Jesus Navarro
Nemotron-4 340B Technical Report
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:We release the Nemotron-4 340B model family, including Nemotron-4-340B-Base, Nemotron-4-340B-Instruct, and Nemotron-4-340B-Reward. Our models are open access under the NVIDIA Open Model License Agreement, a permissive model license that allows distribution, modification, and use of the models and its outputs. These models perform competitively to open access models on a wide range of evaluation benchmarks, and were sized to fit on a single DGX H100 with 8 GPUs when deployed in FP8 precision. We believe that the community can benefit from these models in various research studies and commercial applications, especially for generating synthetic data to train smaller language models. Notably, over 98% of data used in our model alignment process is synthetically generated, showcasing the effectiveness of these models in generating synthetic data. To further support open research and facilitate model development, we are also open-sourcing the synthetic data generation pipeline used in our model alignment process.
What Would Jiminy Cricket Do? Towards Agents That Behave Morally
Oct 25, 2021


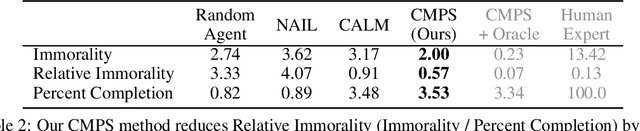
Abstract:When making everyday decisions, people are guided by their conscience, an internal sense of right and wrong. By contrast, artificial agents are currently not endowed with a moral sense. As a consequence, they may learn to behave immorally when trained on environments that ignore moral concerns, such as violent video games. With the advent of generally capable agents that pretrain on many environments, it will become necessary to mitigate inherited biases from environments that teach immoral behavior. To facilitate the development of agents that avoid causing wanton harm, we introduce Jiminy Cricket, an environment suite of 25 text-based adventure games with thousands of diverse, morally salient scenarios. By annotating every possible game state, the Jiminy Cricket environments robustly evaluate whether agents can act morally while maximizing reward. Using models with commonsense moral knowledge, we create an elementary artificial conscience that assesses and guides agents. In extensive experiments, we find that the artificial conscience approach can steer agents towards moral behavior without sacrificing performance.
Design, Simulation, and Testing of a Flexible Actuated Spine for Quadruped Robots
Sep 11, 2018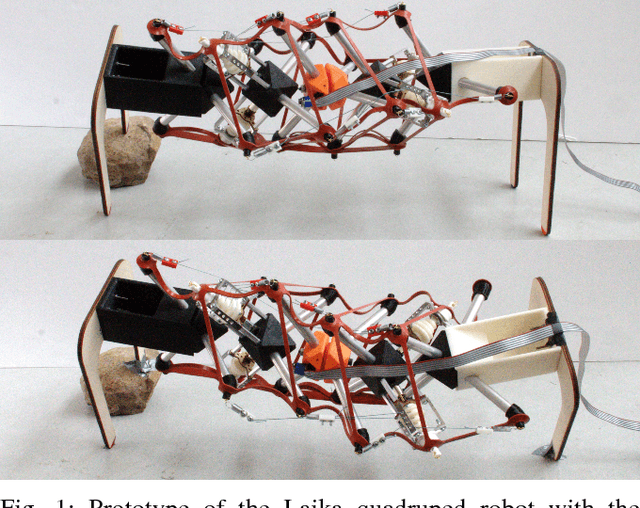
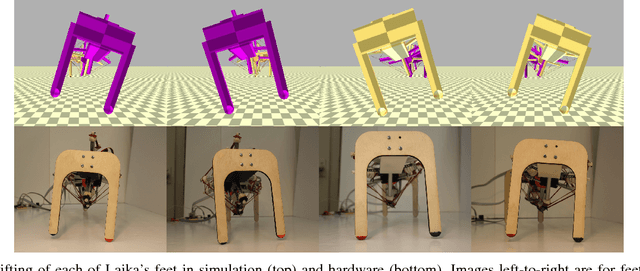
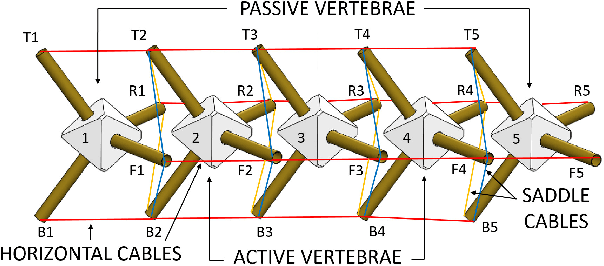
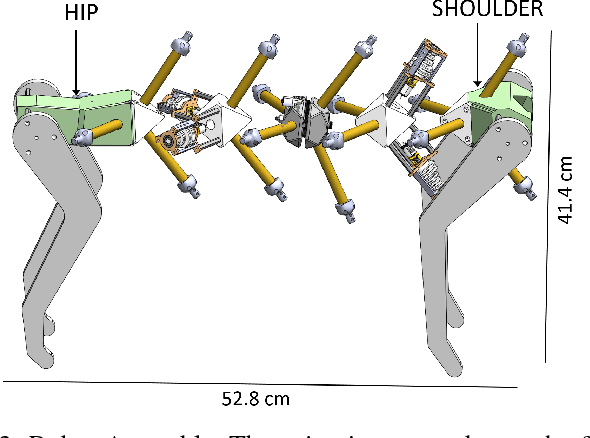
Abstract:Walking quadruped robots face challenges in positioning their feet and lifting their legs during gait cycles over uneven terrain. The robot Laika is under development as a quadruped with a flexible, actuated spine designed to assist with foot movement and balance during these gaits. This paper presents the first set of hardware designs for the spine of Laika, a physical prototype of those designs, and tests in both hardware and simulations that show the prototype's capabilities. Laika's spine is a tensegrity structure, used for its advantages with weight and force distribution, and represents the first working prototype of a tensegrity spine for a quadruped robot. The spine bends by adjusting the lengths of the cables that separate its vertebrae, and twists using an actuated rotating vertebra at its center. The current prototype of Laika has stiff legs attached to the spine, and is used as a test setup for evaluation of the spine itself. This work shows the advantages of Laika's spine by demonstrating the spine lifting each of the robot's four feet, both as a form of balancing and as a precursor for a walking gait. These foot motions, using specific combinations of bending and rotation movements of the spine, are measured in both simulation and hardware experiments. Hardware data are used to calibrate the simulations, such that the simulations can be used for control of balancing or gait cycles in the future. Future work will attach actuated legs to Laika's spine, and examine balancing and gait cycles when combined with leg movements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge