Jeroen Breebaart
Blind Estimation of Sub-band Acoustic Parameters from Ambisonics Recordings using Spectro-Spatial Covariance Features
Nov 05, 2024Abstract:Estimating frequency-varying acoustic parameters is essential for enhancing immersive perception in realistic spatial audio creation. In this paper, we propose a unified framework that blindly estimates reverberation time (T60), direct-to-reverberant ratio (DRR), and clarity (C50) across 10 frequency bands using first-order Ambisonics (FOA) speech recordings as inputs. The proposed framework utilizes a novel feature named Spectro-Spatial Covariance Vector (SSCV), efficiently representing temporal, spectral as well as spatial information of the FOA signal. Our models significantly outperform existing single-channel methods with only spectral information, reducing estimation errors by more than half for all three acoustic parameters. Additionally, we introduce FOA-Conv3D, a novel back-end network for effectively utilising the SSCV feature with a 3D convolutional encoder. FOA-Conv3D outperforms the convolutional neural network (CNN) and recurrent convolutional neural network (CRNN) backends, achieving lower estimation errors and accounting for a higher proportion of variance (PoV) for all 3 acoustic parameters.
Mono-to-stereo through parametric stereo generation
Jun 26, 2023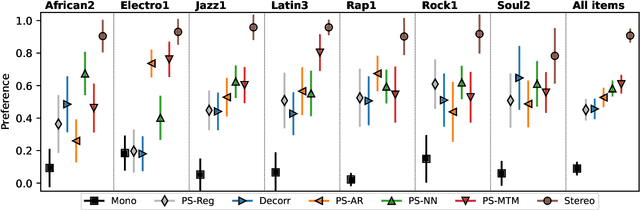
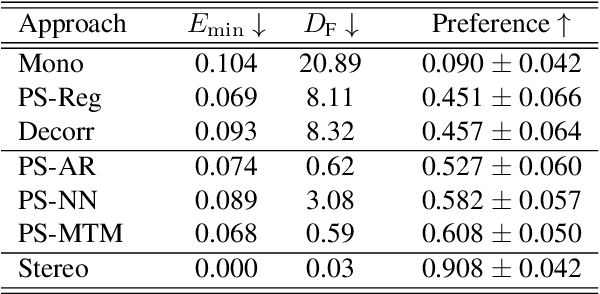
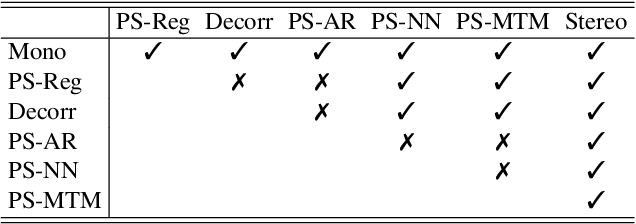
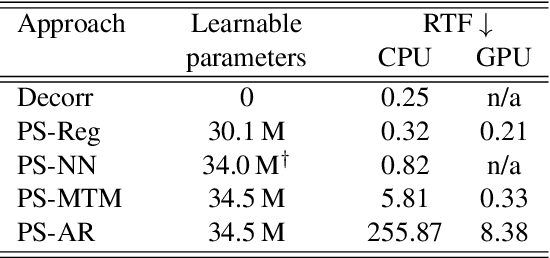
Abstract:Generating a stereophonic presentation from a monophonic audio signal is a challenging open task, especially if the goal is to obtain a realistic spatial imaging with a specific panning of sound elements. In this work, we propose to convert mono to stereo by means of predicting parametric stereo (PS) parameters using both nearest neighbor and deep network approaches. In combination with PS, we also propose to model the task with generative approaches, allowing to synthesize multiple and equally-plausible stereo renditions from the same mono signal. To achieve this, we consider both autoregressive and masked token modelling approaches. We provide evidence that the proposed PS-based models outperform a competitive classical decorrelation baseline and that, within a PS prediction framework, modern generative models outshine equivalent non-generative counterparts. Overall, our work positions both PS and generative modelling as strong and appealing methodologies for mono-to-stereo upmixing. A discussion of the limitations of these approaches is also provided.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge