Jens Drawehn
Fine-tuning and aligning question answering models for complex information extraction tasks
Sep 26, 2023Abstract:The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) has boosted performance and possibilities in various NLP tasks. While the usage of generative AI models like ChatGPT opens up new opportunities for several business use cases, their current tendency to hallucinate fake content strongly limits their applicability to document analysis, such as information retrieval from documents. In contrast, extractive language models like question answering (QA) or passage retrieval models guarantee query results to be found within the boundaries of an according context document, which makes them candidates for more reliable information extraction in productive environments of companies. In this work we propose an approach that uses and integrates extractive QA models for improved feature extraction of German business documents such as insurance reports or medical leaflets into a document analysis solution. We further show that fine-tuning existing German QA models boosts performance for tailored extraction tasks of complex linguistic features like damage cause explanations or descriptions of medication appearance, even with using only a small set of annotated data. Finally, we discuss the relevance of scoring metrics for evaluating information extraction tasks and deduce a combined metric from Levenshtein distance, F1-Score, Exact Match and ROUGE-L to mimic the assessment criteria from human experts.
Combining Deep Learning and Reasoning for Address Detection in Unstructured Text Documents
Feb 07, 2022
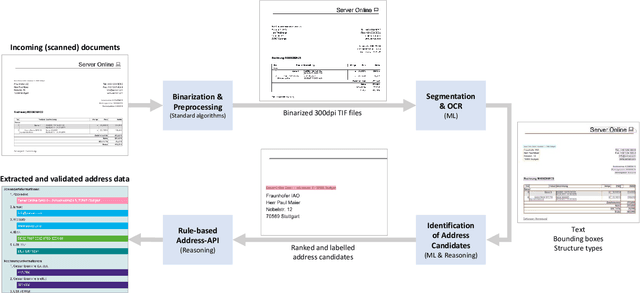

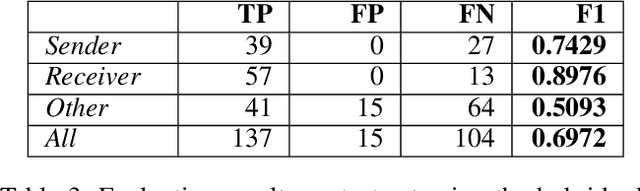
Abstract:Extracting information from unstructured text documents is a demanding task, since these documents can have a broad variety of different layouts and a non-trivial reading order, like it is the case for multi-column documents or nested tables. Additionally, many business documents are received in paper form, meaning that the textual contents need to be digitized before further analysis. Nonetheless, automatic detection and capturing of crucial document information like the sender address would boost many companies' processing efficiency. In this work we propose a hybrid approach that combines deep learning with reasoning for finding and extracting addresses from unstructured text documents. We use a visual deep learning model to detect the boundaries of possible address regions on the scanned document images and validate these results by analyzing the containing text using domain knowledge represented as a rule based system.
VitrAI -- Applying Explainable AI in the Real World
Feb 12, 2021



Abstract:With recent progress in the field of Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) and increasing use in practice, the need for an evaluation of different XAI methods and their explanation quality in practical usage scenarios arises. For this purpose, we present VitrAI, which is a web-based service with the goal of uniformly demonstrating four different XAI algorithms in the context of three real life scenarios and evaluating their performance and comprehensibility for humans. This work reveals practical obstacles when adopting XAI methods and gives qualitative estimates on how well different approaches perform in said scenarios.
Conversational Agents for Insurance Companies: From Theory to Practice
Dec 18, 2019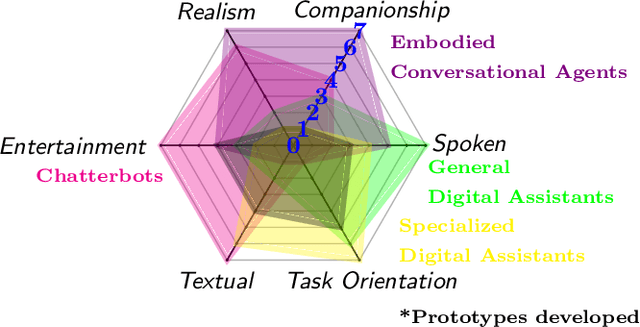
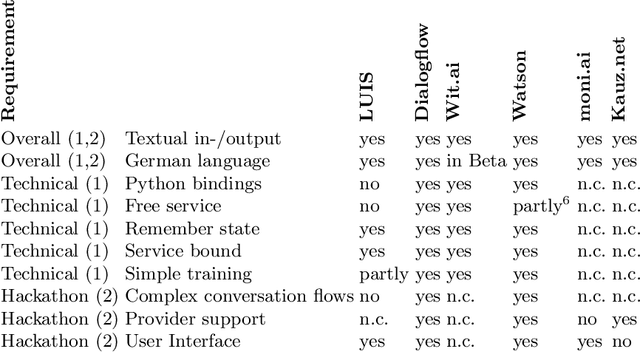
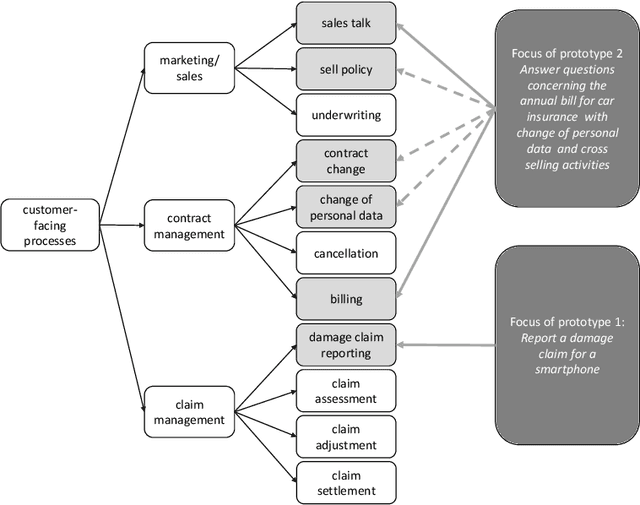

Abstract:Advances in artificial intelligence have renewed interest in conversational agents. Additionally to software developers, today all kinds of employees show interest in new technologies and their possible applications for customers. German insurance companies generally are interested in improving their customer service and digitizing their business processes. In this work we investigate the potential use of conversational agents in insurance companies theoretically by determining which classes of agents exist which are of interest to insurance companies, finding relevant use cases and requirements. We add two practical parts: First we develop a showcase prototype for an exemplary insurance scenario in claim management. Additionally in a second step, we create a prototype focusing on customer service in a chatbot hackathon, fostering innovation in interdisciplinary teams. In this work, we describe the results of both prototypes in detail. We evaluate both chatbots defining criteria for both settings in detail and compare the results and draw conclusions for the maturity of chatbot technology for practical use, describing the opportunities and challenges companies, especially small and medium enterprises, face.
* 26 pages, 7 figures. ICAART 2019 extension. Extension of arXiv:1812.07339
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge