Mahesh K. Marina
On Harnessing Idle Compute at the Edge for Foundation Model Training
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:The ecosystem behind foundation model development today is highly centralized and limited to large-scale cloud data center operators: training foundation models is costly, needing immense compute resources. Decentralized foundation model training across edge devices, leveraging their spare compute, promises a democratized alternative. However, existing edge-training approaches fall short: they struggle to match cloud-based training performance, exhibit limited scalability with model size, exceed device memory capacity, and have prohibitive communication overhead. They also fail to satisfactorily handle device heterogeneity and dynamism. We introduce a new paradigm, Cleave, which finely partitions training operations through a novel selective hybrid tensor parallelism method. Together with a parameter server centric training framework, Cleave copes with device memory limits and avoids communication bottlenecks, thereby enabling efficient training of large models on par with the cloud. Further, with a cost optimization model to guide device selection and training workload distribution, Cleave effectively accounts for device heterogeneity and churn. Our evaluations show that Cleave matches cloud-based GPU training by scaling efficiently to larger models and thousands of devices, supporting up to 8x more devices than baseline edge-training approaches. It outperforms state-of-the-art edge training methods by up to a factor of 10 in per-batch training time and efficiently handles device failures, achieving at least 100x faster recovery than prior methods.
Towards Decentralized and Sustainable Foundation Model Training with the Edge
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:Foundation models are at the forefront of AI research, appealing for their ability to learn from vast datasets and cater to diverse tasks. Yet, their significant computational demands raise issues of environmental impact and the risk of centralized control in their development. We put forward a vision towards decentralized and sustainable foundation model training that leverages the collective compute of sparingly used connected edge AI devices. We present the rationale behind our vision, particularly in support of its sustainability benefit. We further outline a set of challenges that need to be addressed to turn this vision into reality.
HybridServe: Efficient Serving of Large AI Models with Confidence-Based Cascade Routing
May 18, 2025


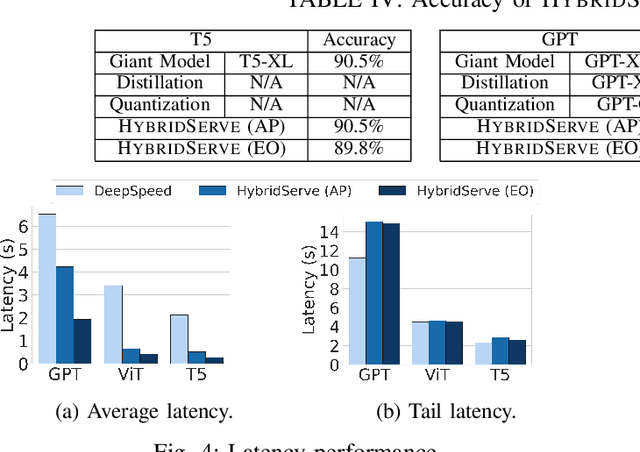
Abstract:Giant Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), have become indispensable for accurate and robust support of large-scale cloud based AI services. However, serving giant DNNs is prohibitively expensive from an energy consumption viewpoint easily exceeding that of training, due to the enormous scale of GPU clusters needed to hold giant DNN model partitions and replicas. Existing approaches can either optimize energy efficiency or inference accuracy but not both. To overcome this status quo, we propose HybridServe, a novel hybrid DNN model serving system that leverages multiple sized versions (small to giant) of the model to be served in tandem. Through a confidence based hybrid model serving dataflow, HybridServe prefers to serve inference requests with energy-efficient smaller models so long as accuracy is not compromised, thereby reducing the number of replicas needed for giant DNNs. HybridServe also features a dataflow planner for efficient partitioning and replication of candidate models to maximize serving system throughput. Experimental results using a prototype implementation of HybridServe show that it reduces energy footprint by up to 19.8x compared to the state-of-the-art DNN model serving systems while matching the accuracy of serving solely with giant DNNs.
PH-Dropout: Practical Epistemic Uncertainty Quantification for View Synthesis
Oct 11, 2024Abstract:View synthesis using Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and Gaussian Splatting (GS) has demonstrated impressive fidelity in rendering real-world scenarios. However, practical methods for accurate and efficient epistemic Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) in view synthesis are lacking. Existing approaches for NeRF either introduce significant computational overhead (e.g., ``10x increase in training time" or ``10x repeated training") or are limited to specific uncertainty conditions or models. Notably, GS models lack any systematic approach for comprehensive epistemic UQ. This capability is crucial for improving the robustness and scalability of neural view synthesis, enabling active model updates, error estimation, and scalable ensemble modeling based on uncertainty. In this paper, we revisit NeRF and GS-based methods from a function approximation perspective, identifying key differences and connections in 3D representation learning. Building on these insights, we introduce PH-Dropout (Post hoc Dropout), the first real-time and accurate method for epistemic uncertainty estimation that operates directly on pre-trained NeRF and GS models. Extensive evaluations validate our theoretical findings and demonstrate the effectiveness of PH-Dropout.
PH-Dropout: Prctical Epistemic Uncertainty Quantification for View Synthesis
Oct 07, 2024Abstract:View synthesis using Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and Gaussian Splatting (GS) has demonstrated impressive fidelity in rendering real-world scenarios. However, practical methods for accurate and efficient epistemic Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) in view synthesis are lacking. Existing approaches for NeRF either introduce significant computational overhead (e.g., ``10x increase in training time" or ``10x repeated training") or are limited to specific uncertainty conditions or models. Notably, GS models lack any systematic approach for comprehensive epistemic UQ. This capability is crucial for improving the robustness and scalability of neural view synthesis, enabling active model updates, error estimation, and scalable ensemble modeling based on uncertainty. In this paper, we revisit NeRF and GS-based methods from a function approximation perspective, identifying key differences and connections in 3D representation learning. Building on these insights, we introduce PH-Dropout (Post hoc Dropout), the first real-time and accurate method for epistemic uncertainty estimation that operates directly on pre-trained NeRF and GS models. Extensive evaluations validate our theoretical findings and demonstrate the effectiveness of PH-Dropout.
Learning High-Frequency Functions Made Easy with Sinusoidal Positional Encoding
Jul 12, 2024



Abstract:Fourier features based positional encoding (PE) is commonly used in machine learning tasks that involve learning high-frequency features from low-dimensional inputs, such as 3D view synthesis and time series regression with neural tangent kernels. Despite their effectiveness, existing PEs require manual, empirical adjustment of crucial hyperparameters, specifically the Fourier features, tailored to each unique task. Further, PEs face challenges in efficiently learning high-frequency functions, particularly in tasks with limited data. In this paper, we introduce sinusoidal PE (SPE), designed to efficiently learn adaptive frequency features closely aligned with the true underlying function. Our experiments demonstrate that SPE, without hyperparameter tuning, consistently achieves enhanced fidelity and faster training across various tasks, including 3D view synthesis, Text-to-Speech generation, and 1D regression. SPE is implemented as a direct replacement for existing PEs. Its plug-and-play nature lets numerous tasks easily adopt and benefit from SPE.
Examining Machine Learning for 5G and Beyond through an Adversarial Lens
Sep 05, 2020



Abstract:Spurred by the recent advances in deep learning to harness rich information hidden in large volumes of data and to tackle problems that are hard to model/solve (e.g., resource allocation problems), there is currently tremendous excitement in the mobile networks domain around the transformative potential of data-driven AI/ML based network automation, control and analytics for 5G and beyond. In this article, we present a cautionary perspective on the use of AI/ML in the 5G context by highlighting the adversarial dimension spanning multiple types of ML (supervised/unsupervised/RL) and support this through three case studies. We also discuss approaches to mitigate this adversarial ML risk, offer guidelines for evaluating the robustness of ML models, and call attention to issues surrounding ML oriented research in 5G more generally.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge