Jiacheng Yuan
Optimal Robotic Velcro Peeling with Force Feedback
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:We study the problem of peeling a Velcro strap from a surface using a robotic manipulator. The surface geometry is arbitrary and unknown. The robot has access to only the force feedback and its end-effector position. This problem is challenging due to the partial observability of the environment and the incompleteness of the sensor feedback. To solve it, we first model the system with simple analytic state and action models based on quasi-static dynamics assumptions. We then study the fully-observable case where the state of both the Velcro and the robot are given. For this case, we obtain the optimal solution in closed-form which minimizes the total energy cost. Next, for the partially-observable case, we design a state estimator which estimates the underlying state using only force and position feedback. Then, we present a heuristics-based controller that balances exploratory and exploitative behaviors in order to peel the velcro efficiently. Finally, we evaluate our proposed method in environments with complex geometric uncertainties and sensor noises, achieving 100% success rate with less than 80% increase in energy cost compared to the optimal solution when the environment is fully-observable, outperforming the baselines by a large margin.
VFAS-Grasp: Closed Loop Grasping with Visual Feedback and Adaptive Sampling
Oct 27, 2023Abstract:We consider the problem of closed-loop robotic grasping and present a novel planner which uses Visual Feedback and an uncertainty-aware Adaptive Sampling strategy (VFAS) to close the loop. At each iteration, our method VFAS-Grasp builds a set of candidate grasps by generating random perturbations of a seed grasp. The candidates are then scored using a novel metric which combines a learned grasp-quality estimator, the uncertainty in the estimate and the distance from the seed proposal to promote temporal consistency. Additionally, we present two mechanisms to improve the efficiency of our sampling strategy: We dynamically scale the sampling region size and number of samples in it based on past grasp scores. We also leverage a motion vector field estimator to shift the center of our sampling region. We demonstrate that our algorithm can run in real time (20 Hz) and is capable of improving grasp performance for static scenes by refining the initial grasp proposal. We also show that it can enable grasping of slow moving objects, such as those encountered during human to robot handover.
HandNeRF: Learning to Reconstruct Hand-Object Interaction Scene from a Single RGB Image
Sep 14, 2023Abstract:This paper presents a method to learn hand-object interaction prior for reconstructing a 3D hand-object scene from a single RGB image. The inference as well as training-data generation for 3D hand-object scene reconstruction is challenging due to the depth ambiguity of a single image and occlusions by the hand and object. We turn this challenge into an opportunity by utilizing the hand shape to constrain the possible relative configuration of the hand and object geometry. We design a generalizable implicit function, HandNeRF, that explicitly encodes the correlation of the 3D hand shape features and 2D object features to predict the hand and object scene geometry. With experiments on real-world datasets, we show that HandNeRF is able to reconstruct hand-object scenes of novel grasp configurations more accurately than comparable methods. Moreover, we demonstrate that object reconstruction from HandNeRF ensures more accurate execution of a downstream task, such as grasping for robotic hand-over.
Active Mass Distribution Estimation from Tactile Feedback
Mar 02, 2023Abstract:In this work, we present a method to estimate the mass distribution of a rigid object through robotic interactions and tactile feedback. This is a challenging problem because of the complexity of physical dynamics modeling and the action dependencies across the model parameters. We propose a sequential estimation strategy combined with a set of robot action selection rules based on the analytical formulation of a discrete-time dynamics model. To evaluate the performance of our approach, we also manufactured re-configurable block objects that allow us to modify the object mass distribution while having access to the ground truth values. We compare our approach against multiple baselines and show that our approach can estimate the mass distribution with around 10% error, while the baselines have errors ranging from 18% to 68%.
ROW-SLAM: Under-Canopy Cornfield Semantic SLAM
Sep 15, 2021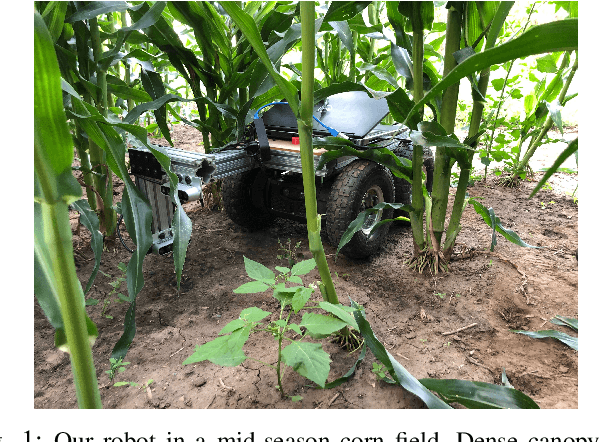
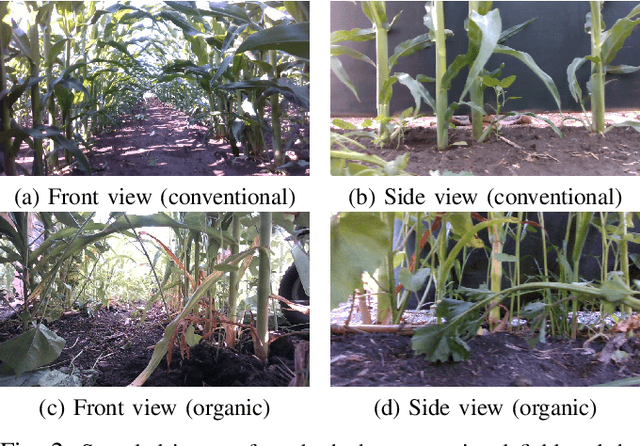
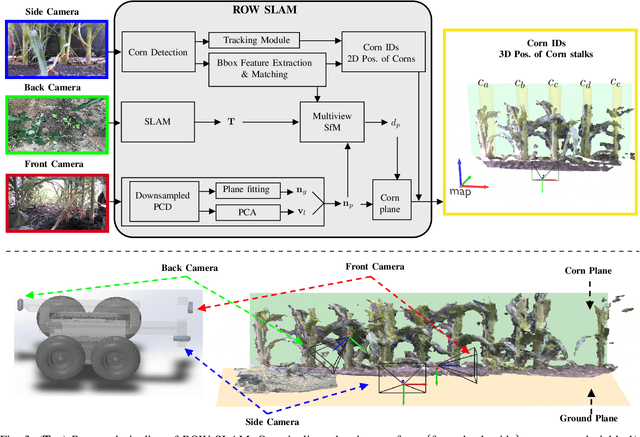
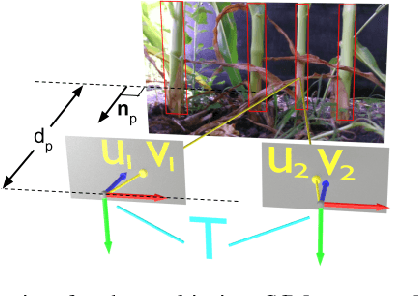
Abstract:We study a semantic SLAM problem faced by a robot tasked with autonomous weeding under the corn canopy. The goal is to detect corn stalks and localize them in a global coordinate frame. This is a challenging setup for existing algorithms because there is very little space between the camera and the plants, and the camera motion is primarily restricted to be along the row. To overcome these challenges, we present a multi-camera system where a side camera (facing the plants) is used for detection whereas front and back cameras are used for motion estimation. Next, we show how semantic features in the environment (corn stalks, ground, and crop planes) can be used to develop a robust semantic SLAM solution and present results from field trials performed throughout the growing season across various cornfields.
Multi-Step Recurrent Q-Learning for Robotic Velcro Peeling
Nov 16, 2020



Abstract:Learning object manipulation is a critical skill for robots to interact with their environment. Even though there has been significant progress in robotic manipulation of rigid objects, interacting with non-rigid objects remains challenging for robots. In this work, we introduce velcro peeling as a representative application for robotic manipulation of non-rigid objects in complex environments. We present a method of learning force-based manipulation from noisy and incomplete sensor inputs in partially observable environments by modeling long term dependencies between measurements with a multi-step deep recurrent network. We present experiments on a real robot to show the necessity of modeling these long term dependencies and validate our approach in simulation and robot experiments. Our results show that using tactile input enables the robot to overcome geometric uncertainties present in the environment with high fidelity in ~90% of all cases, outperforming the baselines by a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge