Jan Oliver Ringert
Model Predictive Control for Crowd Navigation via Learning-Based Trajectory Prediction
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:Safe navigation in pedestrian-rich environments remains a key challenge for autonomous robots. This work evaluates the integration of a deep learning-based Social-Implicit (SI) pedestrian trajectory predictor within a Model Predictive Control (MPC) framework on the physical Continental Corriere robot. Tested across varied pedestrian densities, the SI-MPC system is compared to a traditional Constant Velocity (CV) model in both open-loop prediction and closed-loop navigation. Results show that SI improves trajectory prediction - reducing errors by up to 76% in low-density settings - and enhances safety and motion smoothness in crowded scenes. Moreover, real-world deployment reveals discrepancies between open-loop metrics and closed-loop performance, as the SI model yields broader, more cautious predictions. These findings emphasize the importance of system-level evaluation and highlight the SI-MPC framework's promise for safer, more adaptive navigation in dynamic, human-populated environments.
On Specifying for Trustworthiness
Jun 22, 2022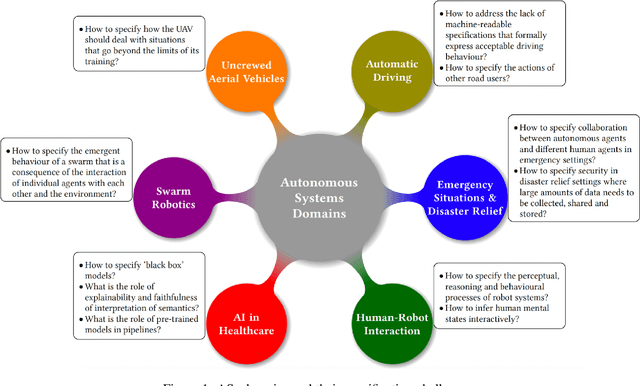
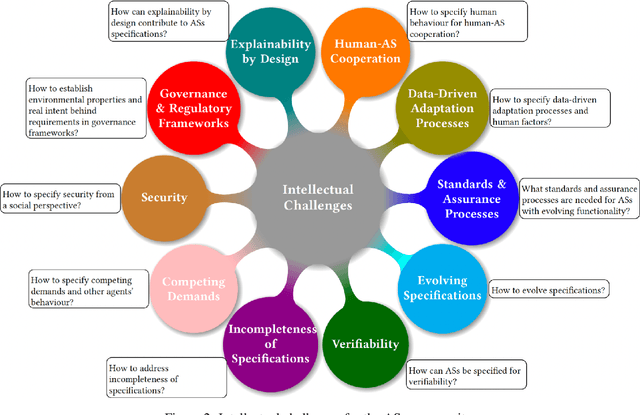
Abstract:As autonomous systems are becoming part of our daily lives, ensuring their trustworthiness is crucial. There are a number of techniques for demonstrating trustworthiness. Common to all these techniques is the need to articulate specifications. In this paper, we take a broad view of specification, concentrating on top-level requirements including but not limited to functionality, safety, security and other non-functional properties. The main contribution of this article is a set of high-level intellectual challenges for the autonomous systems community related to specifying for trustworthiness. We also describe unique specification challenges concerning a number of application domains for autonomous systems.
Black-box Integration of Heterogeneous Modeling Languages for Cyber-Physical Systems
Sep 08, 2014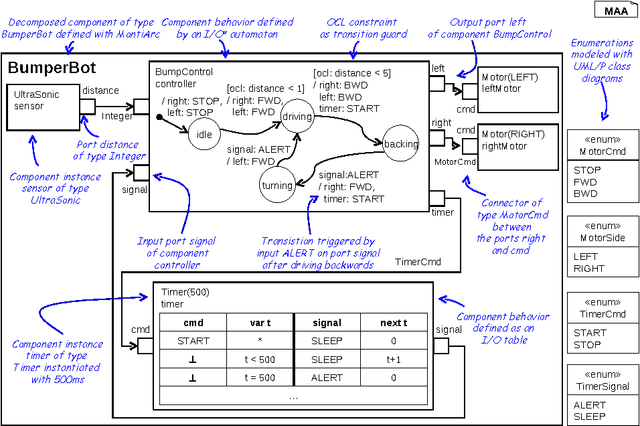
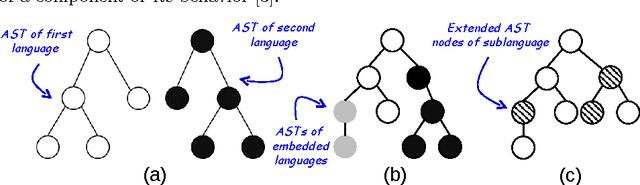
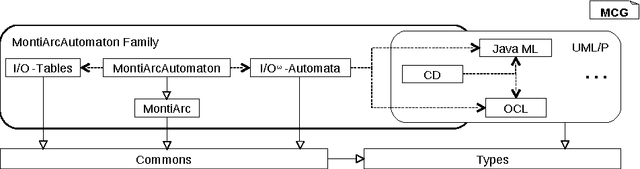
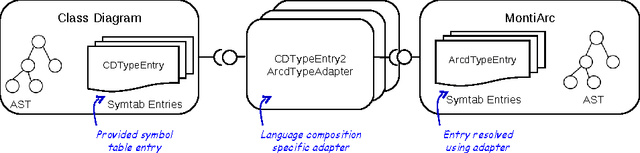
Abstract:Robots belong to a class of Cyber-Physical Systems where complex software as a mobile device has to full tasks in a complex environment. Modeling robotics applications for analysis and code generation requires modeling languages for the logical software architecture and the system behavior. The MontiArcAutomaton modeling framework integrates six independently developed modeling languages to model robotics applications: a component & connector architecture description language, automata, I/O tables, class diagrams, OCL, and a Java DSL. We describe how we integrated these languages into MontiArcAutomaton a-posteriori in a black-box integration fashion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge