Huaijin Wu
JTok: On Token Embedding as another Axis of Scaling Law via Joint Token Self-modulation
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:LLMs have traditionally scaled along dense dimensions, where performance is coupled with near-linear increases in computational cost. While MoE decouples capacity from compute, it introduces large memory overhead and hardware efficiency challenges. To overcome these, we propose token-indexed parameters as a novel, orthogonal scaling axis that decouple model capacity from FLOPs. Specifically, we introduce Joint-Token (JTok) and Mixture of Joint-Token (JTok-M), which augment Transformer layers with modulation vectors retrieved from auxiliary embedding tables. These vectors modulate the backbone via lightweight, element-wise operations, incurring negligible FLOPs overhead. Extensive experiments on both dense and MoE backbones, spanning from 650M (190M + 460M embedding) to 61B (17B + 44B embedding) total parameters, demonstrate that our approach consistently reduces validation loss and significantly improves downstream task performance (e.g., +4.1 on MMLU, +8.3 on ARC, +8.9 on CEval). Rigorous isoFLOPs analysis further confirms that JTok-M fundamentally shifts the quality-compute Pareto frontier, achieving comparable model quality with 35% less compute relative to vanilla MoE architectures, and we validate that token-indexed parameters exhibit a predictable power-law scaling behavior. Moreover, our efficient implementation ensures that the overhead introduced by JTok and JTok-M remains marginal.
Molecule Generation for Drug Design: a Graph Learning Perspective
Feb 18, 2022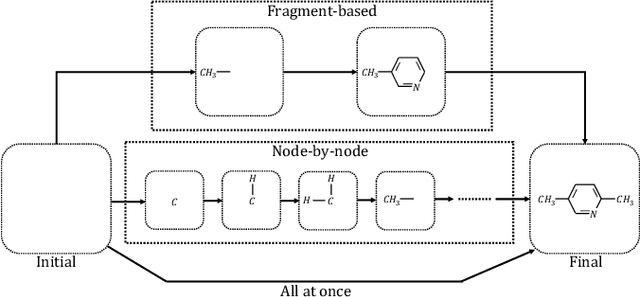
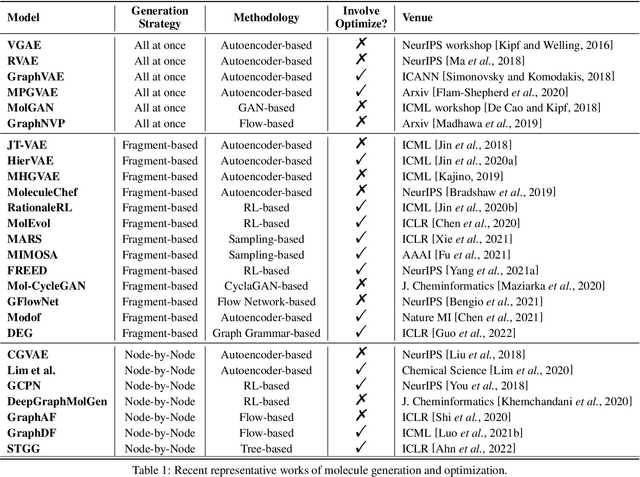
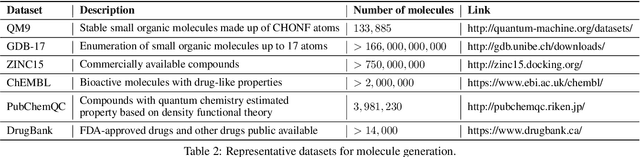
Abstract:Machine learning has revolutionized many fields, and graph learning is recently receiving increasing attention. From the application perspective, one of the emerging and attractive areas is aiding the design and discovery of molecules, especially in drug industry. In this survey, we provide an overview of the state-of-the-art molecule (and mostly for de novo drug) design and discovery aiding methods whose methodology involves (deep) graph learning. Specifically, we propose to categorize these methods into three groups: i) all at once, ii) fragment-based and iii) node-by-node. We further present some representative public datasets and summarize commonly utilized evaluation metrics for generation and optimization, respectively. Finally, we discuss challenges and directions for future research, from the drug design perspective.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge