Hui Liang
Low-Complexity Sparse Superimposed Coding for Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communications
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Sparse superimposed coding (SSC) has emerged as a promising technique for short-packet transmission in ultra-reliable low-latency communication scenarios. However, conventional SSC schemes often suffer from high encoding and decoding complexity due to the use of dense codebook matrices. In this paper, we propose a low-complexity SSC scheme by designing a sparse codebook structure, where each codeword contains only a small number of non-zero elements. The decoding is performed using the traditional multipath matching pursuit algorithm, and the overall complexity is significantly reduced by exploiting the sparsity of the codebook. Simulation results show that the proposed scheme achieves a favorable trade-off between BLER performance and computational complexity, and exhibits strong robustness across different transmission block lengths.
DIFFUMA: High-Fidelity Spatio-Temporal Video Prediction via Dual-Path Mamba and Diffusion Enhancement
Jul 09, 2025



Abstract:Spatio-temporal video prediction plays a pivotal role in critical domains, ranging from weather forecasting to industrial automation. However, in high-precision industrial scenarios such as semiconductor manufacturing, the absence of specialized benchmark datasets severely hampers research on modeling and predicting complex processes. To address this challenge, we make a twofold contribution.First, we construct and release the Chip Dicing Lane Dataset (CHDL), the first public temporal image dataset dedicated to the semiconductor wafer dicing process. Captured via an industrial-grade vision system, CHDL provides a much-needed and challenging benchmark for high-fidelity process modeling, defect detection, and digital twin development.Second, we propose DIFFUMA, an innovative dual-path prediction architecture specifically designed for such fine-grained dynamics. The model captures global long-range temporal context through a parallel Mamba module, while simultaneously leveraging a diffusion module, guided by temporal features, to restore and enhance fine-grained spatial details, effectively combating feature degradation. Experiments demonstrate that on our CHDL benchmark, DIFFUMA significantly outperforms existing methods, reducing the Mean Squared Error (MSE) by 39% and improving the Structural Similarity (SSIM) from 0.926 to a near-perfect 0.988. This superior performance also generalizes to natural phenomena datasets. Our work not only delivers a new state-of-the-art (SOTA) model but, more importantly, provides the community with an invaluable data resource to drive future research in industrial AI.
Efficient Video Instance Segmentation via Tracklet Query and Proposal
Mar 03, 2022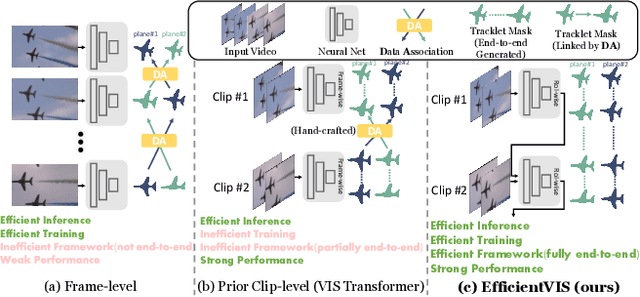
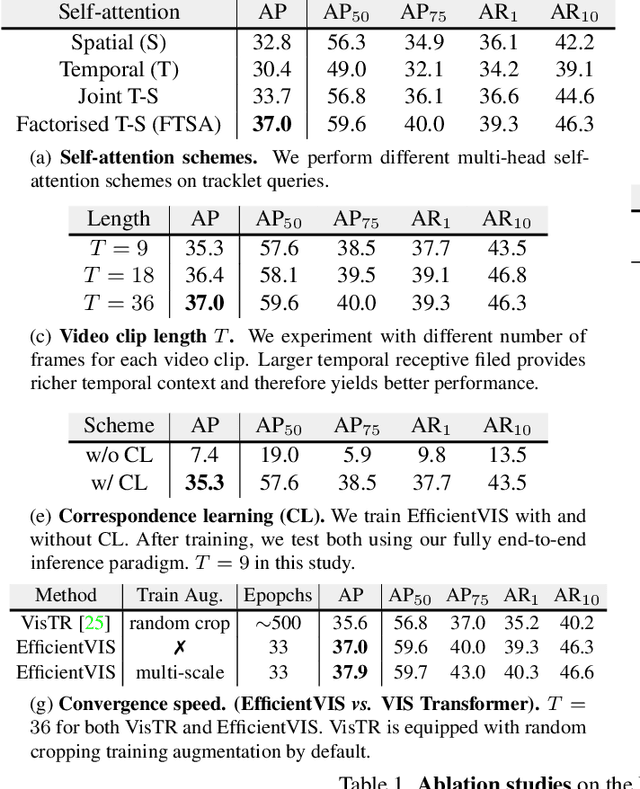
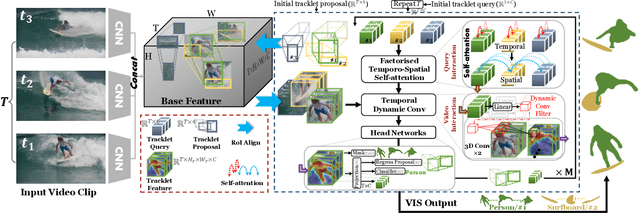
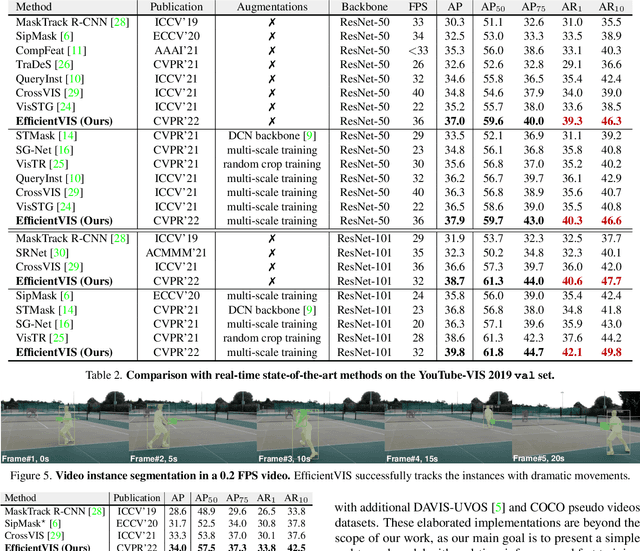
Abstract:Video Instance Segmentation (VIS) aims to simultaneously classify, segment, and track multiple object instances in videos. Recent clip-level VIS takes a short video clip as input each time showing stronger performance than frame-level VIS (tracking-by-segmentation), as more temporal context from multiple frames is utilized. Yet, most clip-level methods are neither end-to-end learnable nor real-time. These limitations are addressed by the recent VIS transformer (VisTR) which performs VIS end-to-end within a clip. However, VisTR suffers from long training time due to its frame-wise dense attention. In addition, VisTR is not fully end-to-end learnable in multiple video clips as it requires a hand-crafted data association to link instance tracklets between successive clips. This paper proposes EfficientVIS, a fully end-to-end framework with efficient training and inference. At the core are tracklet query and tracklet proposal that associate and segment regions-of-interest (RoIs) across space and time by an iterative query-video interaction. We further propose a correspondence learning that makes tracklets linking between clips end-to-end learnable. Compared to VisTR, EfficientVIS requires 15x fewer training epochs while achieving state-of-the-art accuracy on the YouTube-VIS benchmark. Meanwhile, our method enables whole video instance segmentation in a single end-to-end pass without data association at all.
Robust 3D Hand Pose Estimation in Single Depth Images: from Single-View CNN to Multi-View CNNs
Dec 27, 2016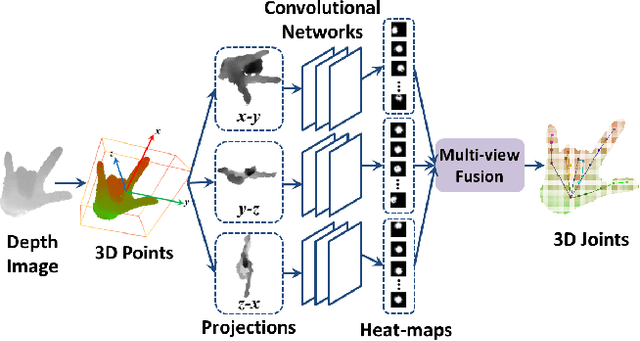
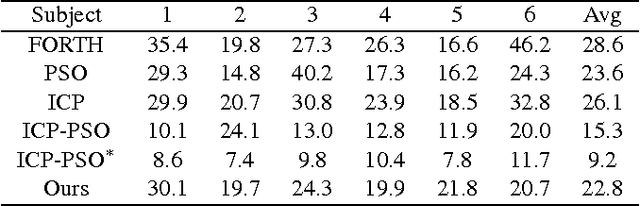
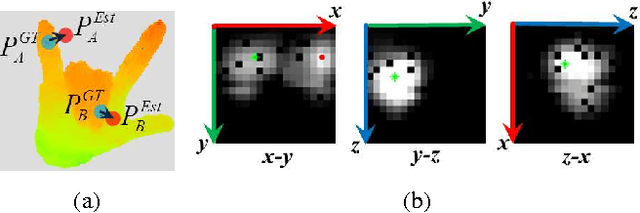
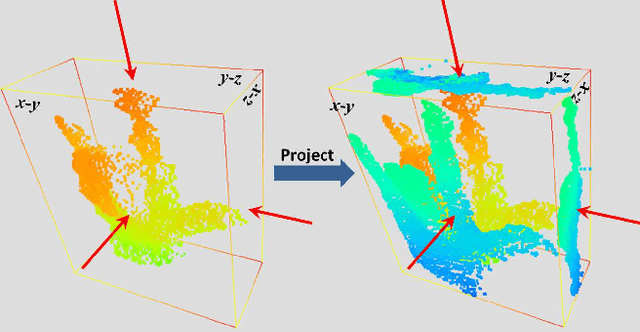
Abstract:Articulated hand pose estimation plays an important role in human-computer interaction. Despite the recent progress, the accuracy of existing methods is still not satisfactory, partially due to the difficulty of embedded high-dimensional and non-linear regression problem. Different from the existing discriminative methods that regress for the hand pose with a single depth image, we propose to first project the query depth image onto three orthogonal planes and utilize these multi-view projections to regress for 2D heat-maps which estimate the joint positions on each plane. These multi-view heat-maps are then fused to produce final 3D hand pose estimation with learned pose priors. Experiments show that the proposed method largely outperforms state-of-the-art on a challenging dataset. Moreover, a cross-dataset experiment also demonstrates the good generalization ability of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge