Inaam Ilahi
Intelligent Resource Allocation in Dense LoRa Networks using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Dec 22, 2020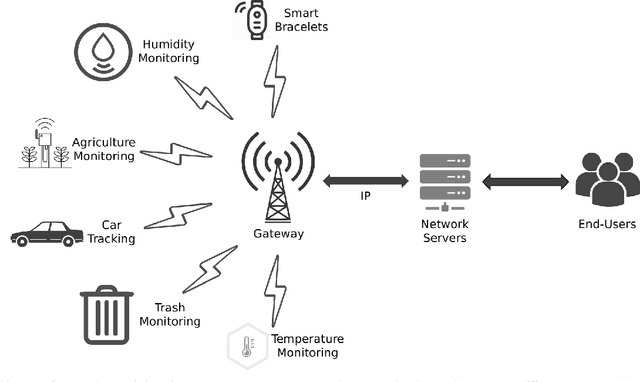
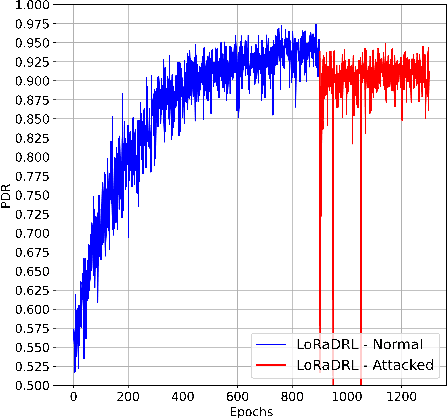
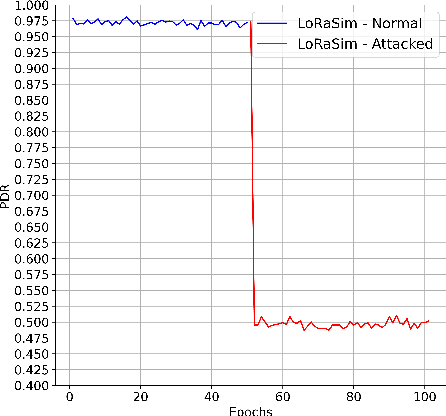
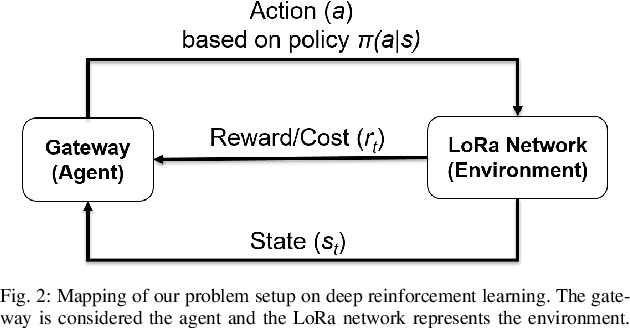
Abstract:The anticipated increase in the count of IoT devices in the coming years motivates the development of efficient algorithms that can help in their effective management while keeping the power consumption low. In this paper, we propose LoRaDRL and provide a detailed performance evaluation. We propose a multi-channel scheme for LoRaDRL. We perform extensive experiments, and our results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm not only significantly improves long-range wide area network (LoRaWAN)'s packet delivery ratio (PDR) but is also able to support mobile end-devices (EDs) while ensuring lower power consumption. Most previous works focus on proposing different MAC protocols for improving the network capacity. We show that through the use of LoRaDRL, we can achieve the same efficiency with ALOHA while moving the complexity from EDs to the gateway thus making the EDs simpler and cheaper. Furthermore, we test the performance of LoRaDRL under large-scale frequency jamming attacks and show its adaptiveness to the changes in the environment. We show that LoRaDRL's output improves the performance of state-of-the-art techniques resulting in some cases an improvement of more than 500% in terms of PDR compared to learning-based techniques.
Examining Machine Learning for 5G and Beyond through an Adversarial Lens
Sep 05, 2020



Abstract:Spurred by the recent advances in deep learning to harness rich information hidden in large volumes of data and to tackle problems that are hard to model/solve (e.g., resource allocation problems), there is currently tremendous excitement in the mobile networks domain around the transformative potential of data-driven AI/ML based network automation, control and analytics for 5G and beyond. In this article, we present a cautionary perspective on the use of AI/ML in the 5G context by highlighting the adversarial dimension spanning multiple types of ML (supervised/unsupervised/RL) and support this through three case studies. We also discuss approaches to mitigate this adversarial ML risk, offer guidelines for evaluating the robustness of ML models, and call attention to issues surrounding ML oriented research in 5G more generally.
Efficient Urdu Caption Generation using Attention based LSTMs
Aug 02, 2020



Abstract:Recent advancements in deep learning has created a lot of opportunities to solve those real world problems which remained unsolved for more than a decade. Automatic caption generation is a major research field, and research community has done a lot of work on this problem on most common languages like English. Urdu is the national language of Pakistan and also much spoken and understood in the sub-continent region of Pakistan-India, and yet no work has been done for Urdu language caption generation. Our research aims to fill this gap by developing an attention-based deep learning model using techniques of sequence modelling specialized for Urdu language. We have prepared a dataset in Urdu language by translating a subset of "Flickr8k" dataset containing 700 'man' images. We evaluate our proposed technique on this dataset and show that it is able to achieve a BLEU score of 0.83 on Urdu language. We improve on the previously proposed techniques by using better CNN architectures and optimization techniques. Furthermore, we also tried adding a grammar loss to the model in order to make the predictions grammatically correct.
Challenges and Countermeasures for Adversarial Attacks on Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jan 27, 2020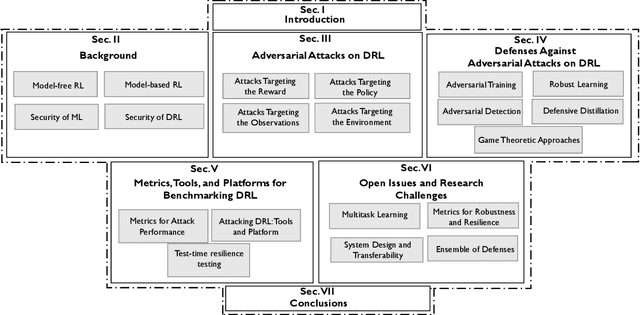
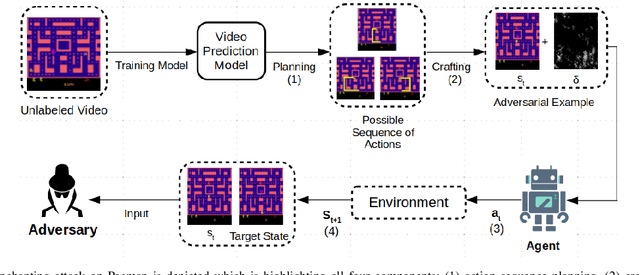
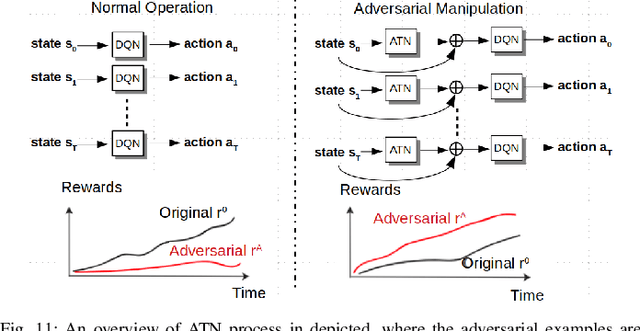
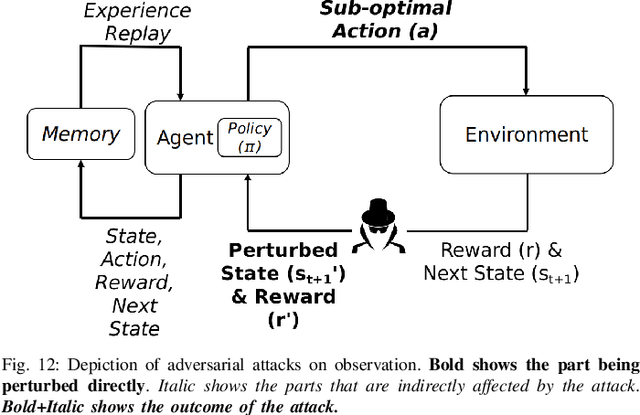
Abstract:Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) has numerous applications in the real world thanks to its outstanding ability in quickly adapting to the surrounding environments. Despite its great advantages, DRL is susceptible to adversarial attacks, which precludes its use in real-life critical systems and applications (e.g., smart grids, traffic controls, and autonomous vehicles) unless its vulnerabilities are addressed and mitigated. Thus, this paper provides a comprehensive survey that discusses emerging attacks in DRL-based systems and the potential countermeasures to defend against these attacks. We first cover some fundamental backgrounds about DRL and present emerging adversarial attacks on machine learning techniques. We then investigate more details of the vulnerabilities that the adversary can exploit to attack DRL along with the state-of-the-art countermeasures to prevent such attacks. Finally, we highlight open issues and research challenges for developing solutions to deal with attacks for DRL-based intelligent systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge