Hassan Dbouk
Multi-Draft Speculative Sampling: Canonical Architectures and Theoretical Limits
Oct 23, 2024Abstract:We consider multi-draft speculative sampling, where the proposal sequences are sampled independently from different draft models. At each step, a token-level draft selection scheme takes a list of valid tokens as input and produces an output token whose distribution matches that of the target model. Previous works have demonstrated that the optimal scheme (which maximizes the probability of accepting one of the input tokens) can be cast as a solution to a linear program. In this work we show that the optimal scheme can be decomposed into a two-step solution: in the first step an importance sampling (IS) type scheme is used to select one intermediate token; in the second step (single-draft) speculative sampling is applied to generate the output token. For the case of two identical draft models we further 1) establish a necessary and sufficient condition on the distributions of the target and draft models for the acceptance probability to equal one and 2) provide an explicit expression for the optimal acceptance probability. Our theoretical analysis also motives a new class of token-level selection scheme based on weighted importance sampling. Our experimental results demonstrate consistent improvements in the achievable block efficiency and token rates over baseline schemes in a number of scenarios.
On the Robustness of Randomized Ensembles to Adversarial Perturbations
Feb 06, 2023



Abstract:Randomized ensemble classifiers (RECs), where one classifier is randomly selected during inference, have emerged as an attractive alternative to traditional ensembling methods for realizing adversarially robust classifiers with limited compute requirements. However, recent works have shown that existing methods for constructing RECs are more vulnerable than initially claimed, casting major doubts on their efficacy and prompting fundamental questions such as: "When are RECs useful?", "What are their limits?", and "How do we train them?". In this work, we first demystify RECs as we derive fundamental results regarding their theoretical limits, necessary and sufficient conditions for them to be useful, and more. Leveraging this new understanding, we propose a new boosting algorithm (BARRE) for training robust RECs, and empirically demonstrate its effectiveness at defending against strong $\ell_\infty$ norm-bounded adversaries across various network architectures and datasets.
Adversarial Vulnerability of Randomized Ensembles
Jun 14, 2022



Abstract:Despite the tremendous success of deep neural networks across various tasks, their vulnerability to imperceptible adversarial perturbations has hindered their deployment in the real world. Recently, works on randomized ensembles have empirically demonstrated significant improvements in adversarial robustness over standard adversarially trained (AT) models with minimal computational overhead, making them a promising solution for safety-critical resource-constrained applications. However, this impressive performance raises the question: Are these robustness gains provided by randomized ensembles real? In this work we address this question both theoretically and empirically. We first establish theoretically that commonly employed robustness evaluation methods such as adaptive PGD provide a false sense of security in this setting. Subsequently, we propose a theoretically-sound and efficient adversarial attack algorithm (ARC) capable of compromising random ensembles even in cases where adaptive PGD fails to do so. We conduct comprehensive experiments across a variety of network architectures, training schemes, datasets, and norms to support our claims, and empirically establish that randomized ensembles are in fact more vulnerable to $\ell_p$-bounded adversarial perturbations than even standard AT models. Our code can be found at https://github.com/hsndbk4/ARC.
Generalized Depthwise-Separable Convolutions for Adversarially Robust and Efficient Neural Networks
Nov 06, 2021



Abstract:Despite their tremendous successes, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) incur high computational/storage costs and are vulnerable to adversarial perturbations. Recent works on robust model compression address these challenges by combining model compression techniques with adversarial training. But these methods are unable to improve throughput (frames-per-second) on real-life hardware while simultaneously preserving robustness to adversarial perturbations. To overcome this problem, we propose the method of Generalized Depthwise-Separable (GDWS) convolution -- an efficient, universal, post-training approximation of a standard 2D convolution. GDWS dramatically improves the throughput of a standard pre-trained network on real-life hardware while preserving its robustness. Lastly, GDWS is scalable to large problem sizes since it operates on pre-trained models and doesn't require any additional training. We establish the optimality of GDWS as a 2D convolution approximator and present exact algorithms for constructing optimal GDWS convolutions under complexity and error constraints. We demonstrate the effectiveness of GDWS via extensive experiments on CIFAR-10, SVHN, and ImageNet datasets. Our code can be found at https://github.com/hsndbk4/GDWS.
Fundamental Limits on Energy-Delay-Accuracy of In-memory Architectures in Inference Applications
Dec 25, 2020



Abstract:This paper obtains fundamental limits on the computational precision of in-memory computing architectures (IMCs). An IMC noise model and associated SNR metrics are defined and their interrelationships analyzed to show that the accuracy of IMCs is fundamentally limited by the compute SNR ($\text{SNR}_{\text{a}}$) of its analog core, and that activation, weight and output precision needs to be assigned appropriately for the final output SNR $\text{SNR}_{\text{T}} \rightarrow \text{SNR}_{\text{a}}$. The minimum precision criterion (MPC) is proposed to minimize the ADC precision. Three in-memory compute models - charge summing (QS), current summing (IS) and charge redistribution (QR) - are shown to underlie most known IMCs. Noise, energy and delay expressions for the compute models are developed and employed to derive expressions for the SNR, ADC precision, energy, and latency of IMCs. The compute SNR expressions are validated via Monte Carlo simulations in a 65 nm CMOS process. For a 512 row SRAM array, it is shown that: 1) IMCs have an upper bound on their maximum achievable $\text{SNR}_{\text{a}}$ due to constraints on energy, area and voltage swing, and this upper bound reduces with technology scaling for QS-based architectures; 2) MPC enables $\text{SNR}_{\text{T}} \rightarrow \text{SNR}_{\text{a}}$ to be realized with minimal ADC precision; 3) QS-based (QR-based) architectures are preferred for low (high) compute SNR scenarios.
DBQ: A Differentiable Branch Quantizer for Lightweight Deep Neural Networks
Jul 19, 2020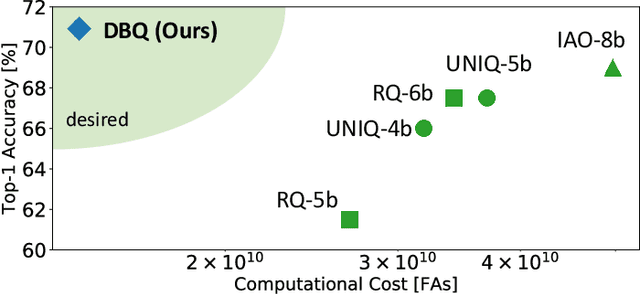
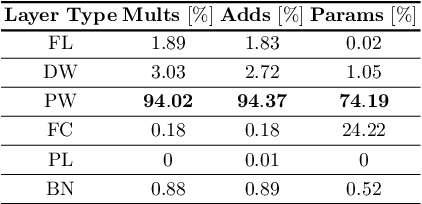
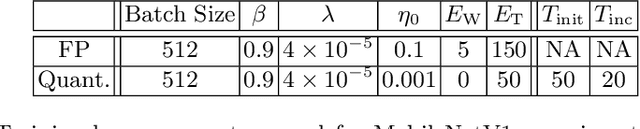
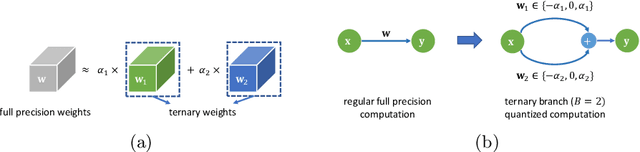
Abstract:Deep neural networks have achieved state-of-the art performance on various computer vision tasks. However, their deployment on resource-constrained devices has been hindered due to their high computational and storage complexity. While various complexity reduction techniques, such as lightweight network architecture design and parameter quantization, have been successful in reducing the cost of implementing these networks, these methods have often been considered orthogonal. In reality, existing quantization techniques fail to replicate their success on lightweight architectures such as MobileNet. To this end, we present a novel fully differentiable non-uniform quantizer that can be seamlessly mapped onto efficient ternary-based dot product engines. We conduct comprehensive experiments on CIFAR-10, ImageNet, and Visual Wake Words datasets. The proposed quantizer (DBQ) successfully tackles the daunting task of aggressively quantizing lightweight networks such as MobileNetV1, MobileNetV2, and ShuffleNetV2. DBQ achieves state-of-the art results with minimal training overhead and provides the best (pareto-optimal) accuracy-complexity trade-off.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge