Hangfang Zhao
Striking The Right Balance: Three-Dimensional Ocean Sound Speed Field Reconstruction Using Tensor Neural Networks
Aug 09, 2023Abstract:Accurately reconstructing a three-dimensional ocean sound speed field (3D SSF) is essential for various ocean acoustic applications, but the sparsity and uncertainty of sound speed samples across a vast ocean region make it a challenging task. To tackle this challenge, a large body of reconstruction methods has been developed, including spline interpolation, matrix/tensor-based completion, and deep neural networks-based reconstruction. However, a principled analysis of their effectiveness in 3D SSF reconstruction is still lacking. This paper performs a thorough analysis of the reconstruction error and highlights the need for a balanced representation model that integrates both expressiveness and conciseness. To meet this requirement, a 3D SSF-tailored tensor deep neural network is proposed, which utilizes tensor computations and deep neural network architectures to achieve remarkable 3D SSF reconstruction. The proposed model not only includes the previous tensor-based SSF representation model as a special case, but also has a natural ability to reject noise. The numerical results using the South China Sea 3D SSF data demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art methods. The code is available at https://github.com/OceanSTARLab/Tensor-Neural-Network.
Multipath Time-delay Estimation with Impulsive Noise via Bayesian Compressive Sensing
Jul 05, 2023Abstract:Multipath time-delay estimation is commonly encountered in radar and sonar signal processing. In some real-life environments, impulse noise is ubiquitous and significantly degrades estimation performance. Here, we propose a Bayesian approach to tailor the Bayesian Compressive Sensing (BCS) to mitigate impulsive noises. In particular, a heavy-tail Laplacian distribution is used as a statistical model for impulse noise, while Laplacian prior is used for sparse multipath modeling. The Bayesian learning problem contains hyperparameters learning and parameter estimation, solved under the BCS inference framework. The performance of our proposed method is compared with benchmark methods, including compressive sensing (CS), BCS, and Laplacian-prior BCS (L-BCS). The simulation results show that our proposed method can estimate the multipath parameters more accurately and have a lower root mean squared estimation error (RMSE) in intensely impulsive noise.
Tensor-based Basis Function Learning for Three-dimensional Sound Speed Fields
Jan 21, 2022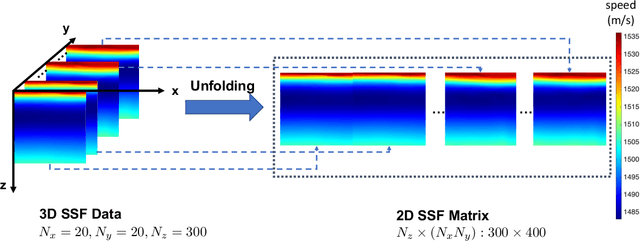
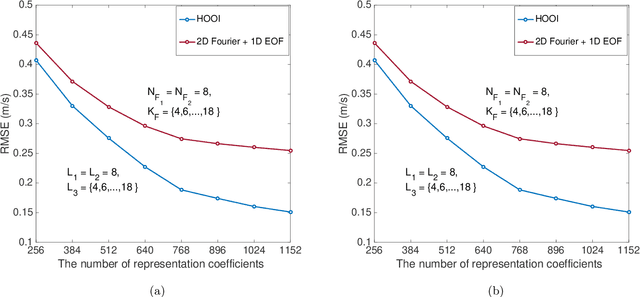
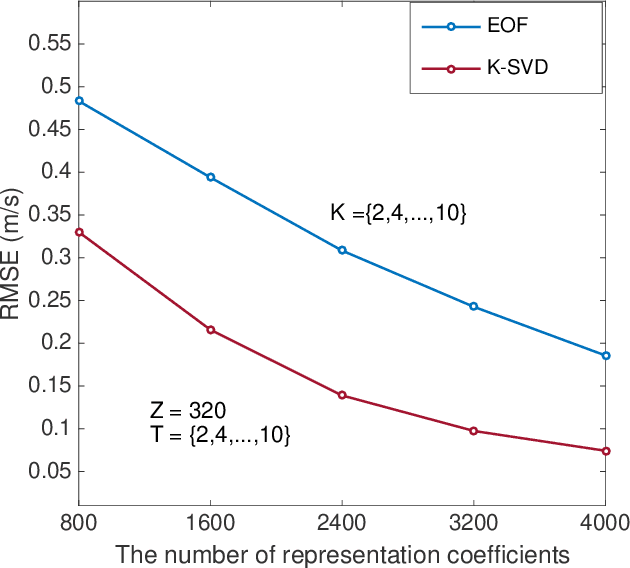
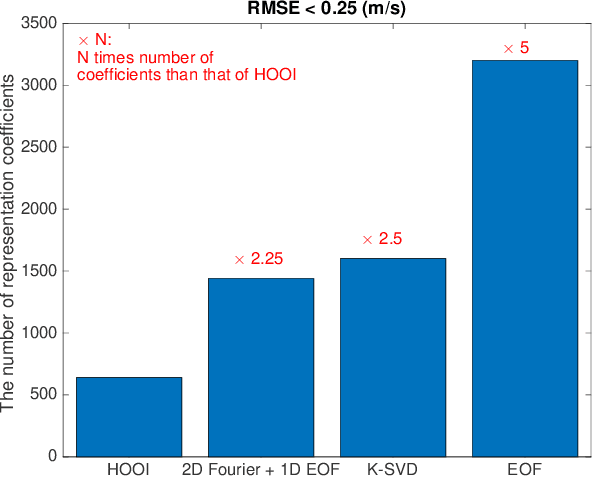
Abstract:Basis function learning is the stepping stone towards effective three-dimensional (3D) sound speed field (SSF) inversion for various acoustic signal processing tasks, including ocean acoustic tomography, underwater target localization/tracking, and underwater communications. Classical basis functions include the empirical orthogonal functions (EOFs), Fourier basis functions, and their combinations. The unsupervised machine learning method, e.g., the K-SVD algorithm, has recently tapped into the basis function design, showing better representation performance than the EOFs. However, existing methods do not consider basis function learning approaches that treat 3D SSF data as a third-order tensor, and thus cannot fully utilize the 3D interactions/correlations therein. To circumvent such a drawback, basis function learning is linked to tensor decomposition in this paper, which is the primary drive for recent multi-dimensional data mining. In particular, a tensor-based basis function learning framework is proposed, which can include the classical basis functions (using EOFs and/or Fourier basis functions) as its special cases. This provides a unified tensor perspective for understanding and representing 3D SSFs. Numerical results using the South China Sea 3D SSF data have demonstrated the excellent performance of the tensor-based basis functions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge