Hahnbeom Park
Recent advances in interpretable machine learning using structure-based protein representations
Sep 26, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in machine learning (ML) are transforming the field of structural biology. For example, AlphaFold, a groundbreaking neural network for protein structure prediction, has been widely adopted by researchers. The availability of easy-to-use interfaces and interpretable outcomes from the neural network architecture, such as the confidence scores used to color the predicted structures, have made AlphaFold accessible even to non-ML experts. In this paper, we present various methods for representing protein 3D structures from low- to high-resolution, and show how interpretable ML methods can support tasks such as predicting protein structures, protein function, and protein-protein interactions. This survey also emphasizes the significance of interpreting and visualizing ML-based inference for structure-based protein representations that enhance interpretability and knowledge discovery. Developing such interpretable approaches promises to further accelerate fields including drug development and protein design.
Conditioning by adaptive sampling for robust design
Feb 06, 2019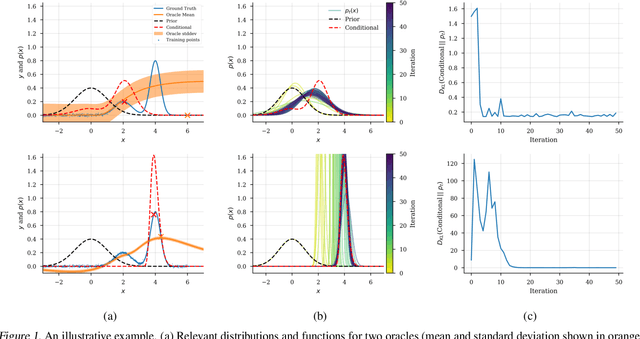
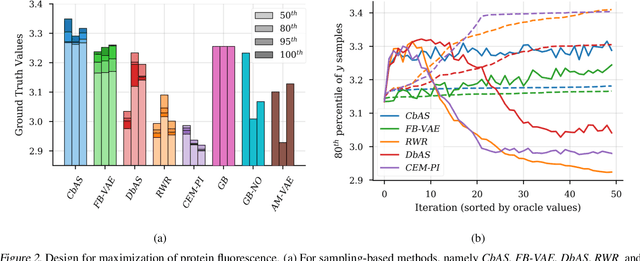
Abstract:We present a new method for design problems wherein the goal is to maximize or specify the value of one or more properties of interest. For example, in protein design, one may wish to find the protein sequence that maximizes fluorescence. We assume access to one or more, potentially black box, stochastic "oracle" predictive functions, each of which maps from input (e.g., protein sequences) design space to a distribution over a property of interest (e.g. protein fluorescence). At first glance, this problem can be framed as one of optimizing the oracle(s) with respect to the input. However, many state-of-the-art predictive models, such as neural networks, are known to suffer from pathologies, especially for data far from the training distribution. Thus we need to modulate the optimization of the oracle inputs with prior knowledge about what makes `realistic' inputs (e.g., proteins that stably fold). Herein, we propose a new method to solve this problem, Conditioning by Adaptive Sampling, which yields state-of-the-art results on a protein fluorescence problem, as compared to other recently published approaches. Formally, our method achieves its success by using model-based adaptive sampling to estimate the conditional distribution of the input sequences given the desired properties.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge