Hongchang Zhang
Unsupervised Data Generation for Offline Reinforcement Learning: A Perspective from Model
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Offline reinforcement learning (RL) recently gains growing interests from RL researchers. However, the performance of offline RL suffers from the out-of-distribution problem, which can be corrected by feedback in online RL. Previous offline RL research focuses on restricting the offline algorithm in in-distribution even in-sample action sampling. In contrast, fewer work pays attention to the influence of the batch data. In this paper, we first build a bridge over the batch data and the performance of offline RL algorithms theoretically, from the perspective of model-based offline RL optimization. We draw a conclusion that, with mild assumptions, the distance between the state-action pair distribution generated by the behavioural policy and the distribution generated by the optimal policy, accounts for the performance gap between the policy learned by model-based offline RL and the optimal policy. Secondly, we reveal that in task-agnostic settings, a series of policies trained by unsupervised RL can minimize the worst-case regret in the performance gap. Inspired by the theoretical conclusions, UDG (Unsupervised Data Generation) is devised to generate data and select proper data for offline training under tasks-agnostic settings. Empirical results demonstrate that UDG can outperform supervised data generation on solving unknown tasks.
Supported Trust Region Optimization for Offline Reinforcement Learning
Nov 15, 2023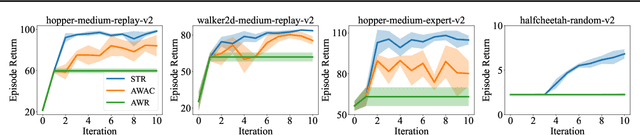

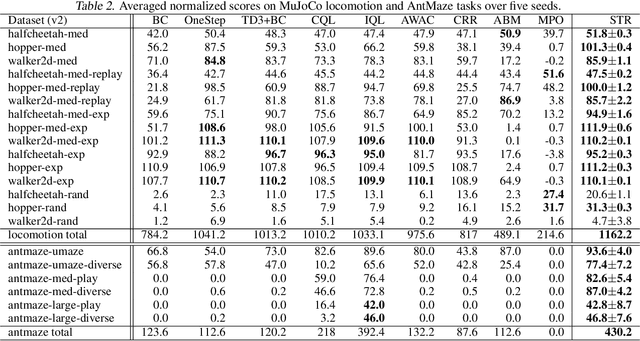
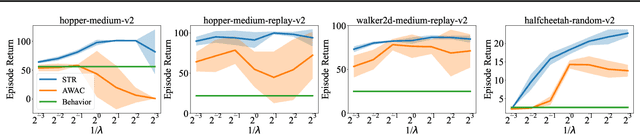
Abstract:Offline reinforcement learning suffers from the out-of-distribution issue and extrapolation error. Most policy constraint methods regularize the density of the trained policy towards the behavior policy, which is too restrictive in most cases. We propose Supported Trust Region optimization (STR) which performs trust region policy optimization with the policy constrained within the support of the behavior policy, enjoying the less restrictive support constraint. We show that, when assuming no approximation and sampling error, STR guarantees strict policy improvement until convergence to the optimal support-constrained policy in the dataset. Further with both errors incorporated, STR still guarantees safe policy improvement for each step. Empirical results validate the theory of STR and demonstrate its state-of-the-art performance on MuJoCo locomotion domains and much more challenging AntMaze domains.
Counterfactual Conservative Q Learning for Offline Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning
Sep 22, 2023



Abstract:Offline multi-agent reinforcement learning is challenging due to the coupling effect of both distribution shift issue common in offline setting and the high dimension issue common in multi-agent setting, making the action out-of-distribution (OOD) and value overestimation phenomenon excessively severe. Tomitigate this problem, we propose a novel multi-agent offline RL algorithm, named CounterFactual Conservative Q-Learning (CFCQL) to conduct conservative value estimation. Rather than regarding all the agents as a high dimensional single one and directly applying single agent methods to it, CFCQL calculates conservative regularization for each agent separately in a counterfactual way and then linearly combines them to realize an overall conservative value estimation. We prove that it still enjoys the underestimation property and the performance guarantee as those single agent conservative methods do, but the induced regularization and safe policy improvement bound are independent of the agent number, which is therefore theoretically superior to the direct treatment referred to above, especially when the agent number is large. We further conduct experiments on four environments including both discrete and continuous action settings on both existing and our man-made datasets, demonstrating that CFCQL outperforms existing methods on most datasets and even with a remarkable margin on some of them.
Wasserstein Unsupervised Reinforcement Learning
Oct 15, 2021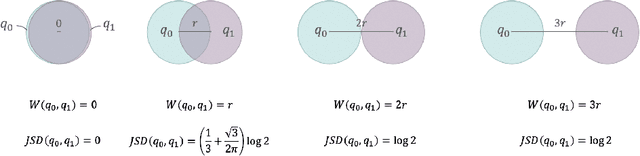
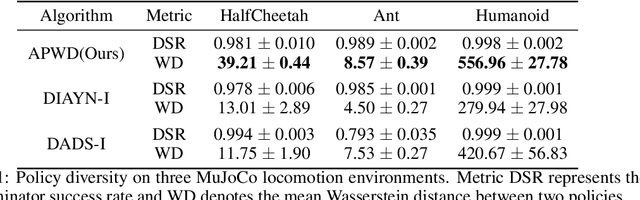
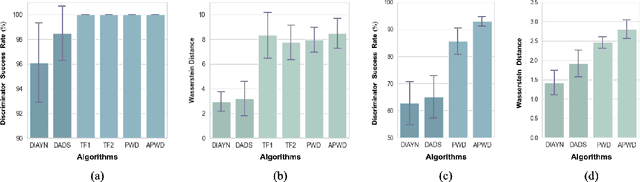

Abstract:Unsupervised reinforcement learning aims to train agents to learn a handful of policies or skills in environments without external reward. These pre-trained policies can accelerate learning when endowed with external reward, and can also be used as primitive options in hierarchical reinforcement learning. Conventional approaches of unsupervised skill discovery feed a latent variable to the agent and shed its empowerment on agent's behavior by mutual information (MI) maximization. However, the policies learned by MI-based methods cannot sufficiently explore the state space, despite they can be successfully identified from each other. Therefore we propose a new framework Wasserstein unsupervised reinforcement learning (WURL) where we directly maximize the distance of state distributions induced by different policies. Additionally, we overcome difficulties in simultaneously training N(N >2) policies, and amortizing the overall reward to each step. Experiments show policies learned by our approach outperform MI-based methods on the metric of Wasserstein distance while keeping high discriminability. Furthermore, the agents trained by WURL can sufficiently explore the state space in mazes and MuJoCo tasks and the pre-trained policies can be applied to downstream tasks by hierarchical learning.
Reducing Conservativeness Oriented Offline Reinforcement Learning
Feb 27, 2021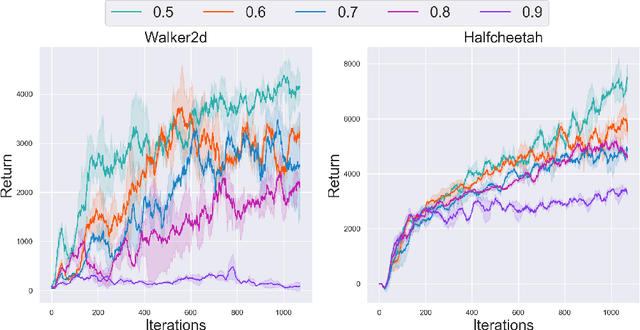
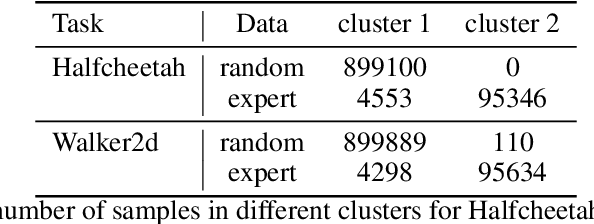
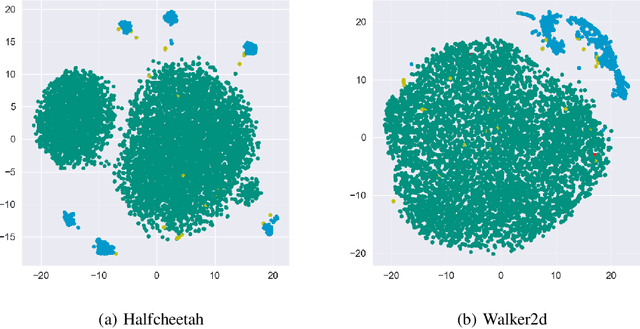
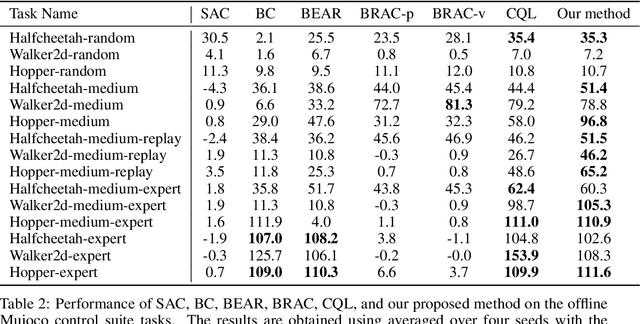
Abstract:In offline reinforcement learning, a policy learns to maximize cumulative rewards with a fixed collection of data. Towards conservative strategy, current methods choose to regularize the behavior policy or learn a lower bound of the value function. However, exorbitant conservation tends to impair the policy's generalization ability and degrade its performance, especially for the mixed datasets. In this paper, we propose the method of reducing conservativeness oriented reinforcement learning. On the one hand, the policy is trained to pay more attention to the minority samples in the static dataset to address the data imbalance problem. On the other hand, we give a tighter lower bound of value function than previous methods to discover potential optimal actions. Consequently, our proposed method is able to tackle the skewed distribution of the provided dataset and derive a value function closer to the expected value function. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in D4RL offline reinforcement learning evaluation tasks and our own designed mixed datasets.
Credit Assignment with Meta-Policy Gradient for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Feb 24, 2021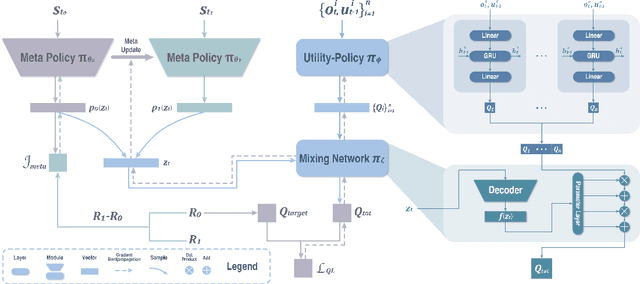
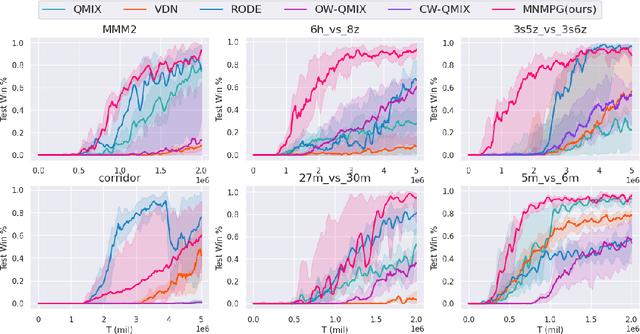
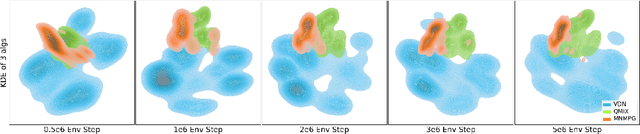
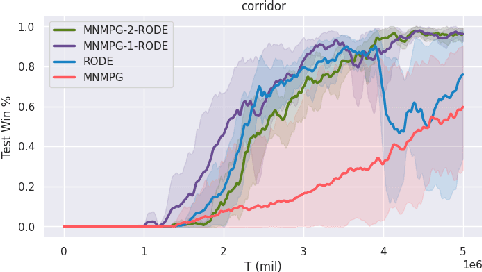
Abstract:Reward decomposition is a critical problem in centralized training with decentralized execution~(CTDE) paradigm for multi-agent reinforcement learning. To take full advantage of global information, which exploits the states from all agents and the related environment for decomposing Q values into individual credits, we propose a general meta-learning-based Mixing Network with Meta Policy Gradient~(MNMPG) framework to distill the global hierarchy for delicate reward decomposition. The excitation signal for learning global hierarchy is deduced from the episode reward difference between before and after "exercise updates" through the utility network. Our method is generally applicable to the CTDE method using a monotonic mixing network. Experiments on the StarCraft II micromanagement benchmark demonstrate that our method just with a simple utility network is able to outperform the current state-of-the-art MARL algorithms on 4 of 5 super hard scenarios. Better performance can be further achieved when combined with a role-based utility network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge