Heinrich Matzinger
Is logical analysis performed by transformers taking place in self-attention or in the fully connected part?
Jan 20, 2025Abstract:Transformers architecture apply self-attention to tokens represented as vectors, before a fully connected (neuronal network) layer. These two parts can be layered many times. Traditionally, self-attention is seen as a mechanism for aggregating information before logical operations are performed by the fully connected layer. In this paper, we show, that quite counter-intuitively, the logical analysis can also be performed within the self-attention. For this we implement a handcrafted single-level encoder layer which performs the logical analysis within self-attention. We then study the scenario in which a one-level transformer model undergoes self-learning using gradient descent. We investigate whether the model utilizes fully connected layers or self-attention mechanisms for logical analysis when it has the choice. Given that gradient descent can become stuck at undesired zeros, we explicitly calculate these unwanted zeros and find ways to avoid them. We do all this in the context of predicting grammatical category pairs of adjacent tokens in a text. We believe that our findings have broader implications for understanding the potential logical operations performed by self-attention.
Recover the spectrum of covariance matrix: a non-asymptotic iterative method
Jan 01, 2022



Abstract:It is well known the sample covariance has a consistent bias in the spectrum, for example spectrum of Wishart matrix follows the Marchenko-Pastur law. We in this work introduce an iterative algorithm 'Concent' that actively eliminate this bias and recover the true spectrum for small and moderate dimensions.
An Analytical Formula for Spectrum Reconstruction
May 30, 2020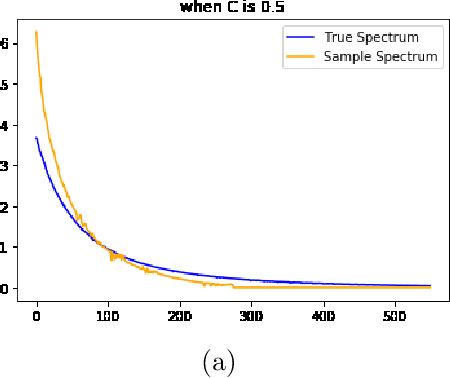
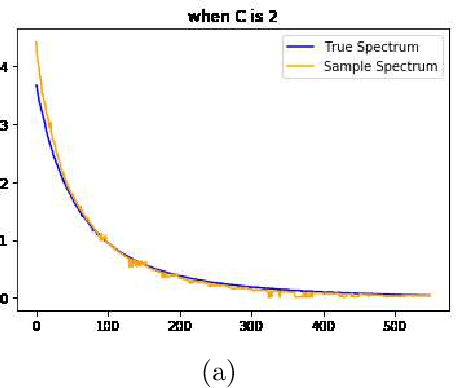
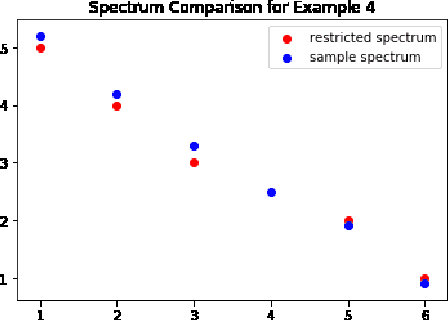
Abstract:We study the spectrum reconstruction technique. As is known to all, eigenvalues play an important role in many research fields and are foundation to many practical techniques such like PCA(Principal Component Analysis). We believe that related algorithms should perform better with more accurate spectrum estimation. There was an approximation formula proposed, however, they didn't give any proof. In our research, we show why the formula works. And when both number of features and dimension of space go to infinity, we find the order of error for the approximation formula, which is related to a constant $c$-the ratio of dimension of space and number of features.
A cost-reducing partial labeling estimator in text classification problem
Jun 10, 2019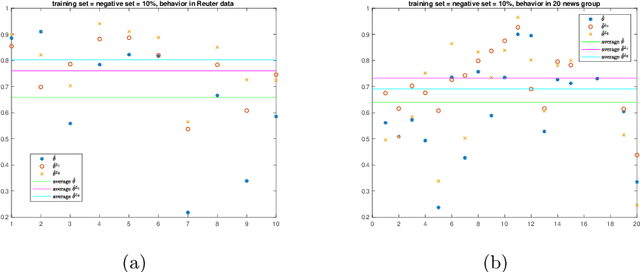
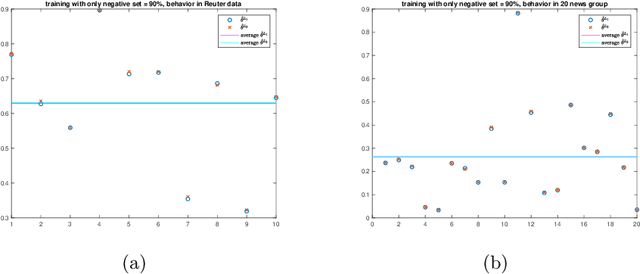
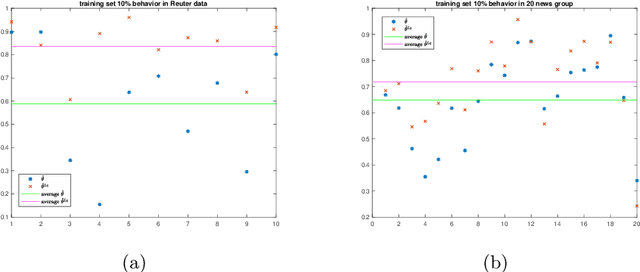
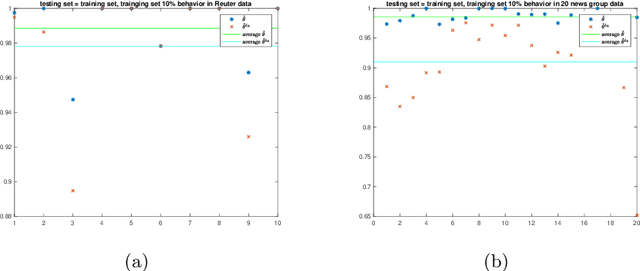
Abstract:We propose a new approach to address the text classification problems when learning with partial labels is beneficial. Instead of offering each training sample a set of candidate labels, we assign negative-oriented labels to the ambiguous training examples if they are unlikely fall into certain classes. We construct our new maximum likelihood estimators with self-correction property, and prove that under some conditions, our estimators converge faster. Also we discuss the advantages of applying one of our estimator to a fully supervised learning problem. The proposed method has potential applicability in many areas, such as crowdsourcing, natural language processing and medical image analysis.
Naive Bayes with Correlation Factor for Text Classification Problem
May 08, 2019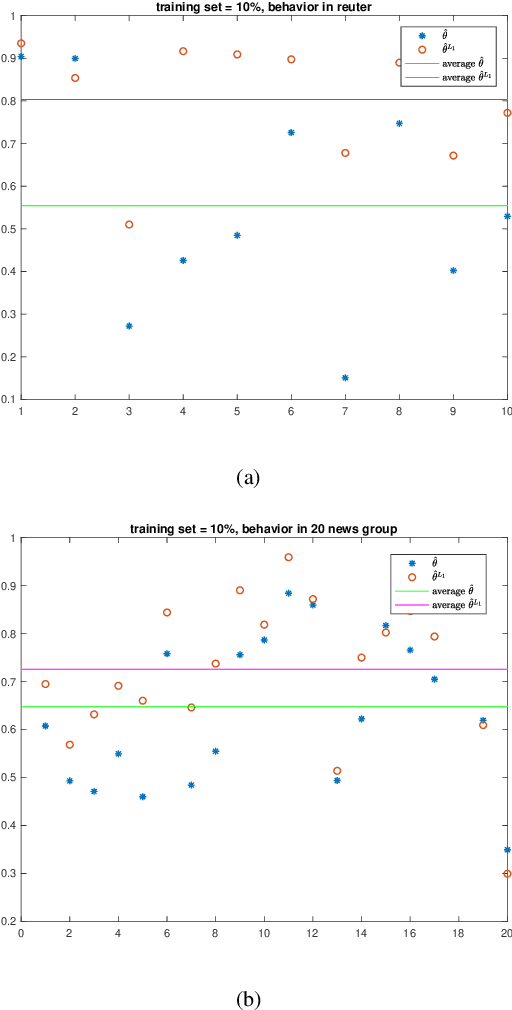
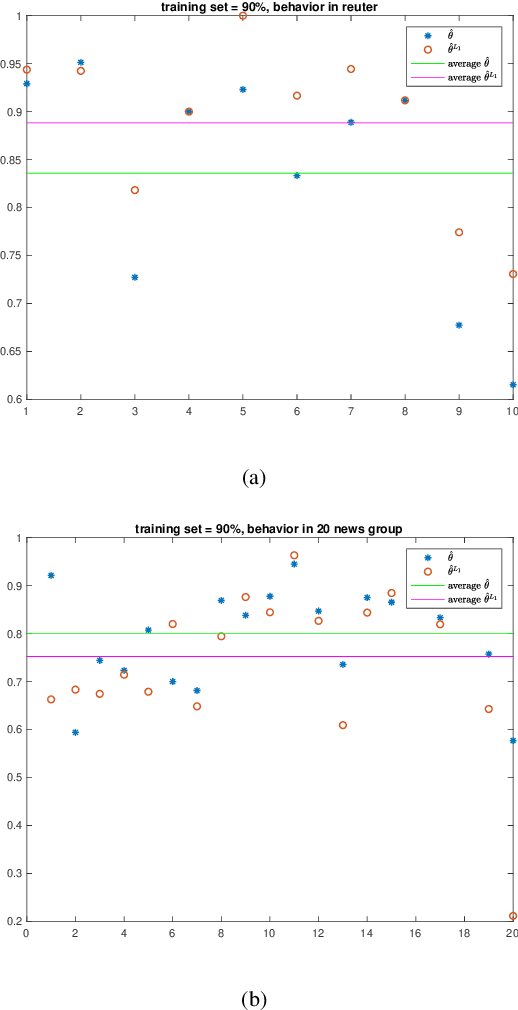
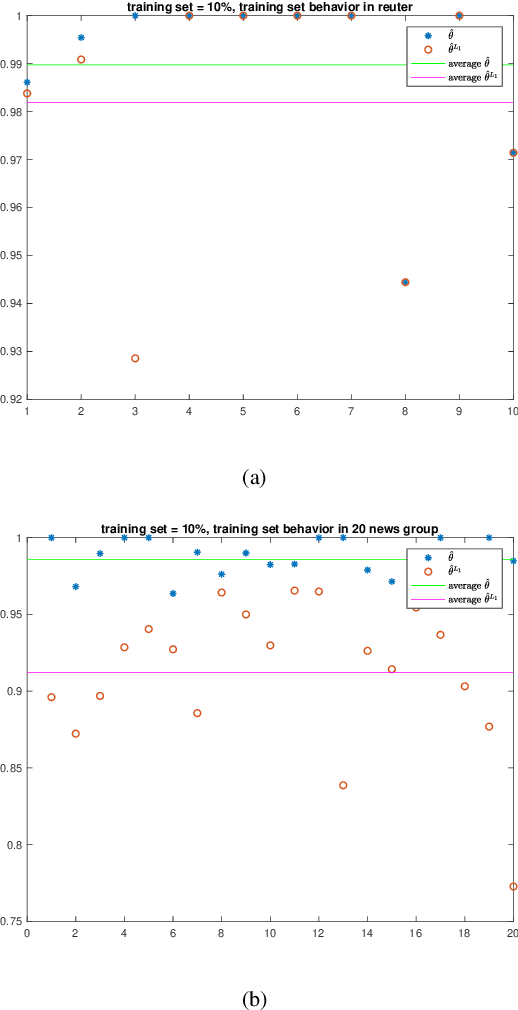
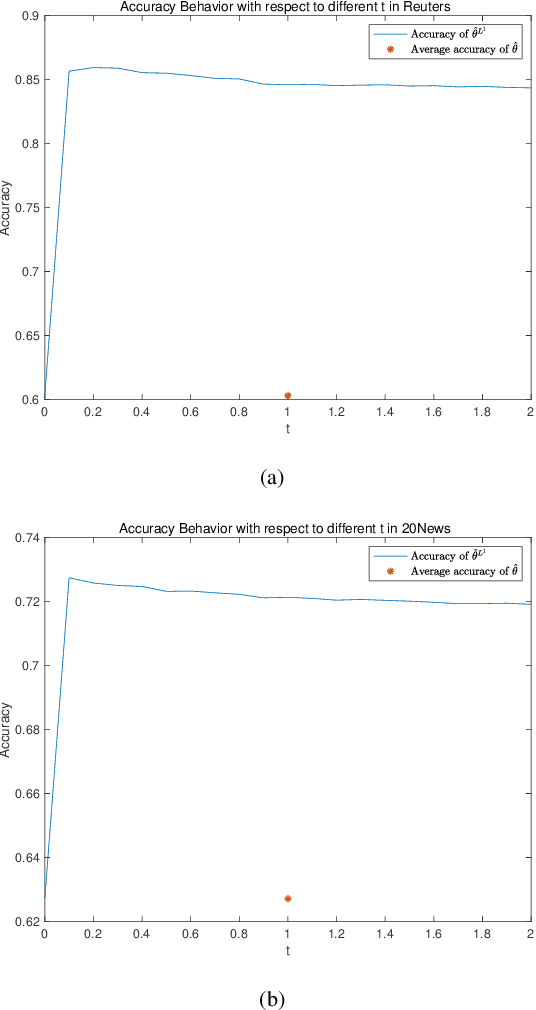
Abstract:Naive Bayes estimator is widely used in text classification problems. However, it doesn't perform well with small-size training dataset. We propose a new method based on Naive Bayes estimator to solve this problem. A correlation factor is introduced to incorporate the correlation among different classes. Experimental results show that our estimator achieves a better accuracy compared with traditional Naive Bayes in real world data.
Centroid estimation based on symmetric KL divergence for Multinomial text classification problem
Oct 24, 2018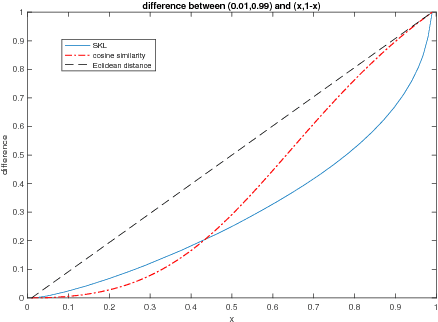
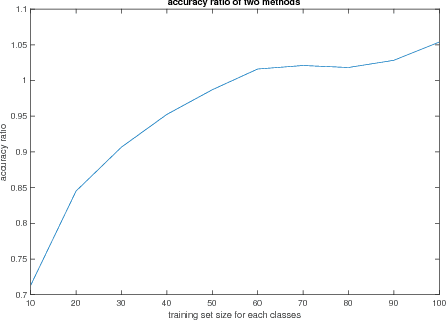
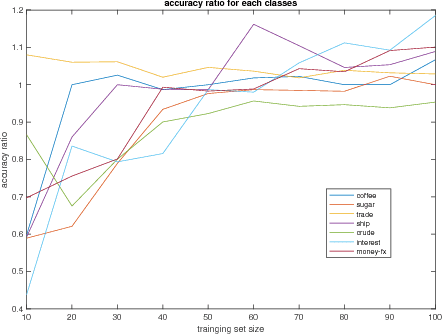
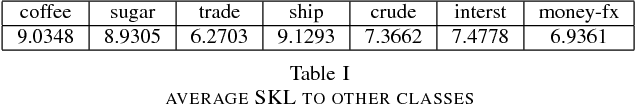
Abstract:We define a new method to estimate centroid for text classification based on the symmetric KL-divergence between the distribution of words in training documents and their class centroids. Experiments on several standard data sets indicate that the new method achieves substantial improvements over the traditional classifiers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge