Jiahui He
SMAFormer: Synergistic Multi-Attention Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation
Aug 31, 2024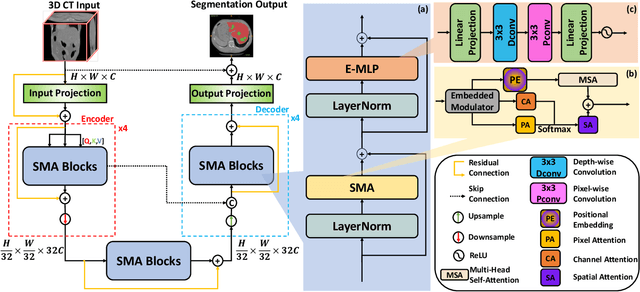
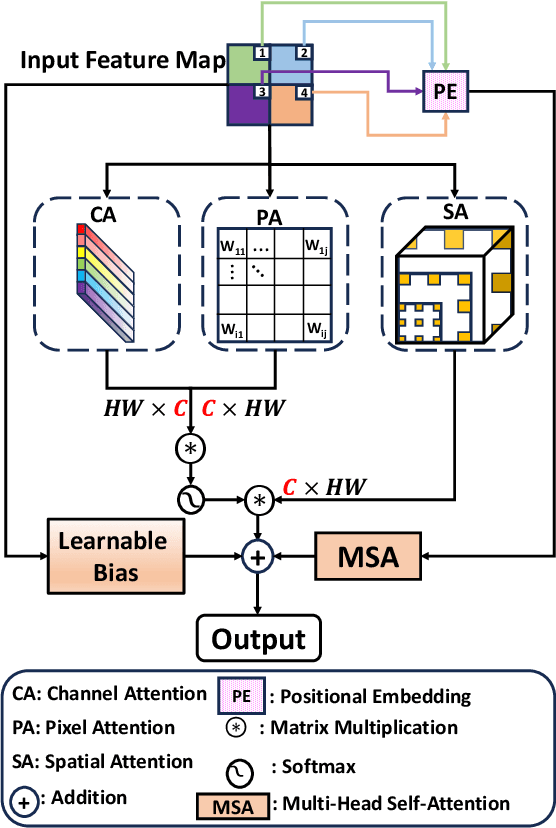
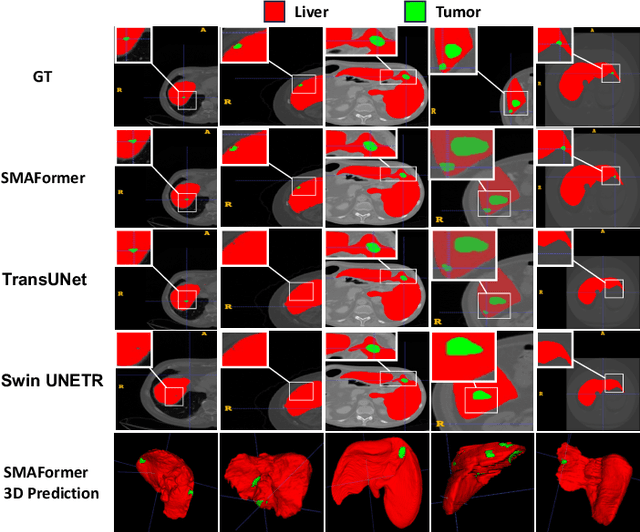
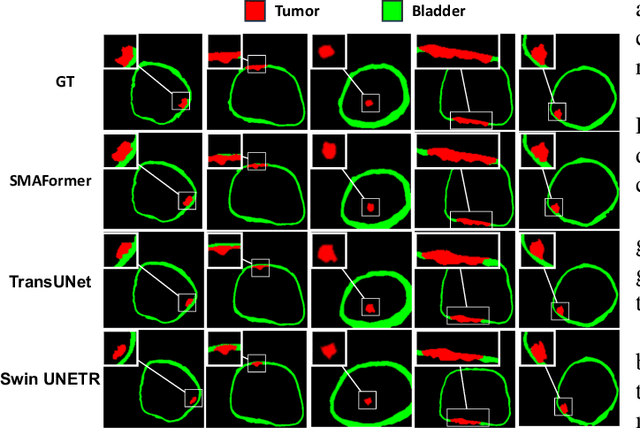
Abstract:In medical image segmentation, specialized computer vision techniques, notably transformers grounded in attention mechanisms and residual networks employing skip connections, have been instrumental in advancing performance. Nonetheless, previous models often falter when segmenting small, irregularly shaped tumors. To this end, we introduce SMAFormer, an efficient, Transformer-based architecture that fuses multiple attention mechanisms for enhanced segmentation of small tumors and organs. SMAFormer can capture both local and global features for medical image segmentation. The architecture comprises two pivotal components. First, a Synergistic Multi-Attention (SMA) Transformer block is proposed, which has the benefits of Pixel Attention, Channel Attention, and Spatial Attention for feature enrichment. Second, addressing the challenge of information loss incurred during attention mechanism transitions and feature fusion, we design a Feature Fusion Modulator. This module bolsters the integration between the channel and spatial attention by mitigating reshaping-induced information attrition. To evaluate our method, we conduct extensive experiments on various medical image segmentation tasks, including multi-organ, liver tumor, and bladder tumor segmentation, achieving state-of-the-art results. Code and models are available at: \url{https://github.com/CXH-Research/SMAFormer}.
Pathological Semantics-Preserving Learning for H&E-to-IHC Virtual Staining
Jul 04, 2024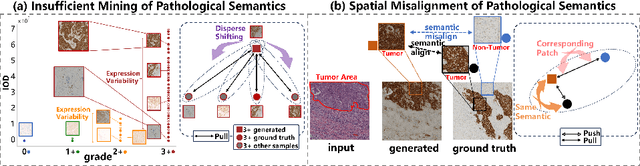
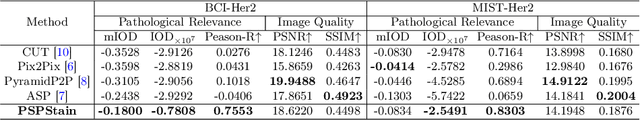
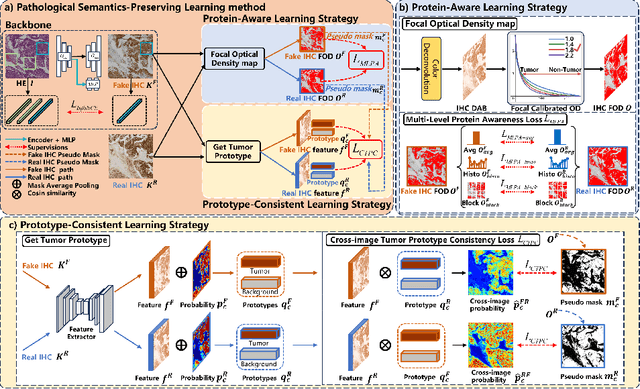
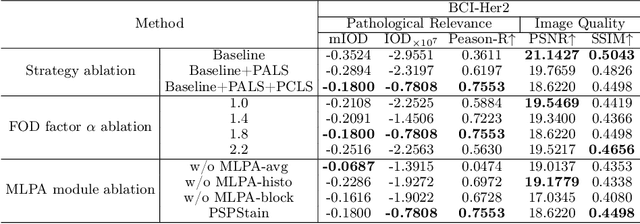
Abstract:Conventional hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining is limited to revealing cell morphology and distribution, whereas immunohistochemical (IHC) staining provides precise and specific visualization of protein activation at the molecular level. Virtual staining technology has emerged as a solution for highly efficient IHC examination, which directly transforms H&E-stained images to IHC-stained images. However, virtual staining is challenged by the insufficient mining of pathological semantics and the spatial misalignment of pathological semantics. To address these issues, we propose the Pathological Semantics-Preserving Learning method for Virtual Staining (PSPStain), which directly incorporates the molecular-level semantic information and enhances semantics interaction despite any spatial inconsistency. Specifically, PSPStain comprises two novel learning strategies: 1) Protein-Aware Learning Strategy (PALS) with Focal Optical Density (FOD) map maintains the coherence of protein expression level, which represents molecular-level semantic information; 2) Prototype-Consistent Learning Strategy (PCLS), which enhances cross-image semantic interaction by prototypical consistency learning. We evaluate PSPStain on two public datasets using five metrics: three clinically relevant metrics and two for image quality. Extensive experiments indicate that PSPStain outperforms current state-of-the-art H&E-to-IHC virtual staining methods and demonstrates a high pathological correlation between the staging of real and virtual stains.
Unlocking the Potential of Early Epochs: Uncertainty-aware CT Metal Artifact Reduction
Jun 18, 2024Abstract:In computed tomography (CT), the presence of metallic implants in patients often leads to disruptive artifacts in the reconstructed images, hindering accurate diagnosis. Recently, a large amount of supervised deep learning-based approaches have been proposed for metal artifact reduction (MAR). However, these methods neglect the influence of initial training weights. In this paper, we have discovered that the uncertainty image computed from the restoration result of initial training weights can effectively highlight high-frequency regions, including metal artifacts. This observation can be leveraged to assist the MAR network in removing metal artifacts. Therefore, we propose an uncertainty constraint (UC) loss that utilizes the uncertainty image as an adaptive weight to guide the MAR network to focus on the metal artifact region, leading to improved restoration. The proposed UC loss is designed to be a plug-and-play method, compatible with any MAR framework, and easily adoptable. To validate the effectiveness of the UC loss, we conduct extensive experiments on the public available Deeplesion and CLINIC-metal dataset. Experimental results demonstrate that the UC loss further optimizes the network training process and significantly improves the removal of metal artifacts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge