Jan Bachmann
The Effects of Randomness on the Stability of Node Embeddings
May 20, 2020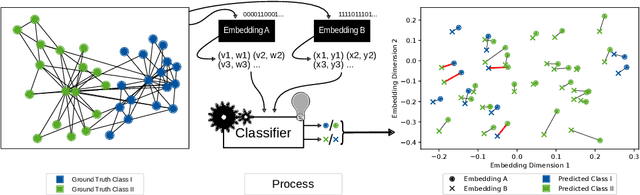
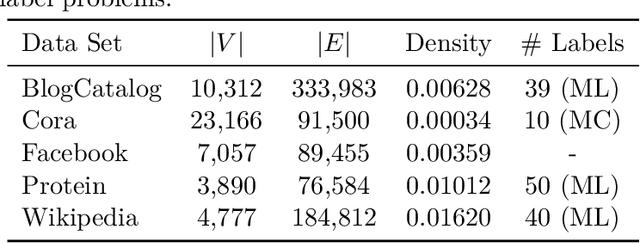
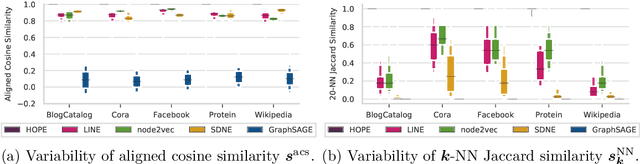
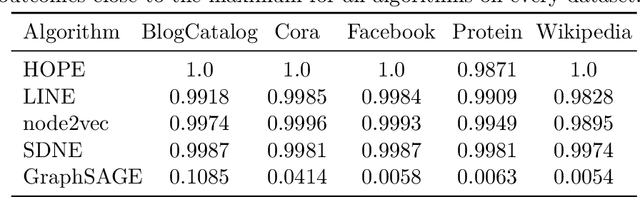
Abstract:We systematically evaluate the (in-)stability of state-of-the-art node embedding algorithms due to randomness, i.e., the random variation of their outcomes given identical algorithms and graphs. We apply five node embeddings algorithms---HOPE, LINE, node2vec, SDNE, and GraphSAGE---to synthetic and empirical graphs and assess their stability under randomness with respect to (i) the geometry of embedding spaces as well as (ii) their performance in downstream tasks. We find significant instabilities in the geometry of embedding spaces independent of the centrality of a node. In the evaluation of downstream tasks, we find that the accuracy of node classification seems to be unaffected by random seeding while the actual classification of nodes can vary significantly. This suggests that instability effects need to be taken into account when working with node embeddings. Our work is relevant for researchers and engineers interested in the effectiveness, reliability, and reproducibility of node embedding approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge