Hy Nguyen
Goal-Oriented Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Decentralized Agent Teams
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Connected and autonomous vehicles across land, water, and air must often operate in dynamic, unpredictable environments with limited communication, no centralized control, and partial observability. These real-world constraints pose significant challenges for coordination, particularly when vehicles pursue individual objectives. To address this, we propose a decentralized Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) framework that enables vehicles, acting as agents, to communicate selectively based on local goals and observations. This goal-aware communication strategy allows agents to share only relevant information, enhancing collaboration while respecting visibility limitations. We validate our approach in complex multi-agent navigation tasks featuring obstacles and dynamic agent populations. Results show that our method significantly improves task success rates and reduces time-to-goal compared to non-cooperative baselines. Moreover, task performance remains stable as the number of agents increases, demonstrating scalability. These findings highlight the potential of decentralized, goal-driven MARL to support effective coordination in realistic multi-vehicle systems operating across diverse domains.
S-Chain: Structured Visual Chain-of-Thought For Medicine
Oct 26, 2025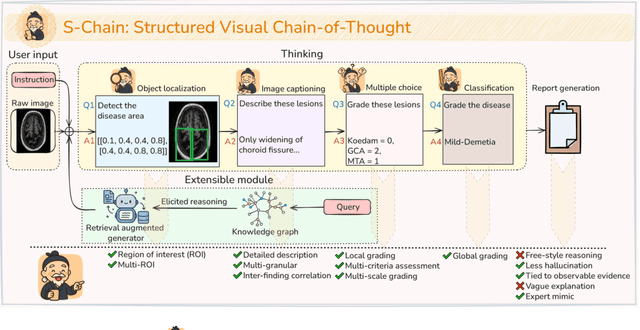
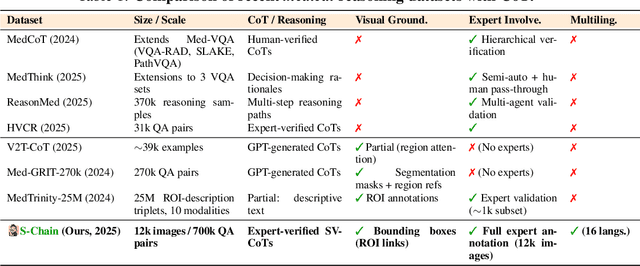
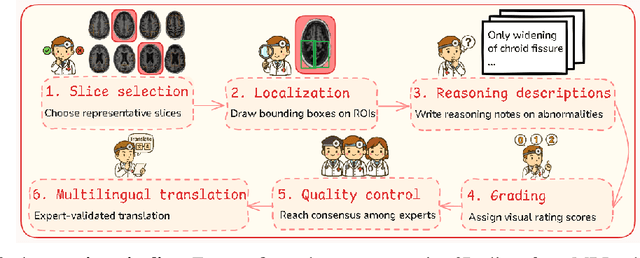
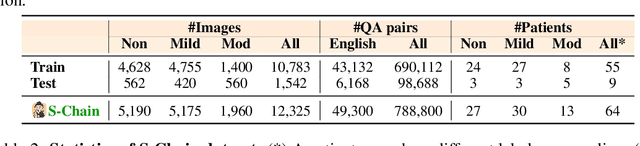
Abstract:Faithful reasoning in medical vision-language models (VLMs) requires not only accurate predictions but also transparent alignment between textual rationales and visual evidence. While Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting has shown promise in medical visual question answering (VQA), no large-scale expert-level dataset has captured stepwise reasoning with precise visual grounding. We introduce S-Chain, the first large-scale dataset of 12,000 expert-annotated medical images with bounding boxes and structured visual CoT (SV-CoT), explicitly linking visual regions to reasoning steps. The dataset further supports 16 languages, totaling over 700k VQA pairs for broad multilingual applicability. Using S-Chain, we benchmark state-of-the-art medical VLMs (ExGra-Med, LLaVA-Med) and general-purpose VLMs (Qwen2.5-VL, InternVL2.5), showing that SV-CoT supervision significantly improves interpretability, grounding fidelity, and robustness. Beyond benchmarking, we study its synergy with retrieval-augmented generation, revealing how domain knowledge and visual grounding interact during autoregressive reasoning. Finally, we propose a new mechanism that strengthens the alignment between visual evidence and reasoning, improving both reliability and efficiency. S-Chain establishes a new benchmark for grounded medical reasoning and paves the way toward more trustworthy and explainable medical VLMs.
The M-factor: A Novel Metric for Evaluating Neural Architecture Search in Resource-Constrained Environments
Jan 29, 2025



Abstract:Neural Architecture Search (NAS) aims to automate the design of deep neural networks. However, existing NAS techniques often focus on maximising accuracy, neglecting model efficiency. This limitation restricts their use in resource-constrained environments like mobile devices and edge computing systems. Moreover, current evaluation metrics prioritise performance over efficiency, lacking a balanced approach for assessing architectures suitable for constrained scenarios. To address these challenges, this paper introduces the M-factor, a novel metric combining model accuracy and size. Four diverse NAS techniques are compared: Policy-Based Reinforcement Learning, Regularised Evolution, Tree-structured Parzen Estimator (TPE), and Multi-trial Random Search. These techniques represent different NAS paradigms, providing a comprehensive evaluation of the M-factor. The study analyses ResNet configurations on the CIFAR-10 dataset, with a search space of 19,683 configurations. Experiments reveal that Policy-Based Reinforcement Learning and Regularised Evolution achieved M-factor values of 0.84 and 0.82, respectively, while Multi-trial Random Search attained 0.75, and TPE reached 0.67. Policy-Based Reinforcement Learning exhibited performance changes after 39 trials, while Regularised Evolution optimised within 20 trials. The research investigates the optimisation dynamics and trade-offs between accuracy and model size for each strategy. Findings indicate that, in some cases, random search performed comparably to more complex algorithms when assessed using the M-factor. These results highlight how the M-factor addresses the limitations of existing metrics by guiding NAS towards balanced architectures, offering valuable insights for selecting strategies in scenarios requiring both performance and efficiency.
Overcoming Semantic Dilution in Transformer-Based Next Frame Prediction
Jan 28, 2025Abstract:Next-frame prediction in videos is crucial for applications such as autonomous driving, object tracking, and motion prediction. The primary challenge in next-frame prediction lies in effectively capturing and processing both spatial and temporal information from previous video sequences. The transformer architecture, known for its prowess in handling sequence data, has made remarkable progress in this domain. However, transformer-based next-frame prediction models face notable issues: (a) The multi-head self-attention (MHSA) mechanism requires the input embedding to be split into $N$ chunks, where $N$ is the number of heads. Each segment captures only a fraction of the original embeddings information, which distorts the representation of the embedding in the latent space, resulting in a semantic dilution problem; (b) These models predict the embeddings of the next frames rather than the frames themselves, but the loss function based on the errors of the reconstructed frames, not the predicted embeddings -- this creates a discrepancy between the training objective and the model output. We propose a Semantic Concentration Multi-Head Self-Attention (SCMHSA) architecture, which effectively mitigates semantic dilution in transformer-based next-frame prediction. Additionally, we introduce a loss function that optimizes SCMHSA in the latent space, aligning the training objective more closely with the model output. Our method demonstrates superior performance compared to the original transformer-based predictors.
Contextual Knowledge Sharing in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning with Decentralized Communication and Coordination
Jan 26, 2025Abstract:Decentralized Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (Dec-MARL) has emerged as a pivotal approach for addressing complex tasks in dynamic environments. Existing Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) methodologies typically assume a shared objective among agents and rely on centralized control. However, many real-world scenarios feature agents with individual goals and limited observability of other agents, complicating coordination and hindering adaptability. Existing Dec-MARL strategies prioritize either communication or coordination, lacking an integrated approach that leverages both. This paper presents a novel Dec-MARL framework that integrates peer-to-peer communication and coordination, incorporating goal-awareness and time-awareness into the agents' knowledge-sharing processes. Our framework equips agents with the ability to (i) share contextually relevant knowledge to assist other agents, and (ii) reason based on information acquired from multiple agents, while considering their own goals and the temporal context of prior knowledge. We evaluate our approach through several complex multi-agent tasks in environments with dynamically appearing obstacles. Our work demonstrates that incorporating goal-aware and time-aware knowledge sharing significantly enhances overall performance.
Do Text-to-Vis Benchmarks Test Real Use of Visualisations?
Jul 29, 2024



Abstract:Large language models are able to generate code for visualisations in response to user requests. This is a useful application, and an appealing one for NLP research because plots of data provide grounding for language. However, there are relatively few benchmarks, and it is unknown whether those that exist are representative of what people do in practice. This paper aims to answer that question through an empirical study comparing benchmark datasets and code from public repositories. Our findings reveal a substantial gap in datasets, with evaluations not testing the same distribution of chart types, attributes, and the number of actions. The only representative dataset requires modification to become an end-to-end and practical benchmark. This shows that new, more benchmarks are needed to support the development of systems that truly address users' visualisation needs. These observations will guide future data creation, highlighting which features hold genuine significance for users.
Meeting Decision Tracker: Making Meeting Minutes with De-Contextualized Utterances
Oct 20, 2022
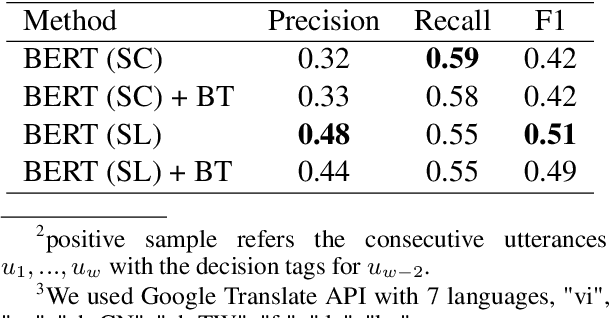

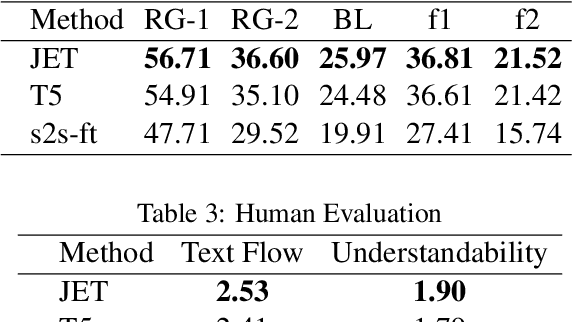
Abstract:Meetings are a universal process to make decisions in business and project collaboration. The capability to automatically itemize the decisions in daily meetings allows for extensive tracking of past discussions. To that end, we developed Meeting Decision Tracker, a prototype system to construct decision items comprising decision utterance detector (DUD) and decision utterance rewriter (DUR). We show that DUR makes a sizable contribution to improving the user experience by dealing with utterance collapse in natural conversation. An introduction video of our system is also available at https://youtu.be/TG1pJJo0Iqo.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge