Jack Culpepper
Training and challenging models for text-guided fashion image retrieval
Apr 23, 2022



Abstract:Retrieving relevant images from a catalog based on a query image together with a modifying caption is a challenging multimodal task that can particularly benefit domains like apparel shopping, where fine details and subtle variations may be best expressed through natural language. We introduce a new evaluation dataset, Challenging Fashion Queries (CFQ), as well as a modeling approach that achieves state-of-the-art performance on the existing Fashion IQ (FIQ) dataset. CFQ complements existing benchmarks by including relative captions with positive and negative labels of caption accuracy and conditional image similarity, where others provided only positive labels with a combined meaning. We demonstrate the importance of multimodal pretraining for the task and show that domain-specific weak supervision based on attribute labels can augment generic large-scale pretraining. While previous modality fusion mechanisms lose the benefits of multimodal pretraining, we introduce a residual attention fusion mechanism that improves performance. We release CFQ and our code to the research community.
Modality-Agnostic Attention Fusion for visual search with text feedback
Jun 30, 2020
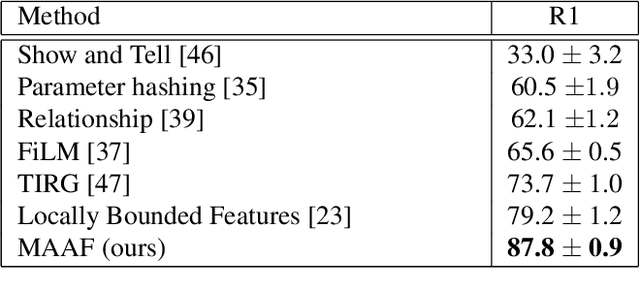
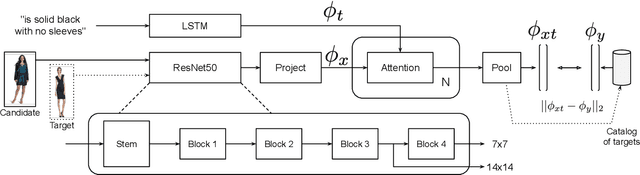
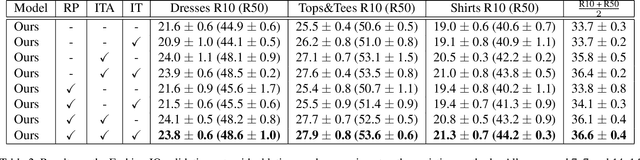
Abstract:Image retrieval with natural language feedback offers the promise of catalog search based on fine-grained visual features that go beyond objects and binary attributes, facilitating real-world applications such as e-commerce. Our Modality-Agnostic Attention Fusion (MAAF) model combines image and text features and outperforms existing approaches on two visual search with modifying phrase datasets, Fashion IQ and CSS, and performs competitively on a dataset with only single-word modifications, Fashion200k. We also introduce two new challenging benchmarks adapted from Birds-to-Words and Spot-the-Diff, which provide new settings with rich language inputs, and we show that our approach without modification outperforms strong baselines. To better understand our model, we conduct detailed ablations on Fashion IQ and provide visualizations of the surprising phenomenon of words avoiding "attending" to the image region they refer to.
Learning Embeddings for Product Visual Search with Triplet Loss and Online Sampling
Oct 10, 2018
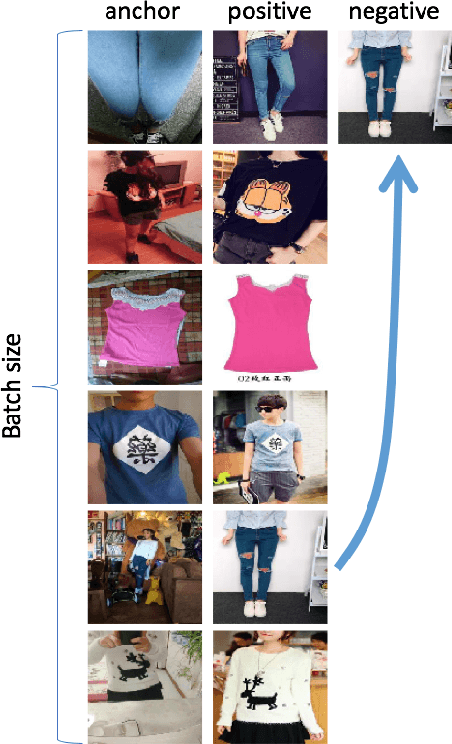
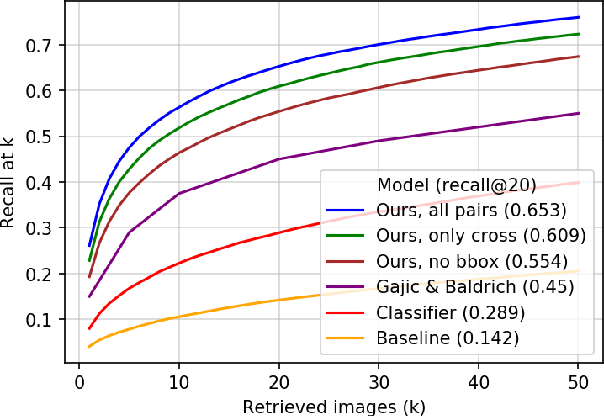
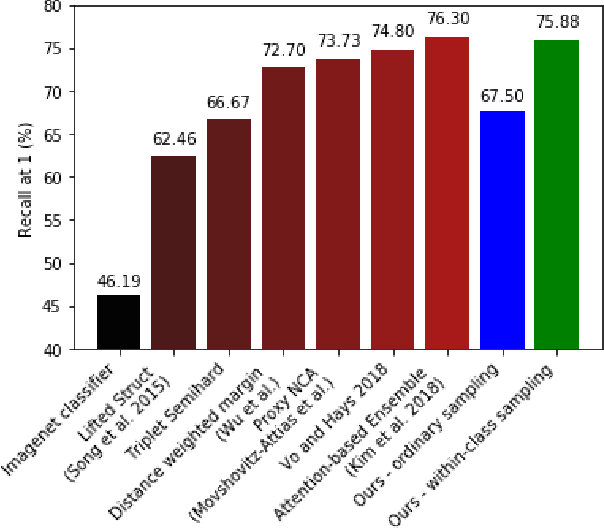
Abstract:In this paper, we propose learning an embedding function for content-based image retrieval within the e-commerce domain using the triplet loss and an online sampling method that constructs triplets from within a minibatch. We compare our method to several strong baselines as well as recent works on the DeepFashion and Stanford Online Product datasets. Our approach significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art on the DeepFashion dataset. With a modification to favor sampling minibatches from a single product category, the same approach demonstrates competitive results when compared to the state-of-the-art for the Stanford Online Products dataset.
Deep Architectures for Face Attributes
Sep 28, 2016



Abstract:We train a deep convolutional neural network to perform identity classification using a new dataset of public figures annotated with age, gender, ethnicity and emotion labels, and then fine-tune it for attribute classification. An optimal sharing pattern of computational resources within this network is determined by experiment, requiring only 1 G flops to produce all predictions. Rather than fine-tune by relearning weights in one additional layer after the penultimate layer of the identity network, we try several different depths for each attribute. We find that prediction of age and emotion is improved by fine-tuning from earlier layers onward, presumably because deeper layers are progressively invariant to non-identity related changes in the input.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge