Hendrik Moeller
Detecting Unforeseen Data Properties with Diffusion Autoencoder Embeddings using Spine MRI data
Oct 14, 2024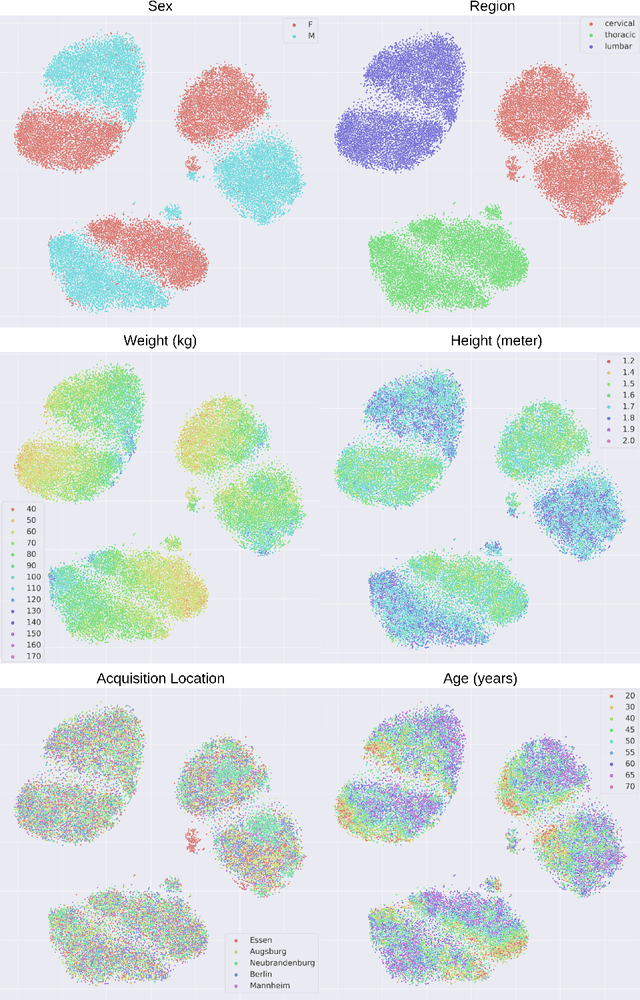

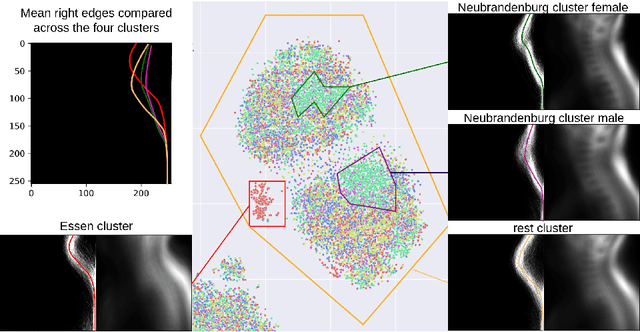
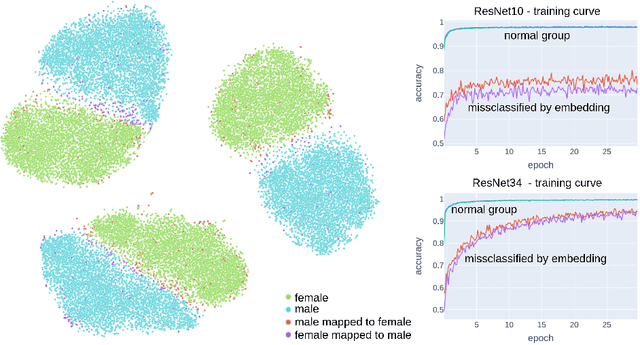
Abstract:Deep learning has made significant strides in medical imaging, leveraging the use of large datasets to improve diagnostics and prognostics. However, large datasets often come with inherent errors through subject selection and acquisition. In this paper, we investigate the use of Diffusion Autoencoder (DAE) embeddings for uncovering and understanding data characteristics and biases, including biases for protected variables like sex and data abnormalities indicative of unwanted protocol variations. We use sagittal T2-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) images of the neck, chest, and lumbar region from 11186 German National Cohort (NAKO) participants. We compare DAE embeddings with existing generative models like StyleGAN and Variational Autoencoder. Evaluations on a large-scale dataset consisting of sagittal T2-weighted MR images of three spine regions show that DAE embeddings effectively separate protected variables such as sex and age. Furthermore, we used t-SNE visualization to identify unwanted variations in imaging protocols, revealing differences in head positioning. Our embedding can identify samples where a sex predictor will have issues learning the correct sex. Our findings highlight the potential of using advanced embedding techniques like DAEs to detect data quality issues and biases in medical imaging datasets. Identifying such hidden relations can enhance the reliability and fairness of deep learning models in healthcare applications, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes.
Counterfactual Explanations for Medical Image Classification and Regression using Diffusion Autoencoder
Aug 02, 2024



Abstract:Counterfactual explanations (CEs) aim to enhance the interpretability of machine learning models by illustrating how alterations in input features would affect the resulting predictions. Common CE approaches require an additional model and are typically constrained to binary counterfactuals. In contrast, we propose a novel method that operates directly on the latent space of a generative model, specifically a Diffusion Autoencoder (DAE). This approach offers inherent interpretability by enabling the generation of CEs and the continuous visualization of the model's internal representation across decision boundaries. Our method leverages the DAE's ability to encode images into a semantically rich latent space in an unsupervised manner, eliminating the need for labeled data or separate feature extraction models. We show that these latent representations are helpful for medical condition classification and the ordinal regression of severity pathologies, such as vertebral compression fractures (VCF) and diabetic retinopathy (DR). Beyond binary CEs, our method supports the visualization of ordinal CEs using a linear model, providing deeper insights into the model's decision-making process and enhancing interpretability. Experiments across various medical imaging datasets demonstrate the method's advantages in interpretability and versatility. The linear manifold of the DAE's latent space allows for meaningful interpolation and manipulation, making it a powerful tool for exploring medical image properties. Our code is available at https://github.com/matanat/dae_counterfactual.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge