Jeffrey Yunfan Liu
Real-Time Neural Rasterization for Large Scenes
Nov 09, 2023Abstract:We propose a new method for realistic real-time novel-view synthesis (NVS) of large scenes. Existing neural rendering methods generate realistic results, but primarily work for small scale scenes (<50 square meters) and have difficulty at large scale (>10000 square meters). Traditional graphics-based rasterization rendering is fast for large scenes but lacks realism and requires expensive manually created assets. Our approach combines the best of both worlds by taking a moderate-quality scaffold mesh as input and learning a neural texture field and shader to model view-dependant effects to enhance realism, while still using the standard graphics pipeline for real-time rendering. Our method outperforms existing neural rendering methods, providing at least 30x faster rendering with comparable or better realism for large self-driving and drone scenes. Our work is the first to enable real-time rendering of large real-world scenes.
GraphPNAS: Learning Distribution of Good Neural Architectures via Deep Graph Generative Models
Nov 28, 2022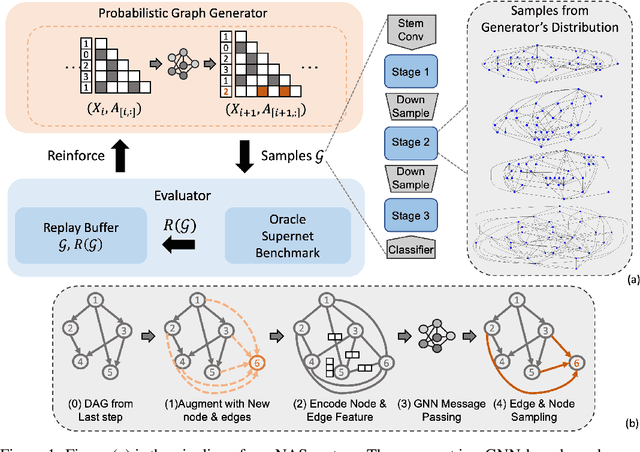



Abstract:Neural architectures can be naturally viewed as computational graphs. Motivated by this perspective, we, in this paper, study neural architecture search (NAS) through the lens of learning random graph models. In contrast to existing NAS methods which largely focus on searching for a single best architecture, i.e, point estimation, we propose GraphPNAS a deep graph generative model that learns a distribution of well-performing architectures. Relying on graph neural networks (GNNs), our GraphPNAS can better capture topologies of good neural architectures and relations between operators therein. Moreover, our graph generator leads to a learnable probabilistic search method that is more flexible and efficient than the commonly used RNN generator and random search methods. Finally, we learn our generator via an efficient reinforcement learning formulation for NAS. To assess the effectiveness of our GraphPNAS, we conduct extensive experiments on three search spaces, including the challenging RandWire on TinyImageNet, ENAS on CIFAR10, and NAS-Bench-101/201. The complexity of RandWire is significantly larger than other search spaces in the literature. We show that our proposed graph generator consistently outperforms RNN-based one and achieves better or comparable performances than state-of-the-art NAS methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge