Hironori Washizaki
Generative AI for Requirements Engineering: A Systematic Literature Review
Sep 10, 2024



Abstract:Context: Generative AI (GenAI) has emerged as a transformative tool in software engineering, with requirements engineering (RE) actively exploring its potential to revolutionize processes and outcomes. The integration of GenAI into RE presents both promising opportunities and significant challenges that necessitate systematic analysis and evaluation. Objective: This paper presents a comprehensive systematic literature review (SLR) analyzing state-of-the-art applications and innovative proposals leveraging GenAI in RE. It surveys studies focusing on the utilization of GenAI to enhance RE processes while identifying key challenges and opportunities in this rapidly evolving field. Method: A rigorous SLR methodology was used to analyze 27 carefully selected primary studies in-depth. The review examined research questions pertaining to the application of GenAI across various RE phases, the models and techniques used, and the challenges encountered in implementation and adoption. Results: The most salient findings include i) a predominant focus on the early stages of RE, particularly the elicitation and analysis of requirements, indicating potential for expansion into later phases; ii) the dominance of large language models, especially the GPT series, highlighting the need for diverse AI approaches; and iii) persistent challenges in domain-specific applications and the interpretability of AI-generated outputs, underscoring areas requiring further research and development. Conclusions: The results highlight the critical need for comprehensive evaluation frameworks, improved human-AI collaboration models, and thorough consideration of ethical implications in GenAI-assisted RE. Future research should prioritize extending GenAI applications across the entire RE lifecycle, enhancing domain-specific capabilities, and developing strategies for responsible AI integration in RE practices.
Refining GPT-3 Embeddings with a Siamese Structure for Technical Post Duplicate Detection
Dec 22, 2023



Abstract:One goal of technical online communities is to help developers find the right answer in one place. A single question can be asked in different ways with different wordings, leading to the existence of duplicate posts on technical forums. The question of how to discover and link duplicate posts has garnered the attention of both developer communities and researchers. For example, Stack Overflow adopts a voting-based mechanism to mark and close duplicate posts. However, addressing these constantly emerging duplicate posts in a timely manner continues to pose challenges. Therefore, various approaches have been proposed to detect duplicate posts on technical forum posts automatically. The existing methods suffer from limitations either due to their reliance on handcrafted similarity metrics which can not sufficiently capture the semantics of posts, or their lack of supervision to improve the performance. Additionally, the efficiency of these methods is hindered by their dependence on pair-wise feature generation, which can be impractical for large amount of data. In this work, we attempt to employ and refine the GPT-3 embeddings for the duplicate detection task. We assume that the GPT-3 embeddings can accurately represent the semantics of the posts. In addition, by training a Siamese-based network based on the GPT-3 embeddings, we obtain a latent embedding that accurately captures the duplicate relation in technical forum posts. Our experiment on a benchmark dataset confirms the effectiveness of our approach and demonstrates superior performance compared to baseline methods. When applied to the dataset we constructed with a recent Stack Overflow dump, our approach attains a Top-1, Top-5, and Top-30 accuracy of 23.1%, 43.9%, and 68.9%, respectively. With a manual study, we confirm our approach's potential of finding unlabelled duplicates on technical forums.
Machine Learning Application Development: Practitioners' Insights
Dec 31, 2021



Abstract:Nowadays, intelligent systems and services are getting increasingly popular as they provide data-driven solutions to diverse real-world problems, thanks to recent breakthroughs in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). However, machine learning meets software engineering not only with promising potentials but also with some inherent challenges. Despite some recent research efforts, we still do not have a clear understanding of the challenges of developing ML-based applications and the current industry practices. Moreover, it is unclear where software engineering researchers should focus their efforts to better support ML application developers. In this paper, we report about a survey that aimed to understand the challenges and best practices of ML application development. We synthesize the results obtained from 80 practitioners (with diverse skills, experience, and application domains) into 17 findings; outlining challenges and best practices for ML application development. Practitioners involved in the development of ML-based software systems can leverage the summarized best practices to improve the quality of their system. We hope that the reported challenges will inform the research community about topics that need to be investigated to improve the engineering process and the quality of ML-based applications.
Preliminary Systematic Literature Review of Machine Learning System Development Process
Oct 12, 2019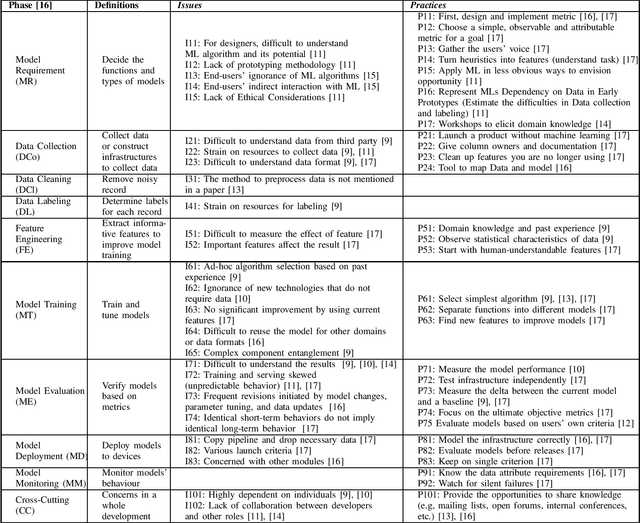

Abstract:Previous machine learning (ML) system development research suggests that emerging software quality attributes are a concern due to the probabilistic behavior of ML systems. Assuming that detailed development processes depend on individual developers and are not discussed in detail. To help developers to standardize their ML system development processes, we conduct a preliminary systematic literature review on ML system development processes. A search query of 2358 papers identified 7 papers as well as two other papers determined in an ad-hoc review. Our findings include emphasized phases in ML system developments, frequently described practices and tailored traditional software development practices.
Studying Software Engineering Patterns for Designing Machine Learning Systems
Oct 11, 2019



Abstract:Machine-learning (ML) techniques have become popular in the recent years. ML techniques rely on mathematics and on software engineering. Researchers and practitioners studying best practices for designing ML application systems and software to address the software complexity and quality of ML techniques. Such design practices are often formalized as architecture patterns and design patterns by encapsulating reusable solutions to commonly occurring problems within given contexts. However, to the best of our knowledge, there has been no work collecting, classifying, and discussing these software-engineering (SE) design patterns for ML techniques systematically. Thus, we set out to collect good/bad SE design patterns for ML techniques to provide developers with a comprehensive and ordered classification of such patterns. We report here preliminary results of a systematic-literature review (SLR) of good/bad design patterns for ML.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge