Jean-Bernard Hayet
Time-adaptive Video Frame Interpolation based on Residual Diffusion
Apr 07, 2025
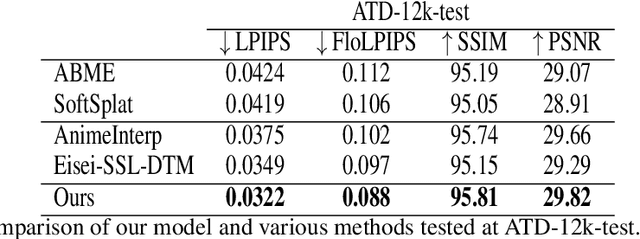


Abstract:In this work, we propose a new diffusion-based method for video frame interpolation (VFI), in the context of traditional hand-made animation. We introduce three main contributions: The first is that we explicitly handle the interpolation time in our model, which we also re-estimate during the training process, to cope with the particularly large variations observed in the animation domain, compared to natural videos; The second is that we adapt and generalize a diffusion scheme called ResShift recently proposed in the super-resolution community to VFI, which allows us to perform a very low number of diffusion steps (in the order of 10) to produce our estimates; The third is that we leverage the stochastic nature of the diffusion process to provide a pixel-wise estimate of the uncertainty on the interpolated frame, which could be useful to anticipate where the model may be wrong. We provide extensive comparisons with respect to state-of-the-art models and show that our model outperforms these models on animation videos.
Context-Aware Timewise VAEs for Real-Time Vehicle Trajectory Prediction
Feb 21, 2023



Abstract:Real-time, accurate prediction of human steering behaviors has wide applications, from developing intelligent traffic systems to deploying autonomous driving systems in both real and simulated worlds. In this paper, we present ContextVAE, a context-aware approach for multi-modal vehicle trajectory prediction. Built upon the backbone architecture of a timewise variational autoencoder, ContextVAE employs a dual attention mechanism for observation encoding that accounts for the environmental context information and the dynamic agents' states in a unified way. By utilizing features extracted from semantic maps during agent state encoding, our approach takes into account both the social features exhibited by agents on the scene and the physical environment constraints to generate map-compliant and socially-aware trajectories. We perform extensive testing on the nuScenes prediction challenge, Lyft Level 5 dataset and Waymo Open Motion Dataset to show the effectiveness of our approach and its state-of-the-art performance. In all tested datasets, ContextVAE models are fast to train and provide high-quality multi-modal predictions in real-time.
SocialVAE: Human Trajectory Prediction using Timewise Latents
Mar 29, 2022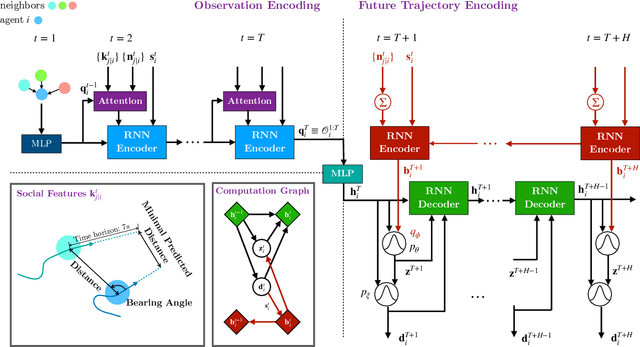
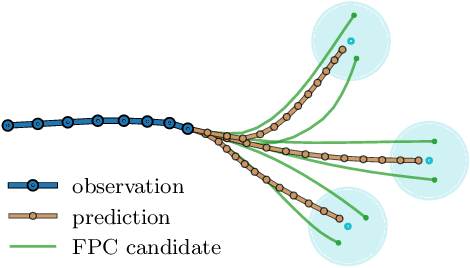
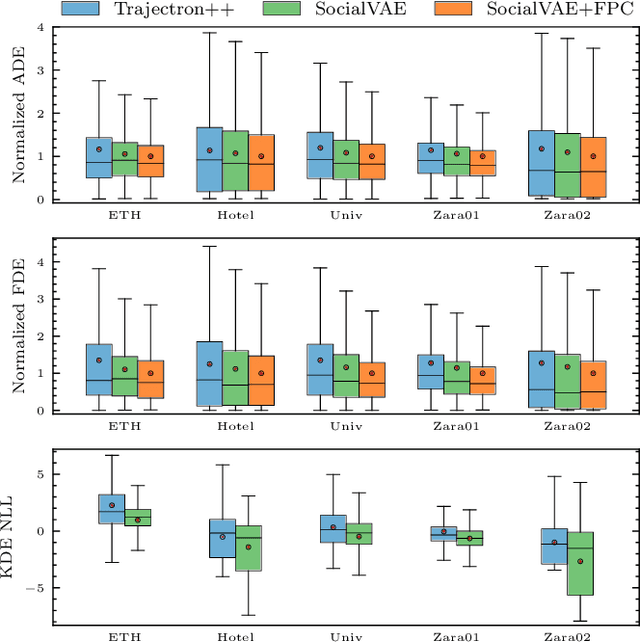
Abstract:Predicting pedestrian movement is critical for human behavior analysis and also for safe and efficient human-agent interactions. However, despite significant advancements, it is still challenging for existing approaches to capture the uncertainty and multimodality of human navigation decision making. In this paper, we propose SocialVAE, a novel approach for human trajectory prediction. The core of SocialVAE is a timewise variational autoencoder architecture that exploits stochastic recurrent neural networks to perform prediction, combined with a social attention mechanism and backward posterior approximation to allow for better extraction of pedestrian navigation strategies. We show that SocialVAE improves current state-of-the-art performance on several pedestrian trajectory prediction benchmarks, including the ETH/UCY benchmark, the Stanford Drone Dataset and SportVU NBA movement dataset. Code is available at: https://github.com/xupei0610/SocialVAE.
What we see and What we don't see: Imputing Occluded Crowd Structures from Robot Sensing
Sep 17, 2021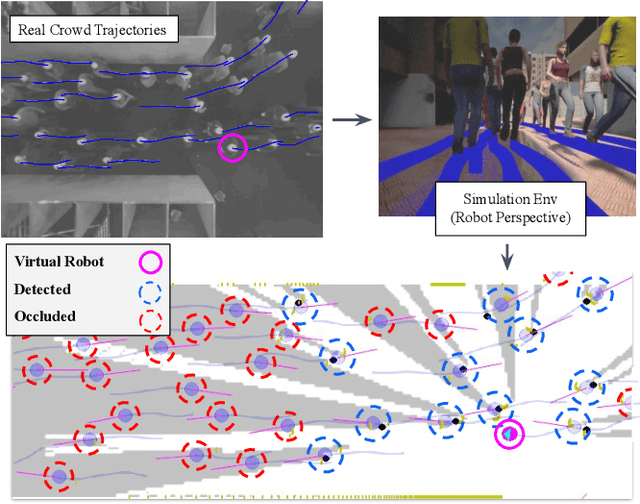
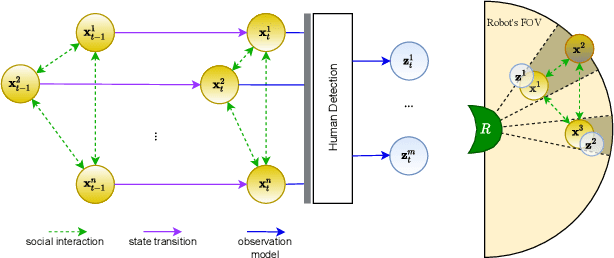
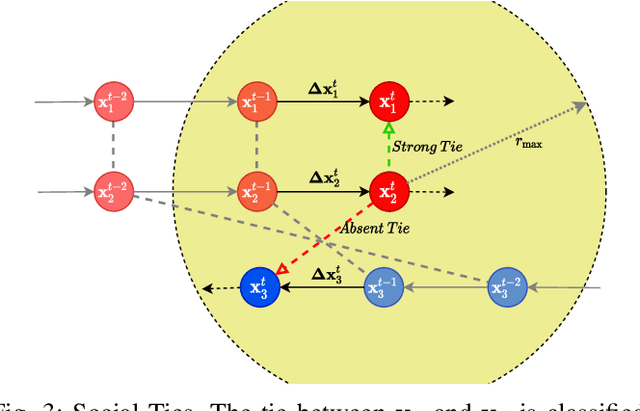
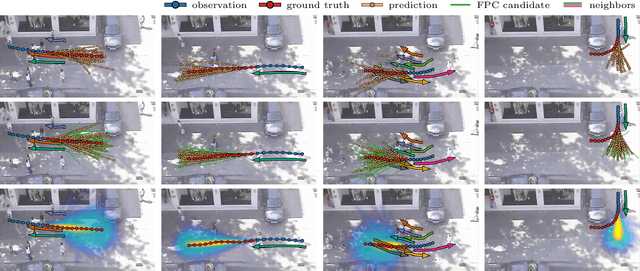
Abstract:We consider the navigation of mobile robots in crowded environments, for which onboard sensing of the crowd is typically limited by occlusions. We address the problem of inferring the human occupancy in the space around the robot, in blind spots, beyond the range of its sensing capabilities. This problem is rather unexplored in spite of the important impact it has on the robot crowd navigation efficiency and safety, which requires the estimation and the prediction of the crowd state around it. In this work, we propose the first solution to sample predictions of possible human presence based on the state of a fewer set of sensed people around the robot as well as previous observations of the crowd activity.
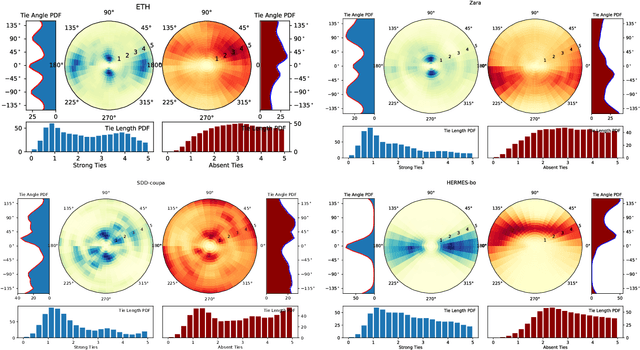
OpenTraj: Assessing Prediction Complexity in Human Trajectories Datasets
Oct 02, 2020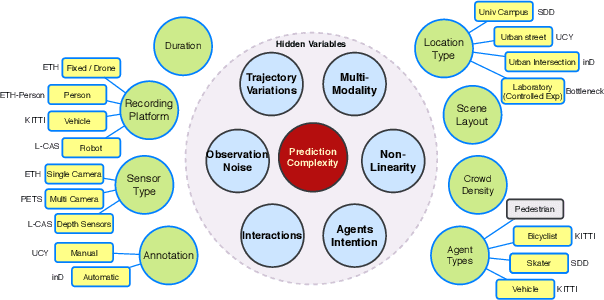
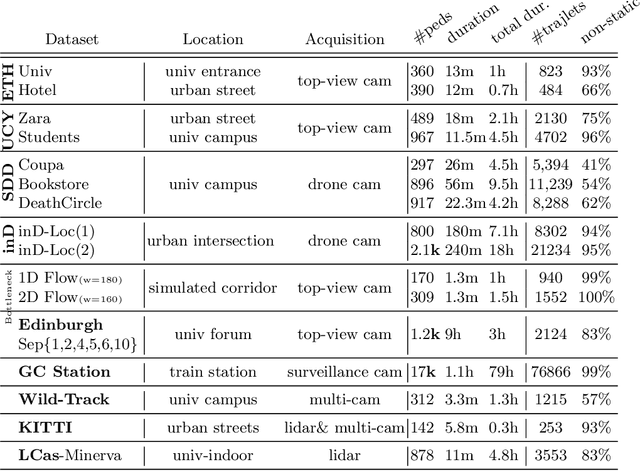
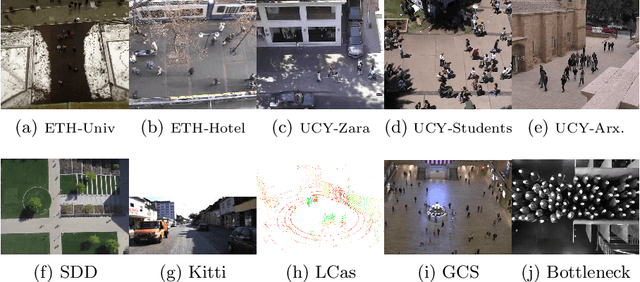
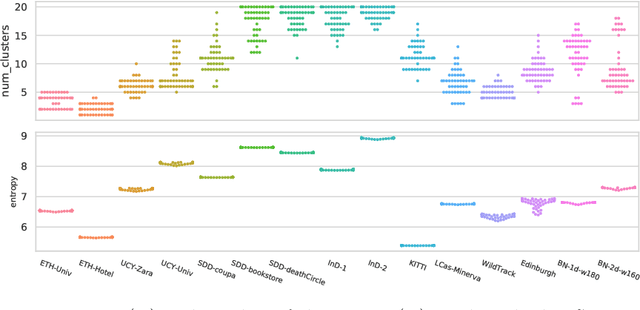
Abstract:Human Trajectory Prediction (HTP) has gained much momentum in the last years and many solutions have been proposed to solve it. Proper benchmarking being a key issue for comparing methods, this paper addresses the question of evaluating how complex is a given dataset with respect to the prediction problem. For assessing a dataset complexity, we define a series of indicators around three concepts: Trajectory predictability; Trajectory regularity; Context complexity. We compare the most common datasets used in HTP in the light of these indicators and discuss what this may imply on benchmarking of HTP algorithms. Our source code is released on
Data-Driven Crowd Simulation with Generative Adversarial Networks
May 23, 2019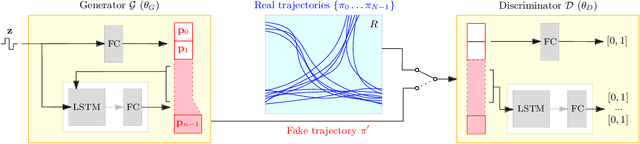

Abstract:This paper presents a novel data-driven crowd simulation method that can mimic the observed traffic of pedestrians in a given environment. Given a set of observed trajectories, we use a recent form of neural networks, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), to learn the properties of this set and generate new trajectories with similar properties. We define a way for simulated pedestrians (agents) to follow such a trajectory while handling local collision avoidance. As such, the system can generate a crowd that behaves similarly to observations, while still enabling real-time interactions between agents. Via experiments with real-world data, we show that our simulated trajectories preserve the statistical properties of their input. Our method simulates crowds in real time that resemble existing crowds, while also allowing insertion of extra agents, combination with other simulation methods, and user interaction.
Social Ways: Learning Multi-Modal Distributions of Pedestrian Trajectories with GANs
Apr 24, 2019
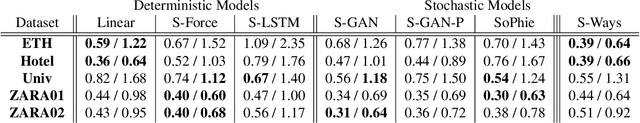
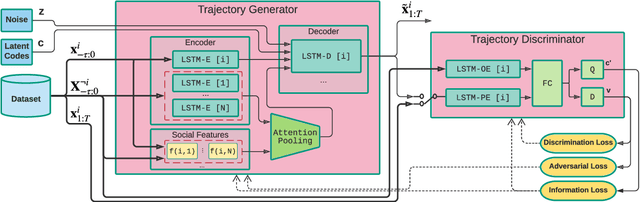
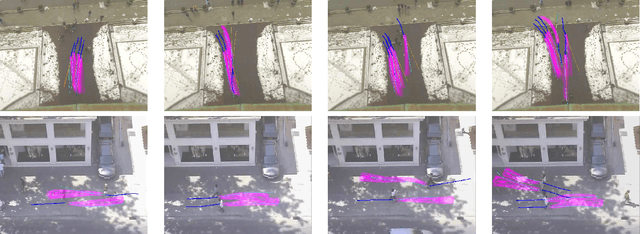
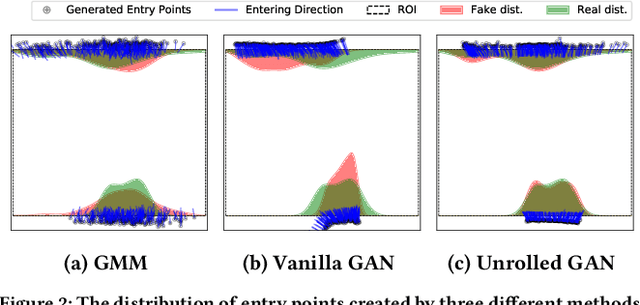
Abstract:This paper proposes a novel approach for predicting the motion of pedestrians interacting with others. It uses a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) to sample plausible predictions for any agent in the scene. As GANs are very susceptible to mode collapsing and dropping, we show that the recently proposed Info-GAN allows dramatic improvements in multi-modal pedestrian trajectory prediction to avoid these issues. We also left out L2-loss in training the generator, unlike some previous works, because it causes serious mode collapsing though faster convergence. We show through experiments on real and synthetic data that the proposed method leads to generate more diverse samples and to preserve the modes of the predictive distribution. In particular, to prove this claim, we have designed a toy example dataset of trajectories that can be used to assess the performance of different methods in preserving the predictive distribution modes.
Bayesian Scale Estimation for Monocular SLAM Based on Generic Object Detection for Correcting Scale Drift
Nov 07, 2017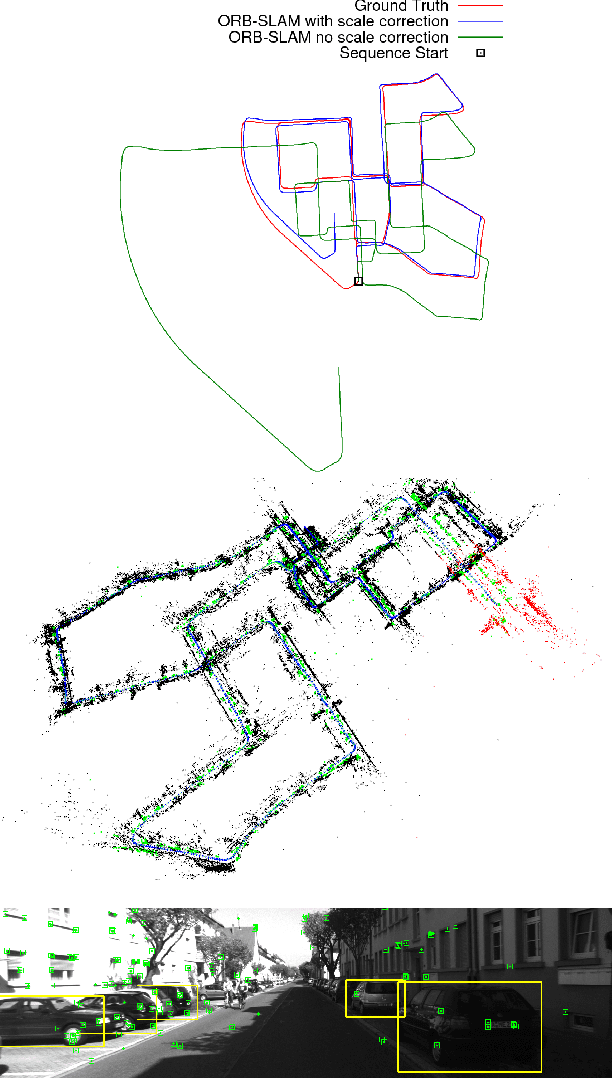
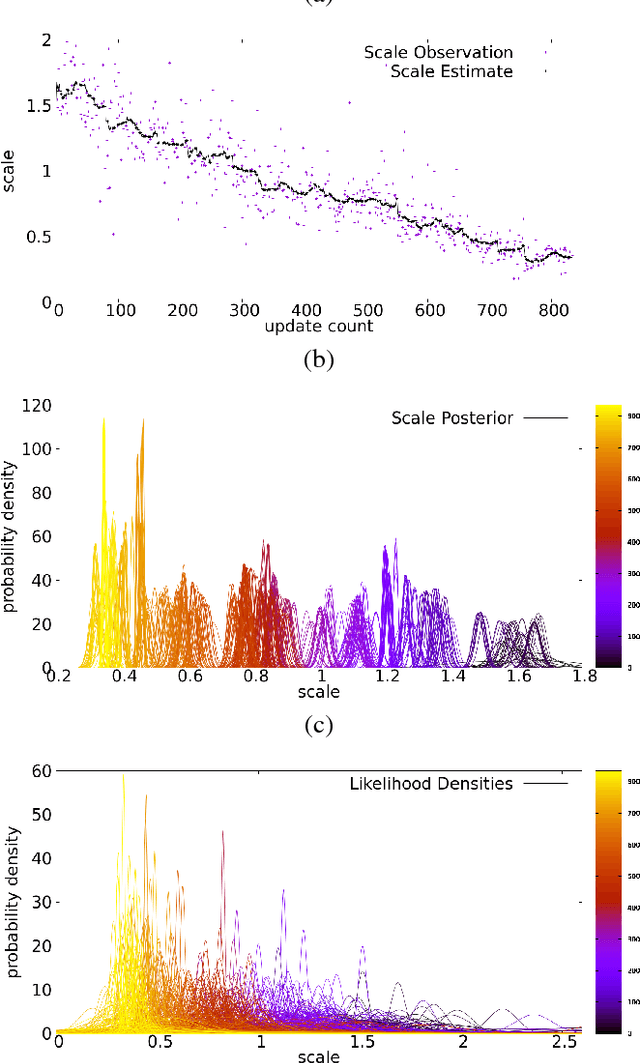
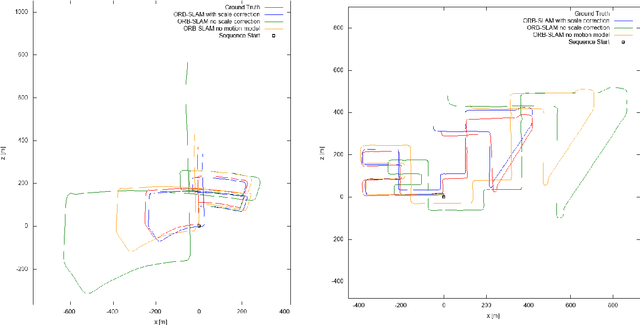
Abstract:This work proposes a new, online algorithm for estimating the local scale correction to apply to the output of a monocular SLAM system and obtain an as faithful as possible metric reconstruction of the 3D map and of the camera trajectory. Within a Bayesian framework, it integrates observations from a deep-learning based generic object detector and a prior on the evolution of the scale drift. For each observation class, a predefined prior on the heights of the class objects is used. This allows to define the observations likelihood. Due to the scale drift inherent to monocular SLAM systems, we integrate a rough model on the dynamics of scale drift. Quantitative evaluations of the system are presented on the KITTI dataset, and compared with different approaches. The results show a superior performance of our proposal in terms of relative translational error when compared to other monocular systems.
Probabilistic Global Scale Estimation for MonoSLAM Based on Generic Object Detection
May 27, 2017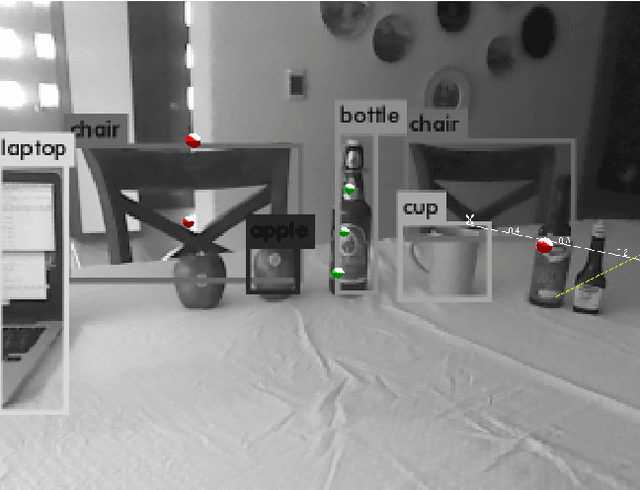
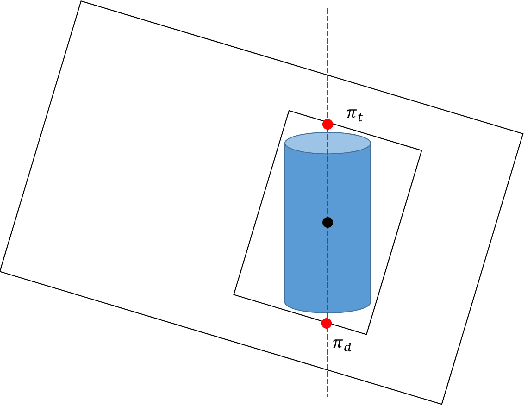
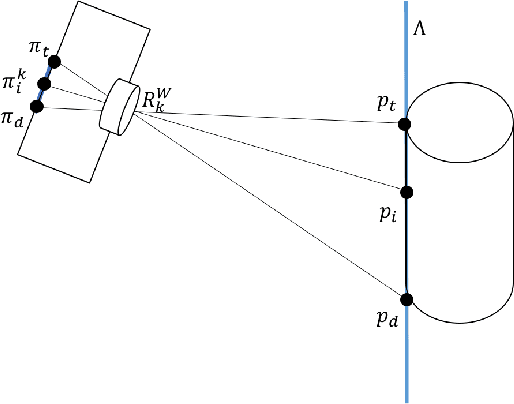
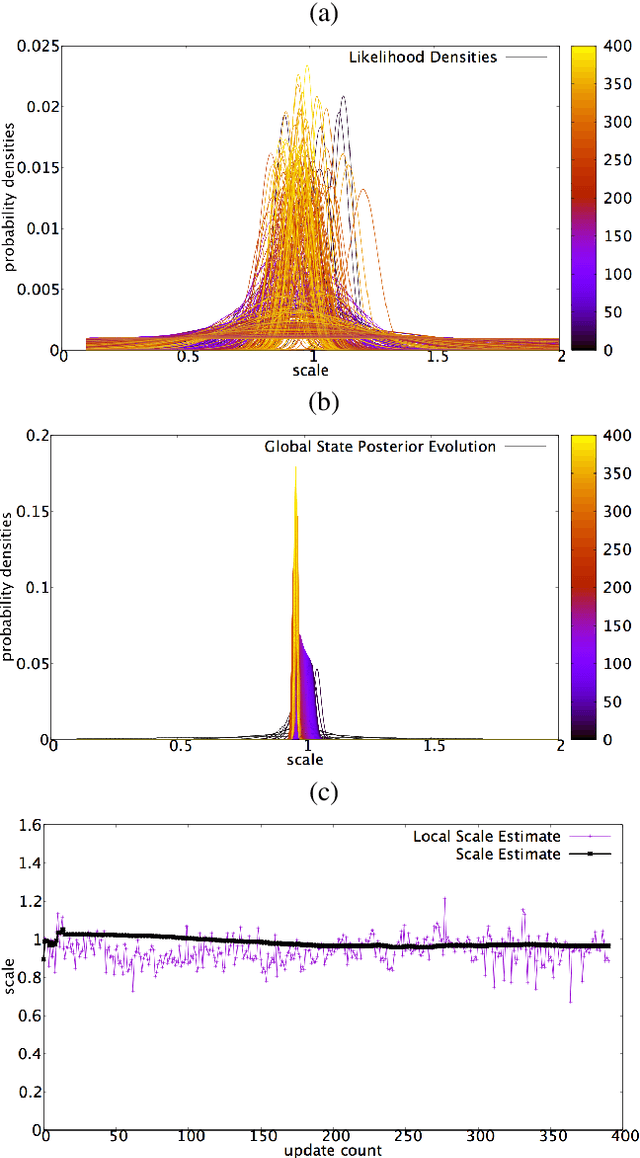
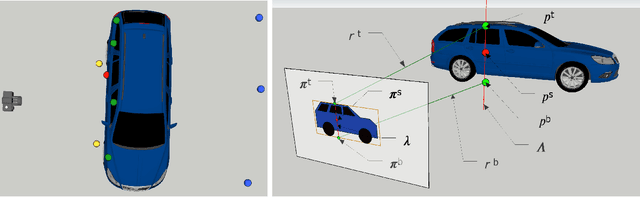
Abstract:This paper proposes a novel method to estimate the global scale of a 3D reconstructed model within a Kalman filtering-based monocular SLAM algorithm. Our Bayesian framework integrates height priors over the detected objects belonging to a set of broad predefined classes, based on recent advances in fast generic object detection. Each observation is produced on single frames, so that we do not need a data association process along video frames. This is because we associate the height priors with the image region sizes at image places where map features projections fall within the object detection regions. We present very promising results of this approach obtained on several experiments with different object classes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge