Helen Han
Fauna Sprout: A lightweight, approachable, developer-ready humanoid robot
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in learned control, large-scale simulation, and generative models have accelerated progress toward general-purpose robotic controllers, yet the field still lacks platforms suitable for safe, expressive, long-term deployment in human environments. Most existing humanoids are either closed industrial systems or academic prototypes that are difficult to deploy and operate around people, limiting progress in robotics. We introduce Sprout, a developer platform designed to address these limitations through an emphasis on safety, expressivity, and developer accessibility. Sprout adopts a lightweight form factor with compliant control, limited joint torques, and soft exteriors to support safe operation in shared human spaces. The platform integrates whole-body control, manipulation with integrated grippers, and virtual-reality-based teleoperation within a unified hardware-software stack. An expressive head further enables social interaction -- a domain that remains underexplored on most utilitarian humanoids. By lowering physical and technical barriers to deployment, Sprout expands access to capable humanoid platforms and provides a practical basis for developing embodied intelligence in real human environments.
Recognizing Image Style
Jul 23, 2014
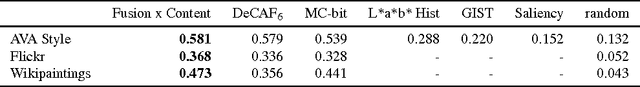

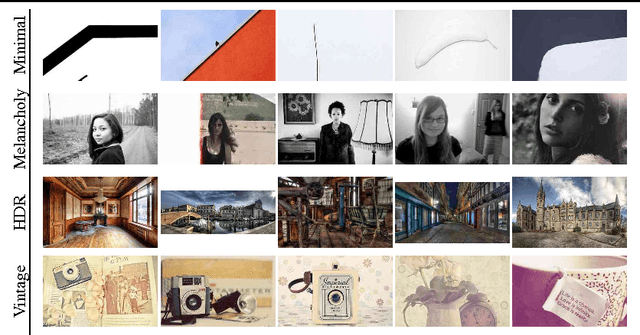
Abstract:The style of an image plays a significant role in how it is viewed, but style has received little attention in computer vision research. We describe an approach to predicting style of images, and perform a thorough evaluation of different image features for these tasks. We find that features learned in a multi-layer network generally perform best -- even when trained with object class (not style) labels. Our large-scale learning methods results in the best published performance on an existing dataset of aesthetic ratings and photographic style annotations. We present two novel datasets: 80K Flickr photographs annotated with 20 curated style labels, and 85K paintings annotated with 25 style/genre labels. Our approach shows excellent classification performance on both datasets. We use the learned classifiers to extend traditional tag-based image search to consider stylistic constraints, and demonstrate cross-dataset understanding of style.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge