Jett Janiak
Chain-of-Thought Reasoning In The Wild Is Not Always Faithful
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning has significantly advanced state-of-the-art AI capabilities. However, recent studies have shown that CoT reasoning is not always faithful, i.e. CoT reasoning does not always reflect how models arrive at conclusions. So far, most of these studies have focused on unfaithfulness in unnatural contexts where an explicit bias has been introduced. In contrast, we show that unfaithful CoT can occur on realistic prompts with no artificial bias. Our results reveal non-negligible rates of several forms of unfaithful reasoning in frontier models: Sonnet 3.7 (16.3%), DeepSeek R1 (5.3%) and ChatGPT-4o (7.0%) all answer a notable proportion of question pairs unfaithfully. Specifically, we find that models rationalize their implicit biases in answers to binary questions ("implicit post-hoc rationalization"). For example, when separately presented with the questions "Is X bigger than Y?" and "Is Y bigger than X?", models sometimes produce superficially coherent arguments to justify answering Yes to both questions or No to both questions, despite such responses being logically contradictory. We also investigate restoration errors (Dziri et al., 2023), where models make and then silently correct errors in their reasoning, and unfaithful shortcuts, where models use clearly illogical reasoning to simplify solving problems in Putnam questions (a hard benchmark). Our findings raise challenges for AI safety work that relies on monitoring CoT to detect undesired behavior.
Characterizing stable regions in the residual stream of LLMs
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:We identify "stable regions" in the residual stream of Transformers, where the model's output remains insensitive to small activation changes, but exhibits high sensitivity at region boundaries. These regions emerge during training and become more defined as training progresses or model size increases. The regions appear to be much larger than previously studied polytopes. Our analysis suggests that these stable regions align with semantic distinctions, where similar prompts cluster within regions, and activations from the same region lead to similar next token predictions. This work provides a promising research direction for understanding the complexity of neural networks, shedding light on training dynamics, and advancing interpretability.
An Adversarial Example for Direct Logit Attribution: Memory Management in gelu-4l
Oct 14, 2023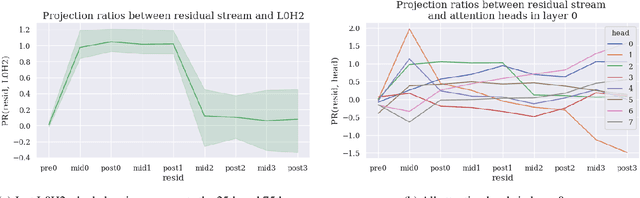
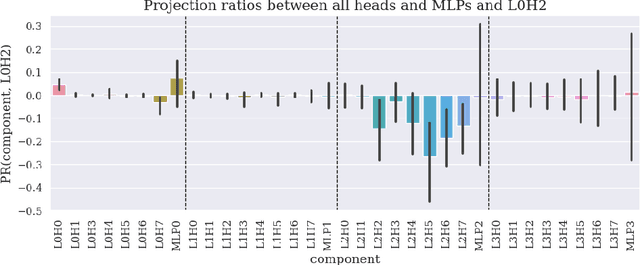
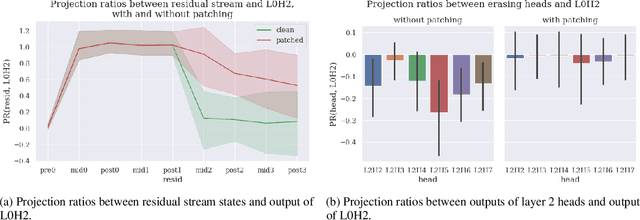
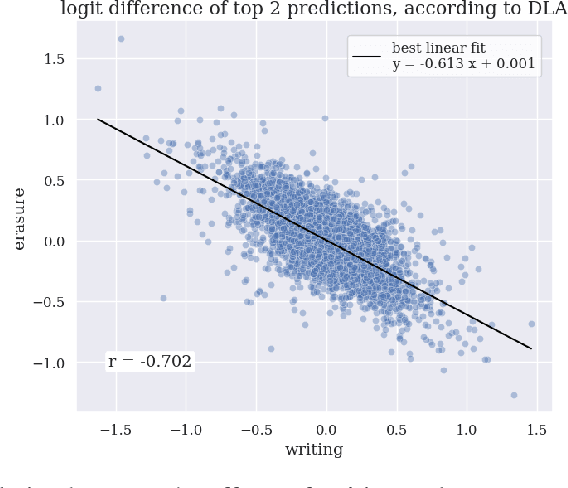
Abstract:We provide concrete evidence for memory management in a 4-layer transformer. Specifically, we identify clean-up behavior, in which model components consistently remove the output of preceeding components during a forward pass. Our findings suggest that the interpretability technique Direct Logit Attribution provides misleading results. We show explicit examples where this technique is inaccurate, as it does not account for clean-up behavior.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge