Issey Sukeda
Interpreting Multi-Attribute Confounding through Numerical Attributes in Large Language Models
Nov 10, 2025



Abstract:Although behavioral studies have documented numerical reasoning errors in large language models (LLMs), the underlying representational mechanisms remain unclear. We hypothesize that numerical attributes occupy shared latent subspaces and investigate two questions:(1) How do LLMs internally integrate multiple numerical attributes of a single entity? (2)How does irrelevant numerical context perturb these representations and their downstream outputs? To address these questions, we combine linear probing with partial correlation analysis and prompt-based vulnerability tests across models of varying sizes. Our results show that LLMs encode real-world numerical correlations but tend to systematically amplify them. Moreover, irrelevant context induces consistent shifts in magnitude representations, with downstream effects that vary by model size. These findings reveal a vulnerability in LLM decision-making and lay the groundwork for fairer, representation-aware control under multi-attribute entanglement.
A Japanese Language Model and Three New Evaluation Benchmarks for Pharmaceutical NLP
May 22, 2025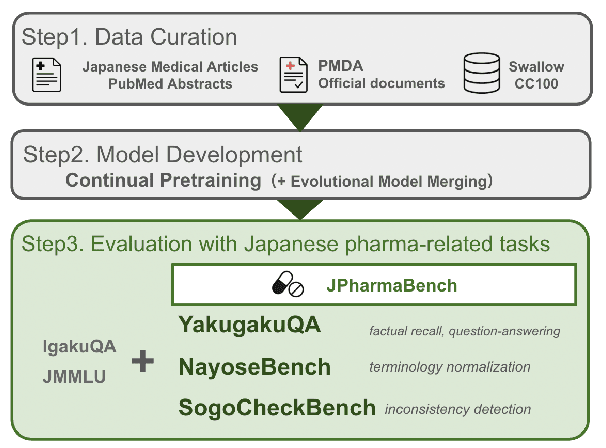

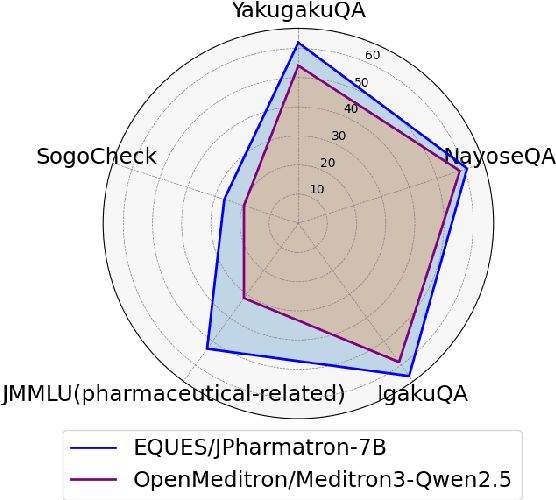
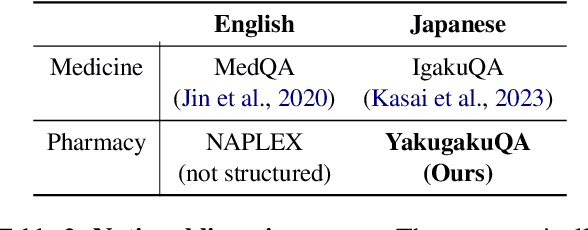
Abstract:We present a Japanese domain-specific language model for the pharmaceutical field, developed through continual pretraining on 2 billion Japanese pharmaceutical tokens and 8 billion English biomedical tokens. To enable rigorous evaluation, we introduce three new benchmarks: YakugakuQA, based on national pharmacist licensing exams; NayoseQA, which tests cross-lingual synonym and terminology normalization; and SogoCheck, a novel task designed to assess consistency reasoning between paired statements. We evaluate our model against both open-source medical LLMs and commercial models, including GPT-4o. Results show that our domain-specific model outperforms existing open models and achieves competitive performance with commercial ones, particularly on terminology-heavy and knowledge-based tasks. Interestingly, even GPT-4o performs poorly on SogoCheck, suggesting that cross-sentence consistency reasoning remains an open challenge. Our benchmark suite offers a broader diagnostic lens for pharmaceutical NLP, covering factual recall, lexical variation, and logical consistency. This work demonstrates the feasibility of building practical, secure, and cost-effective language models for Japanese domain-specific applications, and provides reusable evaluation resources for future research in pharmaceutical and healthcare NLP. Our model, codes, and datasets are released at https://github.com/EQUES-Inc/pharma-LLM-eval.
Exploring the Role of Knowledge Graph-Based RAG in Japanese Medical Question Answering with Small-Scale LLMs
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) perform well in medical QA, but their effectiveness in Japanese contexts is limited due to privacy constraints that prevent the use of commercial models like GPT-4 in clinical settings. As a result, recent efforts focus on instruction-tuning open-source LLMs, though the potential of combining them with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) remains underexplored. To bridge this gap, we are the first to explore a knowledge graph-based (KG) RAG framework for Japanese medical QA small-scale open-source LLMs. Experimental results show that KG-based RAG has only a limited impact on Japanese medical QA using small-scale open-source LLMs. Further case studies reveal that the effectiveness of the RAG is sensitive to the quality and relevance of the external retrieved content. These findings offer valuable insights into the challenges and potential of applying RAG in Japanese medical QA, while also serving as a reference for other low-resource languages.
Development and bilingual evaluation of Japanese medical large language model within reasonably low computational resources
Sep 18, 2024Abstract:The recent success of large language models (LLMs) and the scaling law has led to a widespread adoption of larger models. Particularly in the healthcare industry, there is an increasing demand for locally operated LLMs due to security concerns. However, the majority of high quality open-source LLMs have a size of 70B parameters, imposing significant financial burdens on users for GPU preparation and operation. To overcome these issues, we present a medical adaptation based on the recent 7B models, which enables the operation in low computational resources. We compare the performance on medical question-answering benchmarks in two languages (Japanese and English), demonstrating that its scores reach parity with or surpass those of currently existing medical LLMs that are ten times larger. We find that fine-tuning an English-centric base model on Japanese medical dataset improves the score in both language, supporting the effect of cross-lingual knowledge transfer. We hope that this study will alleviate financial challenges, serving as a stepping stone for clinical institutions to practically utilize LLMs locally. Our evaluation code is available at https://huggingface.co/stardust-coder/jmedllm-7b-v1.
70B-parameter large language models in Japanese medical question-answering
Jun 21, 2024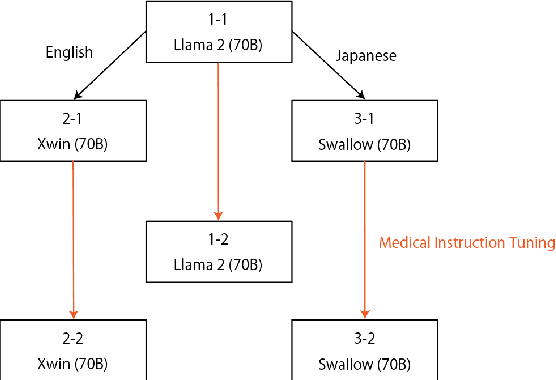
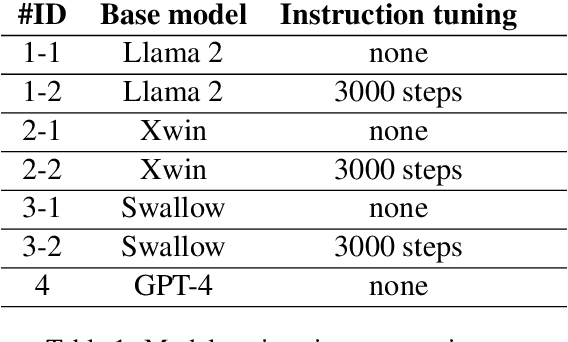
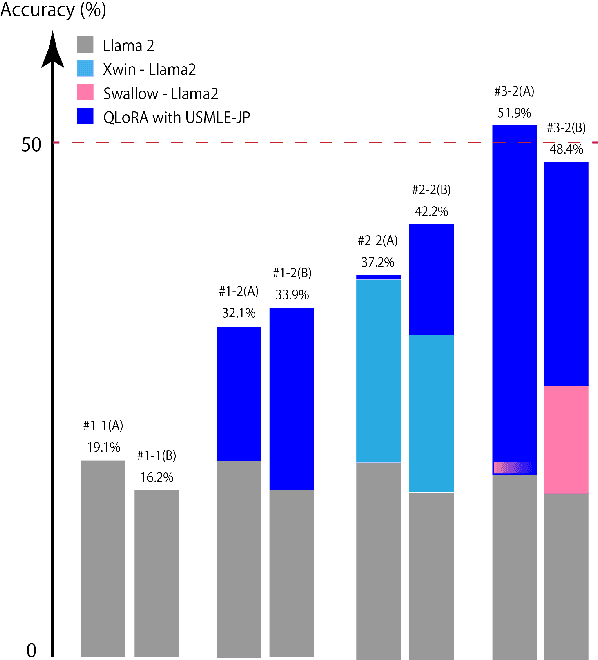
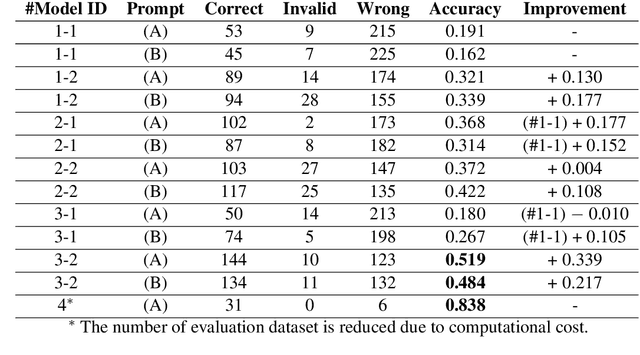
Abstract:Since the rise of large language models (LLMs), the domain adaptation has been one of the hot topics in various domains. Many medical LLMs trained with English medical dataset have made public recently. However, Japanese LLMs in medical domain still lack its research. Here we utilize multiple 70B-parameter LLMs for the first time and show that instruction tuning using Japanese medical question-answering dataset significantly improves the ability of Japanese LLMs to solve Japanese medical license exams, surpassing 50\% in accuracy. In particular, the Japanese-centric models exhibit a more significant leap in improvement through instruction tuning compared to their English-centric counterparts. This underscores the importance of continual pretraining and the adjustment of the tokenizer in our local language. We also examine two slightly different prompt formats, resulting in non-negligible performance improvement.
JMedLoRA:Medical Domain Adaptation on Japanese Large Language Models using Instruction-tuning
Oct 16, 2023Abstract:In the ongoing wave of impact driven by large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, the adaptation of LLMs to medical domain has emerged as a crucial research frontier. Since mainstream LLMs tend to be designed for general-purpose applications, constructing a medical LLM through domain adaptation is a huge challenge. While instruction-tuning is used to fine-tune some LLMs, its precise roles in domain adaptation remain unknown. Here we show the contribution of LoRA-based instruction-tuning to performance in Japanese medical question-answering tasks. In doing so, we employ a multifaceted evaluation for multiple-choice questions, including scoring based on "Exact match" and "Gestalt distance" in addition to the conventional accuracy. Our findings suggest that LoRA-based instruction-tuning can partially incorporate domain-specific knowledge into LLMs, with larger models demonstrating more pronounced effects. Furthermore, our results underscore the potential of adapting English-centric models for Japanese applications in domain adaptation, while also highlighting the persisting limitations of Japanese-centric models. This initiative represents a pioneering effort in enabling medical institutions to fine-tune and operate models without relying on external services.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge