being scaled up to larger structures made of thousands of atoms. Also, the accuracy of the models has kept improving, from empirical to fully ab-initio ones, e.g., density functional theory (DFT). This paper summarizes key (algorithmic) achievements that have allowed us to bring DFT+NEGF simulations closer to the dimensions and functionality of realistic systems. The possibility of leveraging graph neural networks and machine learning to speed up ab-initio device simulations is discussed as well.
Structural Entropy Guided Probabilistic Coding
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:Probabilistic embeddings have several advantages over deterministic embeddings as they map each data point to a distribution, which better describes the uncertainty and complexity of data. Many works focus on adjusting the distribution constraint under the Information Bottleneck (IB) principle to enhance representation learning. However, these proposed regularization terms only consider the constraint of each latent variable, omitting the structural information between latent variables. In this paper, we propose a novel structural entropy-guided probabilistic coding model, named SEPC. Specifically, we incorporate the relationship between latent variables into the optimization by proposing a structural entropy regularization loss. Besides, as traditional structural information theory is not well-suited for regression tasks, we propose a probabilistic encoding tree, transferring regression tasks to classification tasks while diminishing the influence of the transformation. Experimental results across 12 natural language understanding tasks, including both classification and regression tasks, demonstrate the superior performance of SEPC compared to other state-of-the-art models in terms of effectiveness, generalization capability, and robustness to label noise. The codes and datasets are available at https://github.com/SELGroup/SEPC.
Spectrum Gaussian Processes Based On Tunable Basis Functions
Jul 14, 2021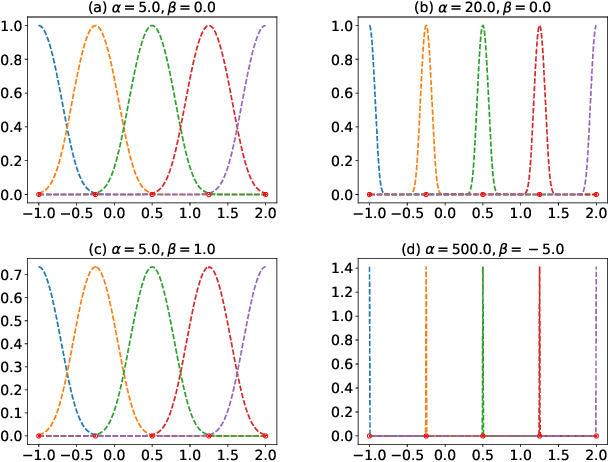
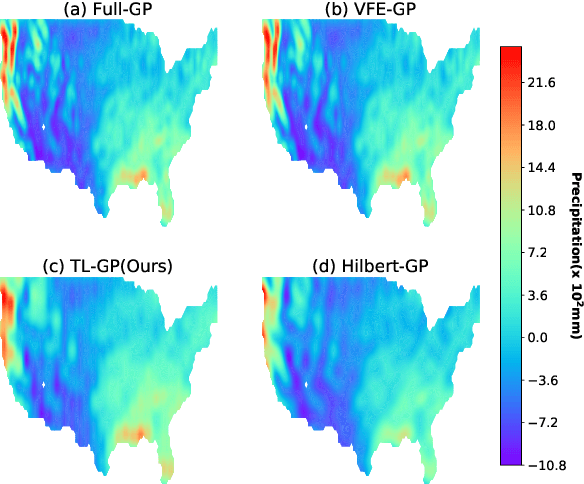
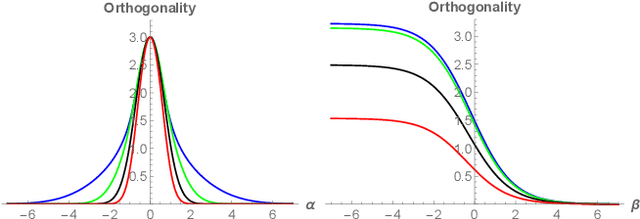
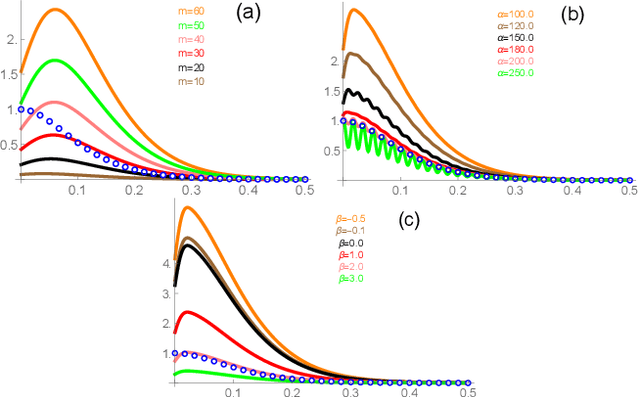
Abstract:Spectral approximation and variational inducing learning for the Gaussian process are two popular methods to reduce computational complexity. However, in previous research, those methods always tend to adopt the orthonormal basis functions, such as eigenvectors in the Hilbert space, in the spectrum method, or decoupled orthogonal components in the variational framework. In this paper, inspired by quantum physics, we introduce a novel basis function, which is tunable, local and bounded, to approximate the kernel function in the Gaussian process. There are two adjustable parameters in these functions, which control their orthogonality to each other and limit their boundedness. And we conduct extensive experiments on open-source datasets to testify its performance. Compared to several state-of-the-art methods, it turns out that the proposed method can obtain satisfactory or even better results, especially with poorly chosen kernel functions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge