Hanjie Li
ITPNet: Towards Instantaneous Trajectory Prediction for Autonomous Driving
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Trajectory prediction of agents is crucial for the safety of autonomous vehicles, whereas previous approaches usually rely on sufficiently long-observed trajectory to predict the future trajectory of the agents. However, in real-world scenarios, it is not realistic to collect adequate observed locations for moving agents, leading to the collapse of most prediction models. For instance, when a moving car suddenly appears and is very close to an autonomous vehicle because of the obstruction, it is quite necessary for the autonomous vehicle to quickly and accurately predict the future trajectories of the car with limited observed trajectory locations. In light of this, we focus on investigating the task of instantaneous trajectory prediction, i.e., two observed locations are available during inference. To this end, we propose a general and plug-and-play instantaneous trajectory prediction approach, called ITPNet. Specifically, we propose a backward forecasting mechanism to reversely predict the latent feature representations of unobserved historical trajectories of the agent based on its two observed locations and then leverage them as complementary information for future trajectory prediction. Meanwhile, due to the inevitable existence of noise and redundancy in the predicted latent feature representations, we further devise a Noise Redundancy Reduction Former, aiming at to filter out noise and redundancy from unobserved trajectories and integrate the filtered features and observed features into a compact query for future trajectory predictions. In essence, ITPNet can be naturally compatible with existing trajectory prediction models, enabling them to gracefully handle the case of instantaneous trajectory prediction. Extensive experiments on the Argoverse and nuScenes datasets demonstrate ITPNet outperforms the baselines, and its efficacy with different trajectory prediction models.
Robust Knowledge Adaptation for Dynamic Graph Neural Networks
Jul 22, 2022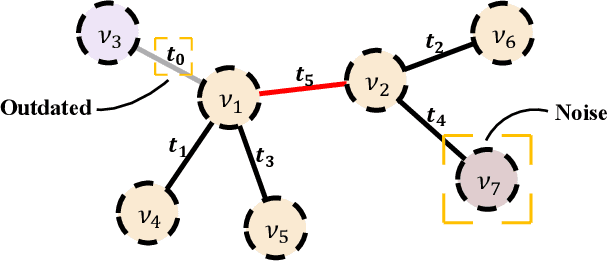
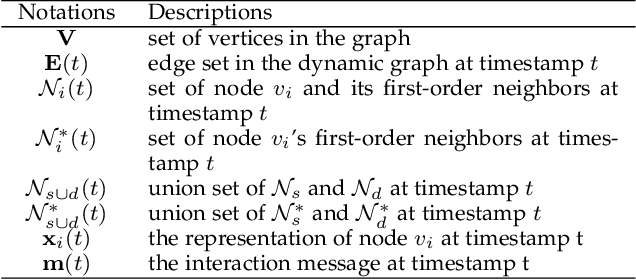
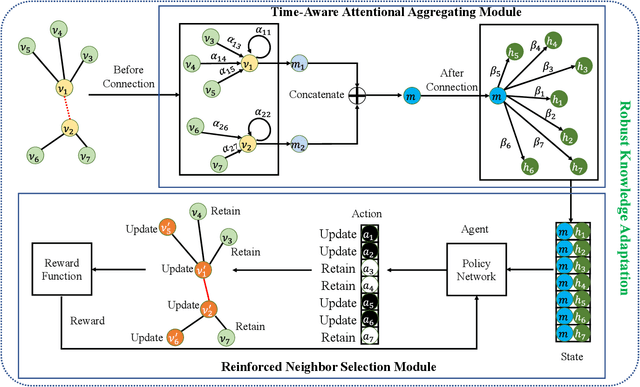
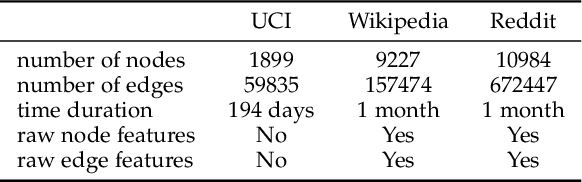
Abstract:Graph structured data often possess dynamic characters in nature, e.g., the addition of links and nodes, in many real-world applications. Recent years have witnessed the increasing attentions paid to dynamic graph neural networks for modelling such graph data, where almost all the existing approaches assume that when a new link is built, the embeddings of the neighbor nodes should be updated by learning the temporal dynamics to propagate new information. However, such approaches suffer from the limitation that if the node introduced by a new connection contains noisy information, propagating its knowledge to other nodes is not reliable and even leads to the collapse of the model. In this paper, we propose AdaNet: a robust knowledge Adaptation framework via reinforcement learning for dynamic graph neural Networks. In contrast to previous approaches immediately updating the embeddings of the neighbor nodes once adding a new link, AdaNet attempts to adaptively determine which nodes should be updated because of the new link involved. Considering that the decision whether to update the embedding of one neighbor node will have great impact on other neighbor nodes, we thus formulate the selection of node update as a sequence decision problem, and address this problem via reinforcement learning. By this means, we can adaptively propagate knowledge to other nodes for learning robust node embedding representations. To the best of our knowledge, our approach constitutes the first attempt to explore robust knowledge adaptation via reinforcement learning for dynamic graph neural networks. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that AdaNet achieves the state-of-the-art performance. In addition, we perform the experiments by adding different degrees of noise into the dataset, quantitatively and qualitatively illustrating the robustness of AdaNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge