Haoyuan Peng
LLMs can Find Mathematical Reasoning Mistakes by Pedagogical Chain-of-Thought
May 09, 2024Abstract:Self-correction is emerging as a promising approach to mitigate the issue of hallucination in Large Language Models (LLMs). To facilitate effective self-correction, recent research has proposed mistake detection as its initial step. However, current literature suggests that LLMs often struggle with reliably identifying reasoning mistakes when using simplistic prompting strategies. To address this challenge, we introduce a unique prompting strategy, termed the Pedagogical Chain-of-Thought (PedCoT), which is specifically designed to guide the identification of reasoning mistakes, particularly mathematical reasoning mistakes. PedCoT consists of pedagogical principles for prompts (PPP) design, two-stage interaction process (TIP) and grounded PedCoT prompts, all inspired by the educational theory of the Bloom Cognitive Model (BCM). We evaluate our approach on two public datasets featuring math problems of varying difficulty levels. The experiments demonstrate that our zero-shot prompting strategy significantly outperforms strong baselines. The proposed method can achieve the goal of reliable mathematical mistake identification and provide a foundation for automatic math answer grading. The results underscore the significance of educational theory, serving as domain knowledge, in guiding prompting strategy design for addressing challenging tasks with LLMs effectively.
VKIE: The Application of Key Information Extraction on Video Text
Oct 18, 2023
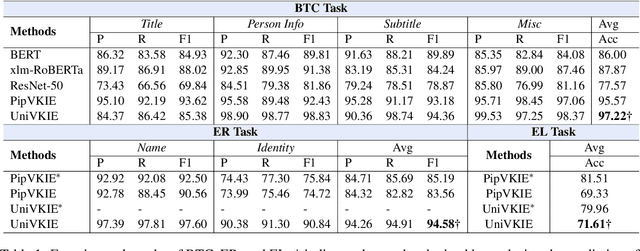
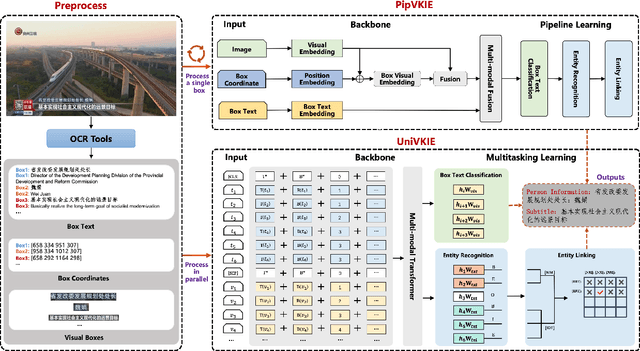
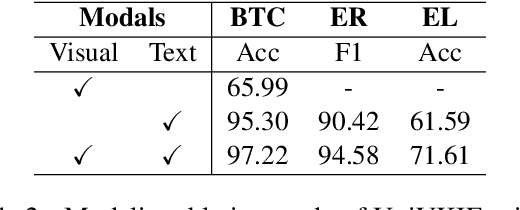
Abstract:Extracting structured information from videos is critical for numerous downstream applications in the industry. In this paper, we define a significant task of extracting hierarchical key information from visual texts on videos. To fulfill this task, we decouples it into four subtasks and introduce two implementation solutions called PipVKIE and UniVKIE. PipVKIE sequentially completes the four subtasks in continuous stages, while UniVKIE is improved by unifying all the subtasks into one backbone. Both PipVKIE and UniVKIE leverage multimodal information from vision, text, and coordinates for feature representation. Extensive experiments on one well-defined dataset demonstrate that our solutions can achieve remarkable performance and efficient inference speed. The code and dataset will be publicly available.
Grafting Pre-trained Models for Multimodal Headline Generation
Nov 14, 2022



Abstract:Multimodal headline utilizes both video frames and transcripts to generate the natural language title of the videos. Due to a lack of large-scale, manually annotated data, the task of annotating grounded headlines for video is labor intensive and impractical. Previous researches on pre-trained language models and video-language models have achieved significant progress in related downstream tasks. However, none of them can be directly applied to multimodal headline architecture where we need both multimodal encoder and sentence decoder. A major challenge in simply gluing language model and video-language model is the modality balance, which is aimed at combining visual-language complementary abilities. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to graft the video encoder from the pre-trained video-language model on the generative pre-trained language model. We also present a consensus fusion mechanism for the integration of different components, via inter/intra modality relation. Empirically, experiments show that the grafted model achieves strong results on a brand-new dataset collected from real-world applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge